
Category: computing

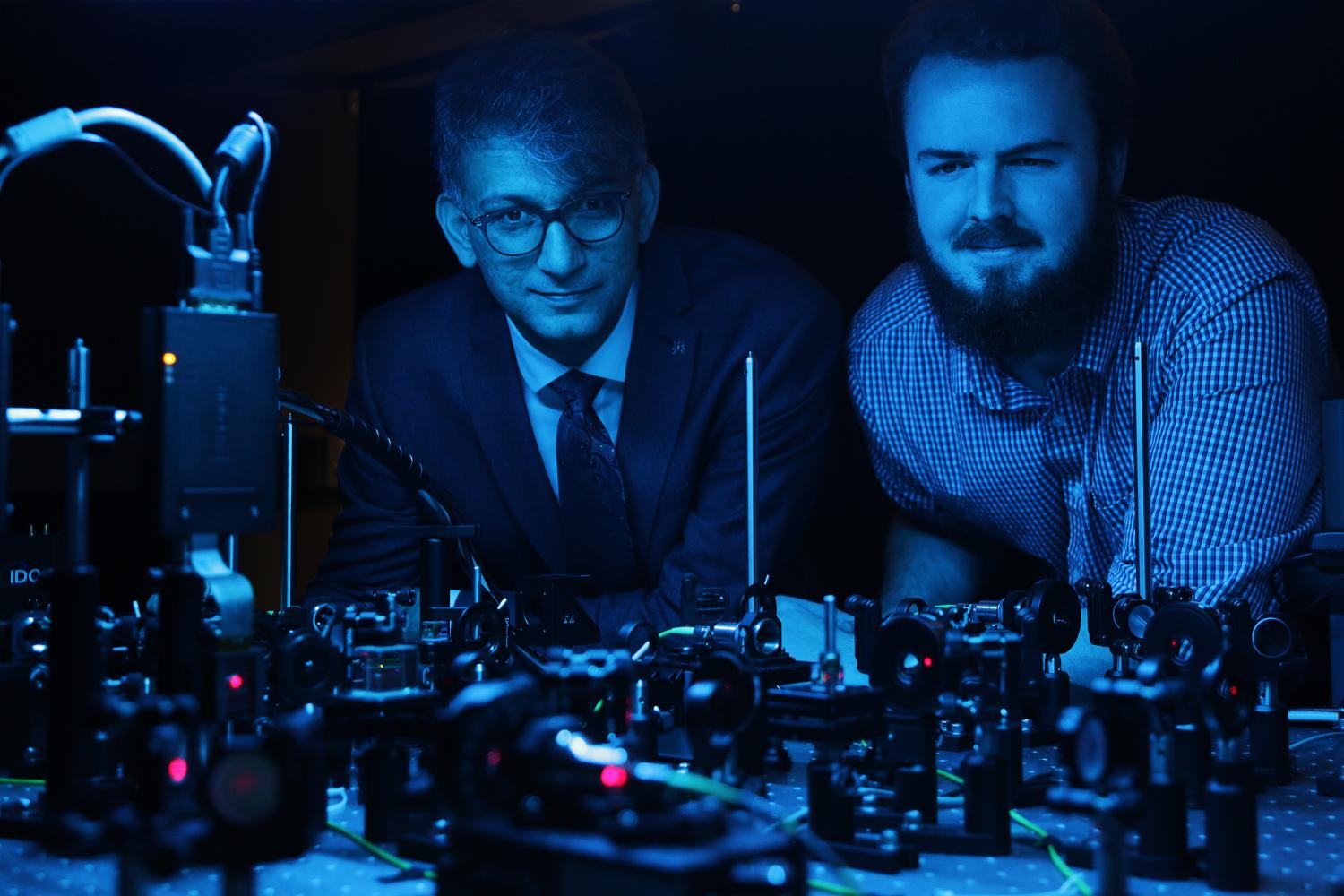
Protecting quantum computing networks against hacking threats
Wish these guys a lot of luck; however, they need to hurry up soon as China is already had a head start with QC.
As we saw during the 2016 US election, protecting traditional computer systems, which use zeros and ones, from hackers is not a perfect science. Now consider the complex world of quantum computing, where bits of information can simultaneously hold multiple states beyond zero and one, and the potential threats become even trickier to tackle. Even so, researchers at the University of Ottawa have uncovered clues that could help administrators protect quantum computing networks from external attacks.
“Our team has built the first high-dimensional quantum cloning machine capable of performing quantum hacking to intercept a secure quantum message,” said University of Ottawa Department of Physics professor Ebrahim Karimi, who holds the Canada Research Chair in Structured Light. “Once we were able to analyze the results, we discovered some very important clues to help protect quantum computing networks against potential hacking threats.”
Quantum systems were believed to provide perfectly secure data transmission because until now, attempts to copy the transmitted information resulted in an altered or deteriorated version of the original information, thereby defeating the purpose of the initial hack. Traditional computing allows a hacker to simply copy and paste information and replicate it exactly, but this doesn’t hold true in the quantum computing world, where attempts to copy quantum information-or qudits-result in what Karimi refers to as “bad” copies. Until now.
Quantum RAM: Modelling the big questions with the very small
Nice write up. What is interesting is that most folks still have not fully understood the magnitude of quantum and how as well as why we will see it as the fundamental ingredient to all things and will be key in our efforts around singularity.
When it comes to studying transportation systems, stock markets and the weather, quantum mechanics is probably the last thing to come to mind. However, scientists at Australia’s Griffith University and Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University have just performed a ‘proof of principle’ experiment showing that when it comes to simulating such complex processes in the macroscopic world quantum mechanics can provide an unexpected advantage.
Griffith’s Professor Geoff Pryde, who led the project, says that such processes could be simulated using a “quantum hard drive”, much smaller than the memory required for conventional simulations.
“Stephen Hawking once stated that the 21st century is the ‘century of complexity’, as many of today’s most pressing problems, such as understanding climate change or designing transportation system, involve huge networks of interacting components,” he says.

