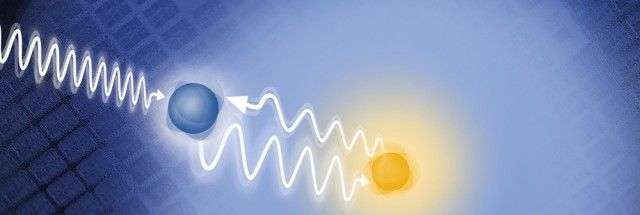
Se in Si —
Back to the future: Silicon may work for quantum computing.
The qualities of hydrogen and skill with silicon make for bright qubit future.

A quick look at synthetic biology and its potential for health and treating age-related diseases.
All living organisms contain an instruction set that determines what they look like and what they do. These instructions are encoded in the organism’s DNA within every cell, this is an organism’s genetic code (or “genome”).
Mankind has been altering the genetic code of plants and animals for thousands of years, by selectively breeding individuals with desired features. Over time we have become experts at viewing and manipulating this code, and we can now take genetic information associated with the desired features from one organism, and add it into another one. This is the basis of genetic engineering, which has allowed us to speed up the process of developing new breeds of plants and animals.
More recent advances however have enabled scientists to create new sequences of DNA from scratch. By combining these advances in biology with modern engineering, chemistry and computer science, researchers can now design and construct new organisms with cells that perform new useful functions. This “customised” cell biology is the essence of synthetic biology.

The emerging discipline of synthetic biology sits at the crux of the intersection between design, biology, computing and manufacturing…[I]t appears more and more probable that we are on the cusp of a paradigm shift, where…biology is adopted as the next big manufacturing technology.
[The objective of Ginkgo Bioworks, an “organism design” company,] is to take synthetic biology techniques to an industrial level, machine-injecting DNA sequences into baker’s yeast creating “living organism” products like perfumes, sweeteners, cosmetics and other things that are typically extracted from plants.
There are two main potential benefits from the technology. Replacing consumption of finite natural resources with lab-grown alternatives, and the potential to replicate actual genes to produce authentic fragrances replacing chemical synthetic scented products that currently dominate the marketplace.
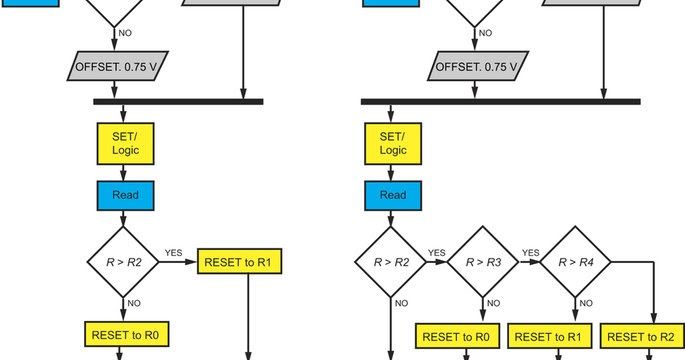
Nice; ReRam with multi-state processing and reliable storage.
Short of full blown molecular computers or universal quantum computers or optical computers memristors have the most potential for a hardware change to dramatically boost the power and capabilities of computers. The boost to computer power could be nearly a million times by fully leveraging memristors. It would likely be more like a thousand times with more near to mid term usage of memristors.
Memristors (aka ReRAM) could become computer memory that is over 10 times denser than Flash or DRAM in two dimensions. Memristors like flash would be nonvolatile memory that would not need power for retain memory. Memristors are created from nanowire lattices which could be stacked in three dimensions. Memristors have also previously been shown to behave like brain synapses which could be used for computer architectures that emulate the human brain for neuromorphic computing. Now there is work on multistate memristors that perform computation. This means that eventually processing and memory could be tightly integrated.
Light travels 30 centimeters in 1 nanosecond. Wires have an approximate propagation delay of 1 ns for every 6 inches (15 cm) of length. Logic gates can have propagation delays ranging from more than 10 ns down to the picosecond range, depending on the technology being used.


