Other than the United States, 5 U.S. territories and 12 sovereign nations use the US dollar as their legal currency. (Note that Micronesia covers six sovereign countries).
Additionally, I have traveled to island nations and some countries in Asia and Pacific that peg their currency to the US dollar. In these regions, citizens accept US dollars interchangeably with their own national currency, and their governments don’t seem to discourage or prosecute such transactions.
What gives value to paper?
Around 350 BC, Aristotle worked for the Greek council, trying to get farmers, weavers, chariot makers and tradesman to use government issued currency for the exchange of goods and services, rather than bartering with neighbors. This would not only facilitate taxation and public works, but it would help farmers to store and forward their wealth, instead of seeing their assets perish with each change of season.
He reflected on what makes a currency trusted and functional. He felt that one critical trait was “intrinsic value”. Today, most economists interpret this phrase as a currency having inherent or self-contained value. That is, it mustn’t be paper nor even a promise of redemption (for example, a picture of Caesar). And it mustn’t rely on the ‘good faith and credit’ of citizens. After all, nations are subject to the whims of transient politicians and any economy can collapse because of war, drought or over-spending. Rather, the money must be made from something of useful and dense value. For example, it could be gold, silver or some useful thing, like chocolate, coveted jewelry or a tool.
Today, money is no longer backed by gold or even a government promise of redemption (offering to exchange dollars for gold, grain, goats or land). For developed nations, this backing—a method of establishing intrinsic value—ended between 1971~1973, when President Richard Nixon dissolved the Bretton Woods Agreement and withdrew the promise of a conversion guaranty.
Instead, today, the value of national currencies floats in response to supply and demand.
Supply and demand is a natural economic mechanism, and for fluid and widely distributed commodities, it can be an elegant solution to the problem of establishing value, function and durability—but only if the supply is capped or very tightly regulated and the issuer is trusted by individuals, organizations and nations that quote prices, save or trade with the currency.
Unfortunately, this is not the case for any national currency across the world.
- Supply: National currencies increase in supply when the government spends more than it raises from fees, taxes, government owned industries and borrowing—or whenever it cannot meet debt obligations. With fiat currency, the supply is open ended and uncertain.
- Demand: The demand for a currency is a function of its issuer’s economy: How much are its people producing? How high are their debts? Do creditors believe that they will repay their debts in kind?—at least, someday, down the road.
Today, it’s all about trust—Trust in the ability of a country to return the goods and services that were bought by their people and trust in their government to avoid printing more money, which depreciates savings, redistributes wealth, and cheats creditors through the insipid dilution of inflation.
Whenever a government prints money, it reneges on debt and breeches the trust of creditors.
Why would any country substitute the currency of another country?
One need only look at this Zimbabwe money to understand why an independent nation might substitute the US dollar as legal tender. The same has happened to Argentina, Greece, Venezuela and Germany between the wars.
It was withdrawn from circulation in 2008. At the time, it was worth US 40¢ (40 cents). Today, Zimbabwe uses the US dollar as its legal currency, because its spending value is stable relative to monies issued African central banks. That is, the citizens trust the US dollar to resist inflation—and so they use it to store and trade their hard-earned wealth.
Is Adoption of the US Dollar growing around the world?
The days of our friends and enemies trusting the dollar or even using it to negotiate large international trades is gradually coming to an end. This is changing, because:
1. Bitcoin is gradually displacing the dollar as the world’s reserve currency. Even though it is slow to gain traction as a commercial and consumer payment instrument, it has all the components of an ideal currency for large international quotation, exchange and settlement.
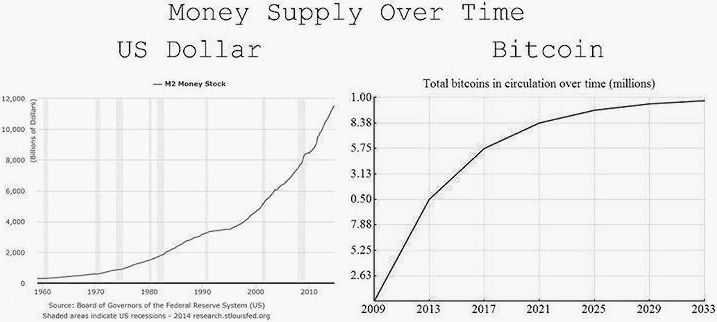
The fundamental reason for the gradual trust in Bitcoin is illustrated by these graphs. Bitcoin is a capped commodity backed by a robust 2-sided network. Understanding and trust in its distributed consensus mechanism is growing. It cannot be manipulated by transient politicians. Nations that use it for significant transactions cannot be cheated when their trading partner or a 3rd party prints money to cover their own shortfall. It is an ideal reserve settlement instrument.
2. In recent decades, the dollar is built on debt rather than domestic output, a trade surplus, or high quality credit. This creates the potential for a collapse, if US citizens or creditor nations begin to doubt the likelihood of the United States reversing its slumping exports and staggering trade imbalance.
3. In recent years, the United States has lost gravitas in world forums due to the projection of power beyond its borders without a clear mandate or international support, and its recent lack of leadership in issues like the environment, trade accords and arbitrating regional peace agreements. This impression—along with the erratic statements and behavior of U.S. politicians causes both allies and enemies to seek an alternate reserve currency. Why so? …
A reserve currency is an international quotation and settlement instrument—even when the United States is not a party to a sale or transaction, and even if one or both parties is not a US ally. Many countries, banks and producers (of oil, food, military gear, etc) do not desire or appreciate the tremendous side-benefit that accrues to USA.
In effect, when you adopt the currency of one nation as the reserve currency for others, you grant credit to that country, without collateral. You allow them to print money without substantive backing, guarantees or even a balance of trade that makes it likely you will be repaid without the dilution of inflation.
Ellery Davies co-chairs CRYPSA, hosts the New York Bitcoin Event and is keynote speaker at Cryptocurrency Conferences. He sits on the New Money Systems board of Lifeboat Foundation. Book a presentation or consulting engagement.







 I am not an academic economist, but I have certainly been recognized as a practical economist. Beyond investor, and business columnist, I have been
I am not an academic economist, but I have certainly been recognized as a practical economist. Beyond investor, and business columnist, I have been