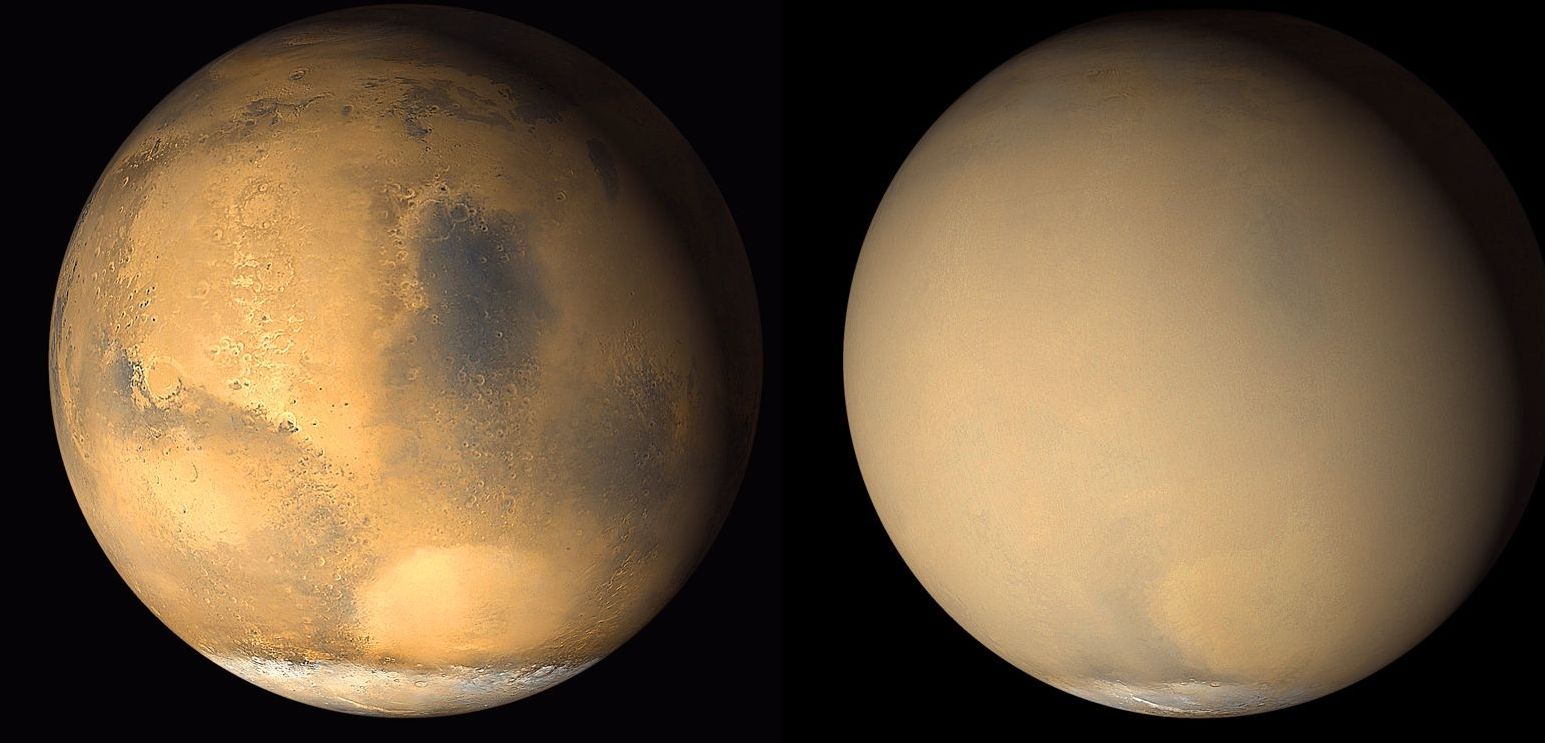
The dust is settling on the Red Planet. Is the remaining Mars Exploration Rover about to rise and shine after three months of slumber? MER Project Manager John Callas returns with a realistic yet hopeful assessment. He also tells us what Opportunity will be asked to do after we hear from her. Planetary Society Senior Editor Emily Lakdawalla returns with a preview of China’s next two missions to the Moon, one of which will make the first-ever farside landing. How close is the nearest black hole? We’ll get the answer as Bruce and Mat explore the night sky in this week’s What’s Up.