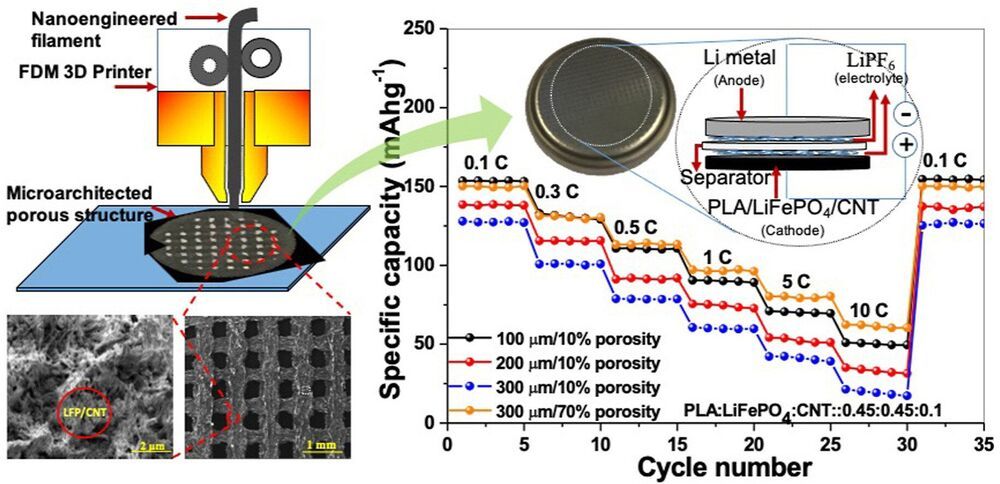
A new type of 3D-printed battery which uses electrodes made from vegetable starch and carbon nanotubes could provide mobile devices with a more environmentally-friendly, higher-capacity source of power.
A team of engineers led from the University of Glasgow have developed the battery in a bid to make more sustainable lithium-ion batteries capable of storing and delivering power more efficiently. The battery’s design and fabrication is outlined in a paper published in the Journal of Power Sources.
Lithium-ion batteries provide a useful combination of lightweight, compact form factors and the ability to withstand many cycles of charging and discharging. That has made them ideally suited for use in a wide array of devices, including laptops, mobile phones, smart watches, and electric vehicles.