New article on how tech can help achieve free education while also shrinking the prison system:
Micro drones, robot guards, and tracking chips will turn convicts into tax-paying, law-abiding citizens.

New article on how tech can help achieve free education while also shrinking the prison system:
Micro drones, robot guards, and tracking chips will turn convicts into tax-paying, law-abiding citizens.
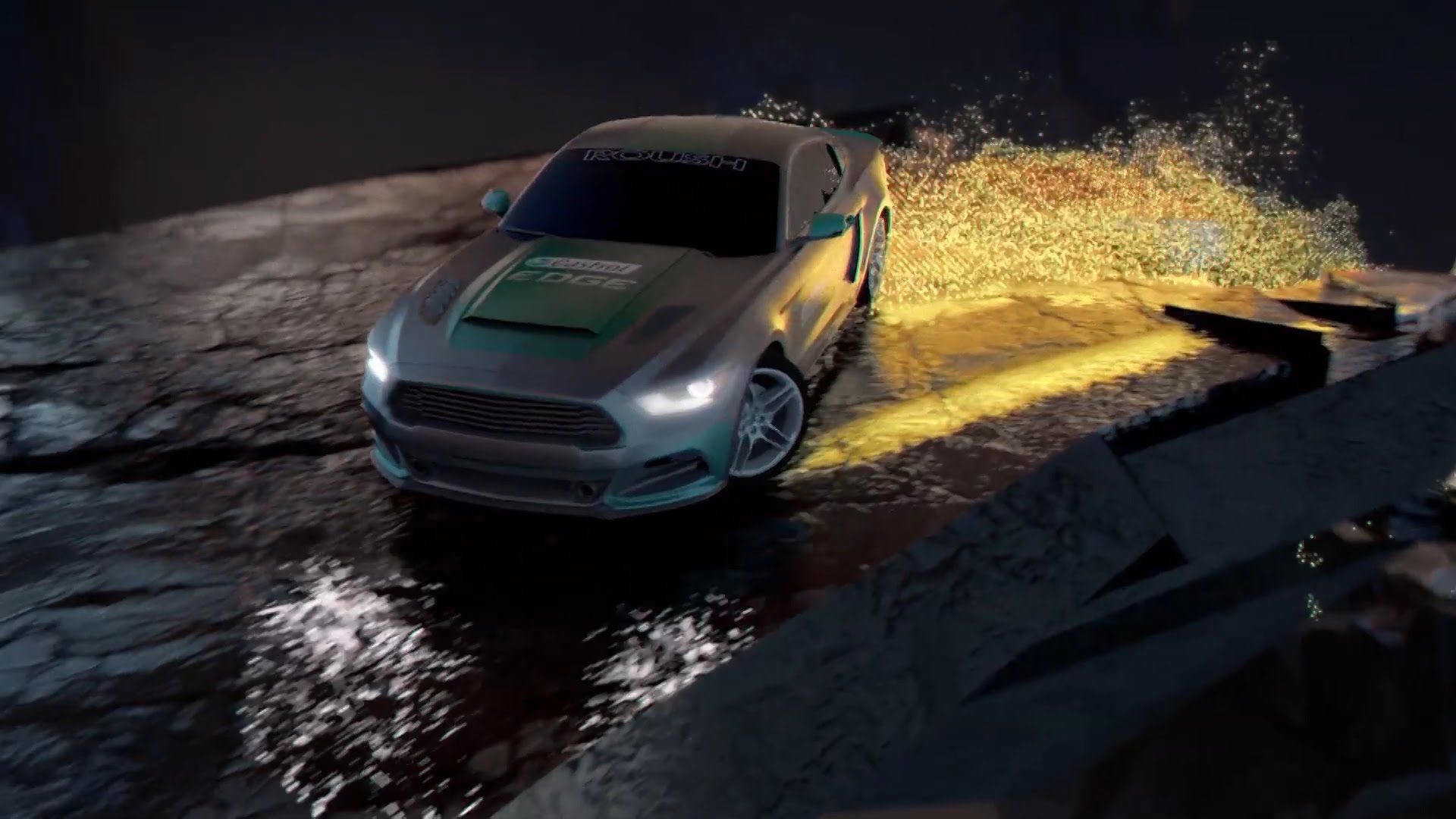