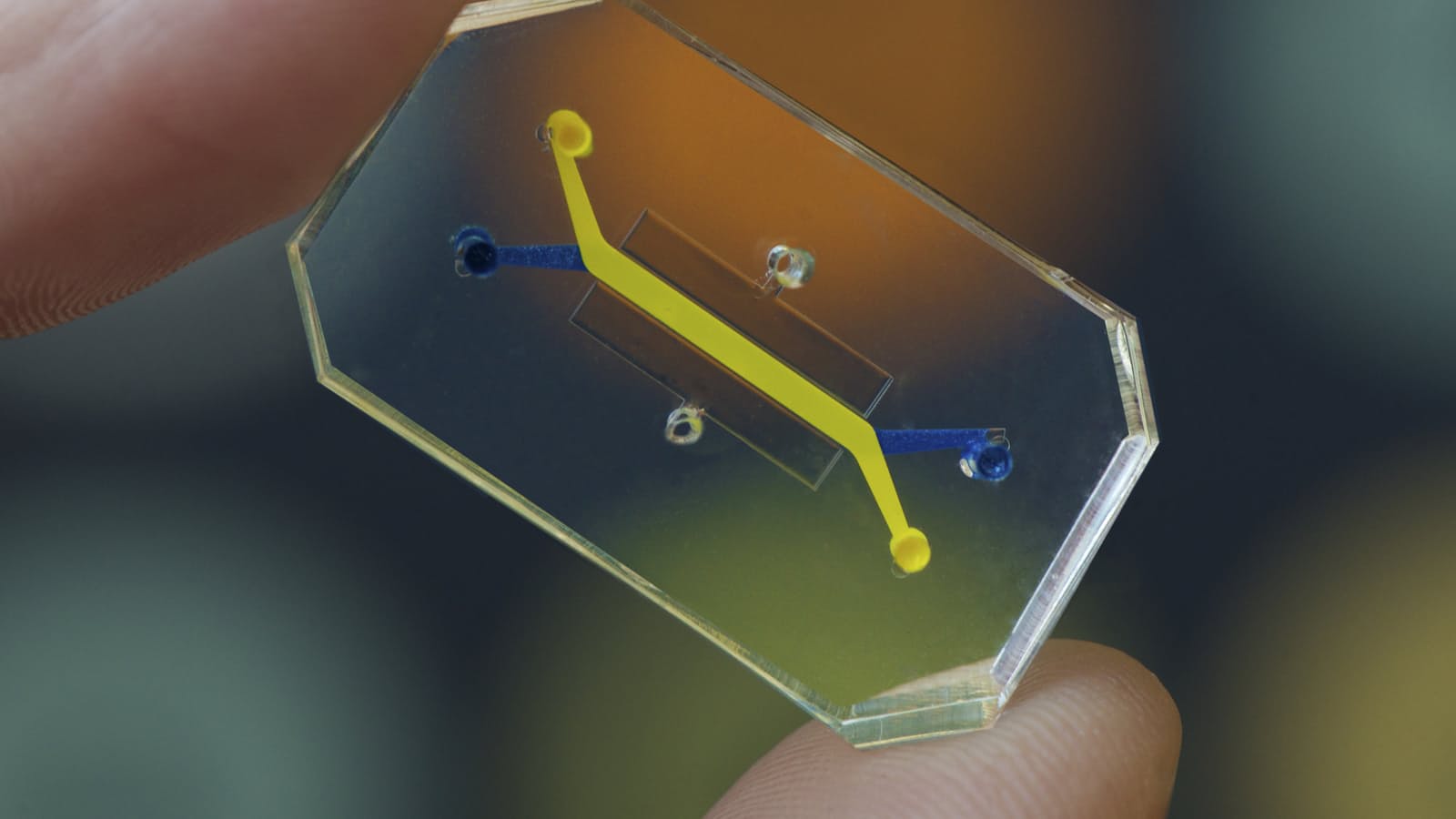
Biological engineers at Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering have invented a microchip that can be lined with living human cells in order to revolutionise medicine, particularly relating to drug testing, disease modelling and personalised medicine.
The ‘human organs-on-chip’ is a microchip made from a clear flexible polymer that contains hollow microfluidic channels that are lined with living human cells, together with an interface that lines the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, known as an endothelium.
The idea is that the microchip can emulate the microarchitecture and functions of multiple human organs such as the lungs, kidneys, skin, bone marrow, intestines and blood-brain barrier. And if you were able to do this, you could then test out drugs and study how diseases affect the body without having to endanger human patients, or waste precious organs needed for transplants.

Pathetic. This is truly a new low for Ransomware hackers.
MUNCIE — An Indiana cancer services agency says it will replace and rebuild its data after a computer hack demanding a ransom.
Cancer Services of East Central Indiana-Little Red Door in Muncie says it was hacked Jan. 11 and the hackers demanded a ransom of 50 bitcoins, or about $43,000, for access to its data.
Executive Director Aimee Fant says most of the agency’s data is in cloud storage and it will replace its server with a secure, cloud-based system. She says it won’t pay a ransom when all of its funds must go toward serving cancer patients and their families and preventative screenings, and it will be back up and running at full capacity by the end of the week.

Many who worked closely with me at Microsoft use to say I had a Crystal ball and was psychic; maybe I have met my match for a career — LOL.
A number of job adverts suggest that Facebook is taking social networking to a different level of science fiction.
The social networking giant has advertised for a Haptics Engineer, a Neural Imaging Engineer, a Signal Processing Engineer and a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Engineer – leading people to think Facebook is working on mind reading technology.
This is supported by each of the job descriptions. The roles are based in Facebook’s elusive ‘Building 8’ in California, where the team will “apply DARPA-style breakthrough development at the intersection of ambitious science and product development.”