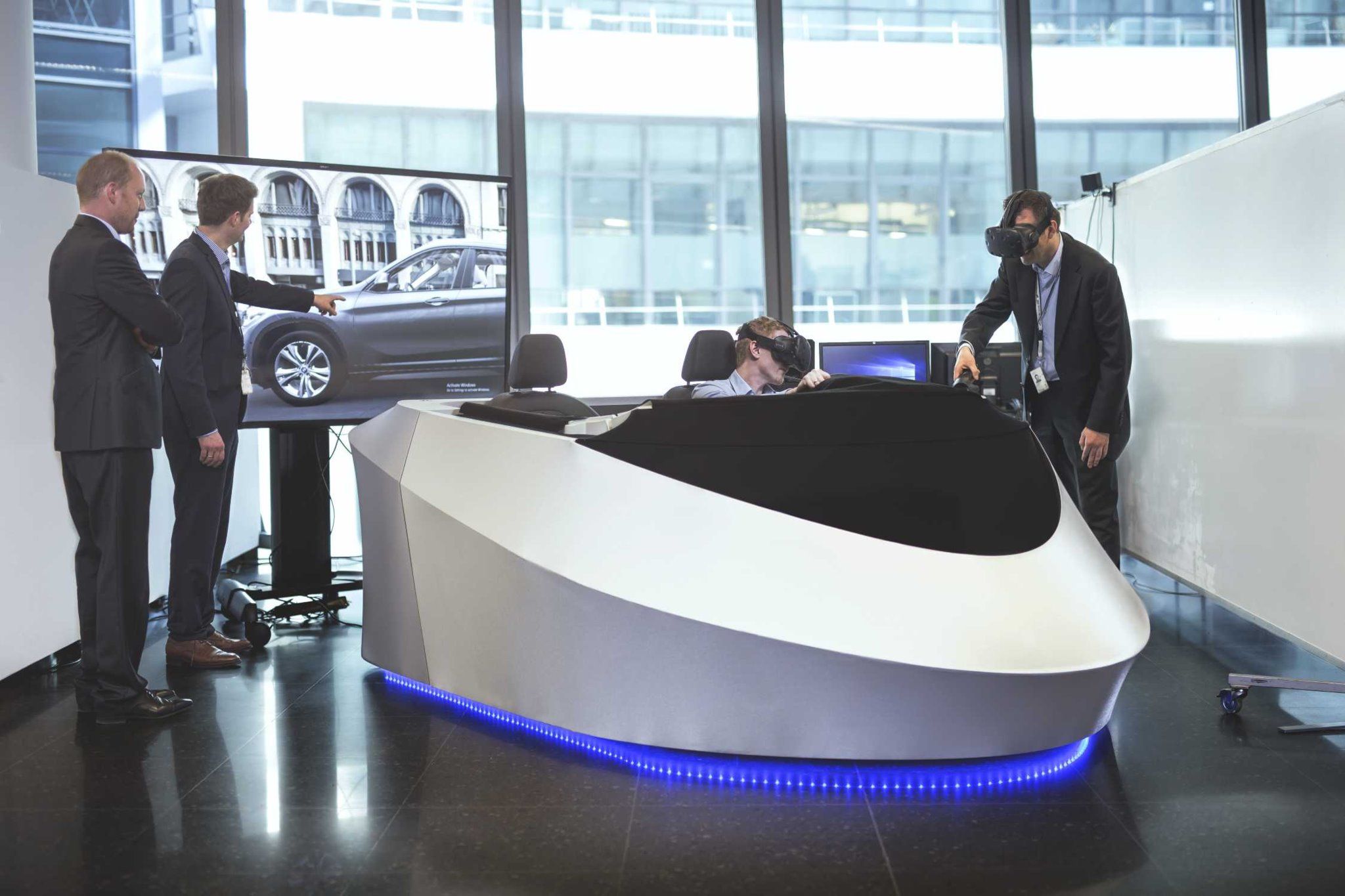
Munich. BMW has become the first car manufacturer to introduce a mixed reality system into vehicle development that has been devised entirely using components from the computer games industry. This offers some significant advantages over the VR systems that have existed to date, and is the first step towards making virtual reality a very real part of many developer workstations in the not-too-distant future.
The adoption of this computer system makes it possible to save a great deal of time and effort, especially during the early stages of development. VR investigations could previously only be conducted at costly specialised facilities. By incorporating consumer electronics, the developers gain an unprecedented degree of flexibility, because any modifications can be implemented and tested very quickly. In addition to this, developers around the globe will be able to take part in the decision-making process from their own office without having to travel too far. Only once the draft designs have been approved with the help of the 3D headsets will they actually be built for further testing.
BMW has been employing VR systems in the development process since the 1990s. It is now reaffirming its pioneering status by systematically implementing technology from a sector which has not previously been the focal point of industrial applications. Since this spring, components from the computer games industry have been allowing engineers and designers to immerse themselves more and more often in virtual worlds that are increasingly realistic. The shorter innovation cycles of consumer electronics result in a far wider scope of functions together with lower costs. This thereby enables more vehicle functions to be translated to a VR model in ever more realistic fashion. It is furthermore possible to scale the system to many different developer workstations with little effort.