Castrol Edge & Video Games technologies: Racing a Real Car in Virtual Reality.
Castrol EDGE has premiered its latest Titanium Trial driving challenge, featuring Formula Drift professional Matt Powers driving his Roush Stage 3 Mustang whilst wearing a state-of-the-art Oculus Rift Development Kit 2 headset: blind to the real world around him, but fully-immersed in a rapidly changing 3D virtual world.
In a world first, Castrol EDGE fused video games technology and a real world driving experience, using a modified car and virtual reality technology, so a computergenerated world responded to the driver’s and car’s movements in real time.
The video game-like experience featured a mind-blowing landscape of falling boulders, crumbling track, tunnels, sheer cliff drops and even a cameo virtual appearance from another racing icon — with the landscape’s shifts reacting to Matt Powers’ every driving move.
The challenge was part of Castrol EDGE’s Titanium Trials, a series of high-powered challenges that bring man and machine together to push the boundaries of performance enabled by the strength of Castrol EDGE boosted with fluid Titanium technology – Castrol’s most technologically advanced and strongest oil.
After taking on the VIRTUAL DRIFT Trial, Matt Powers said: “Virtual Drift was exhilarating and challenging like nothing I’ve ever done before. It’s been awesome not only being involved and testing this next generation of gaming technology but the possibilities this opens up for motor sport in general are mind blowing. I had to rely on my instincts and the car to perform, with the strength of Castrol EDGE in the engine to give me the reassurance that the car would reach its maximum performance.”

MIRI is a research nonprofit specializing in a poorly-explored set of problems in theoretical computer science. GiveDirectly is a cash transfer service that gives money to poor households in East Africa. What kind of conference would bring together representatives from such disparate organizations — alongside policy analysts, philanthropists, philosophers, and many more?
Effective Altruism Global, which is beginning its Oxford session in a few hours, is that kind of conference. Effective altruism (EA) is a diverse community of do-gooders with a common interest in bringing the tools of science to bear on the world’s biggest problems. EA organizations like GiveDirectly, the Centre for Effective Altruism, and the charity evaluator GiveWell have made a big splash by calling for new standards of transparency and humanitarian impact in the nonprofit sector.
What is MIRI’s connection to effective altruism? In what sense is safety research in artificial intelligence “altruism,” and why do we assign a high probability to this being a critically important area of computer science in the coming decades? I’ll give quick answers to each of those questions below.

Most cancer-busting strategies focus on removing cancerous cells. While this approach has proved extremely effective on many patients, most treatments have unpleasant side effects and there are many strains which prove extremely challenging to remove. An alternative model to this is to alter instead of remove — fixing cancerous behaviour by ‘reprogramming’ cells that go rogue; essentially swiss finishing school for cellular miscreants. A study published in Nature Cell Biology now provides hope that this tactic could in fact work in many cancers.
Researchers from Mayo Clinic’s Florida campus have found that adhesion proteins, which act like a glue sticking cells together, actually interact with a cell’s ‘microprocessor’. This processor creates molecules called miRNAs, which regulate multiple genes and essentially activate or de-activate different behavioural programs (like commands in computer programming). When healthy cells bump into a neighbour and begin to glue together, these adhesion proteins normally influence both cells — tuning down growth pathways. In cancer, the lab found this adhesion is perturbed; de-regulating miRNA production and enabling rampant growth. When scientists corrected these miRNA levels, the growth was arrested.
“The study brings together two so-far unrelated research fields — cell-to-cell adhesion and miRNA biology — to resolve a long-standing problem about the role of adhesion proteins in cell behavior that was baffling scientists. Most significantly, it uncovers a new strategy for cancer therapy”
New imaging technology fits on a tiny chip and, from a distance, can form a high-resolution three-dimensional image of an object on the scale of micrometers.
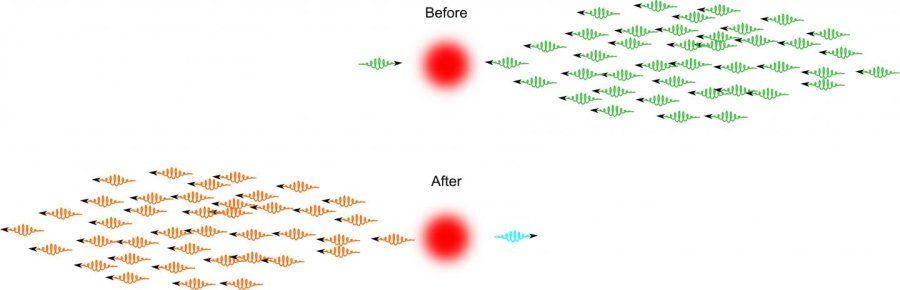
A team of physicists has taken a step toward making the essential building block of quantum computers out of pure light. Their advance has to do with logic gates that perform operations on input data to create new outputs.

https://youtube.com/watch?v=c_YV_omTtAg
But the ultimate goals of the project are nothing short of amazing: “The best possible outcome is to map the entirety of existing cache of neural network algorithms and applications to this energy-efficient substrate,” said Modha. “And, to invent entirely new algorithms that were hereto before impossible to imagine.”
IBM scientists are advancing toward “neuromorphic” computing — digital systems that process information like the brain — and launching a complete ecosystem for brain-like computing, with important near-term applications and visionary long-term prospects.
“For decades, computer scientists have been pursuing two elusive goals in parallel: engineering energy-efficient computers modeled on the human brain and designing smart computing systems that learn on their own — like humans do — and are not programmed like today’s computers,” said Dharmendra S. Modha, IBM Fellow and Chief Scientist for brain-inspired computing.
Computer scientists have found that robots evolve more quickly and efficiently after a virtual mass extinction modeled after real-life disasters such as the one that killed off the dinosaurs. Beyond implications for artificial intelligence, the research supports the idea that mass extinctions actually speed up evolution by unleashing new creativity in adaptations.
Photo credit: Joel Lehman.

Within the coming decades we’ll have the ability to create computers with greater than human intelligence, bio-engineer our species and redesign matter through nanotechnology, what will it mean to be human? Acclaimed as “a large-scale achievement in its documentation of futurist and counter-futurist ideas” and “the best documentary on the Singularity to date,” THE SINGULARITY is rich with insight, while remaining accessible to mainstream audiences. Some of the world’s leading thinkers, futurists and counter-futurists are interviewed, including Ray Kurzweil, Leon Panetta, Bill McKibben and Richard A. Clarke. THE SINGULARITY is an engaging tool for critical thinking about future technologies.
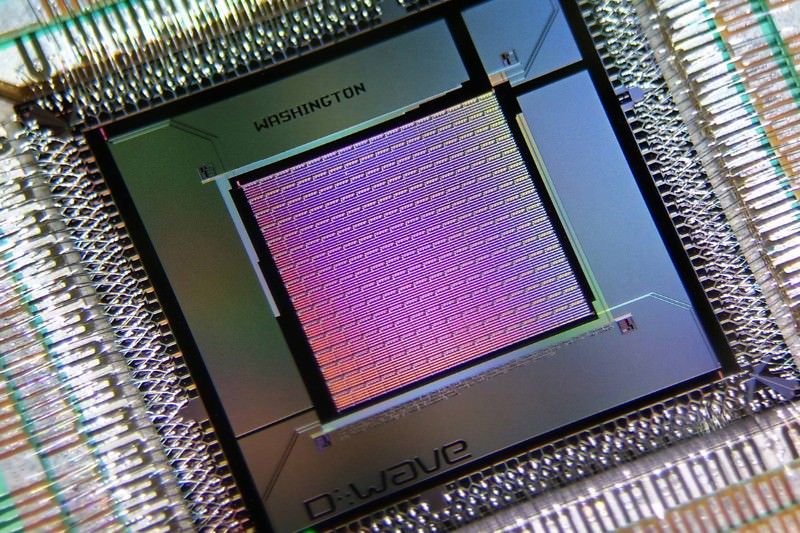
The world only quantum computer maker says its upgraded chip is 15 times faster than ordinary computers, but experts doubt the comparison is a fair test.