The next step in nanotechnology
Nearly every other year the transistors that power silicon computer chip shrink in size by half and double in performance, enabling our devices to become more mobile and accessible. But what happens when these components can’t get any smaller? George Tulevski researches the unseen and untapped world of nanomaterials. His current work: developing chemical processes to compel billions of carbon nanotubes to assemble themselves into the patterns needed to build circuits, much the same way natural organisms build intricate, diverse and elegant structures. Could they hold the secret to the next generation of computing?
TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world’s leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes (or less). Look for talks on Technology, Entertainment and Design — plus science, business, global issues, the arts and much more.
Find closed captions and translated subtitles in many languages at http://www.ted.com/translate
Follow TED news on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/tednews
Like TED on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TED
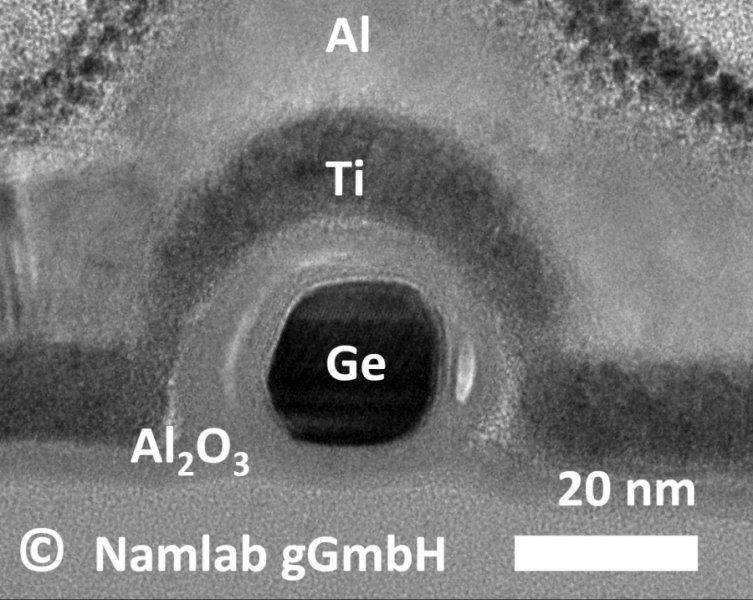
Cleaning up quantum devices
Latest update on the NPL Research on how to have cleaner Quantum Devices.
A paper, based on NPL collaborative research, has been published in the journal Physical Review Letters The work paves the way for the identification and elimination of small amounts of surface defects whose presence on the surfaces of solid state quantum devices is detrimental to their performance.
The research was the result of a fruitful collaboration between NPL’s Quantum Detection Group, the Quantum Device Physics Laboratory at Chalmers University of Technology and the Institute of Chemical Physics at the University of Latvia.
Artistic impression of noise in quantum circuits
The advancement of quantum computing faces a tremendous challenge in improving the reproducibility and robustness of quantum circuits. One of the biggest problems in this field is the presence of noise intrinsic to all these devices, the origin of which has puzzled scientists for many decades.

How we can finally win the fight against aging
I really wanna know why people don’t get this.
For more information on Aubrey de Grey, please visit our website www.tedxmuenchen.de
Dr. Aubrey de Grey is a biomedical gerontologist based Mountain View, California, USA, and is the Chief Science Officer of SENS Research Foundation, a California-based 501©(3) biomedical research charity that performs and funds laboratory research dedicated to combating the aging process. He is also Editor-in-Chief of Rejuvenation Research, the world’s highest-impact peer-reviewed journal focused on intervention in aging. He received his BA in computer science and Ph.D. in biology from the University of Cambridge. His research interests encompass the characterisation of all the accumulating and eventually pathogenic molecular and cellular side-effects of metabolism (“damage”) that constitute mammalian aging and the design of interventions to repair and/or obviate that damage.
Twitter: @aubreydegrey
This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.

Boston startup Whitewood Encryption Systems awarded patent for encryption to fend off quantum computers
Hmmmm.
Computers based on quantum mechanics have been in the realm of science fiction for years, but recently companies like Google (Nasdaq: GOOGL), and even the National Security Agency, have started to think practically about what their existence would mean.
These super-powerful computers would be exciting in many respects, but they would also be able to break the methods of data encryption that currently make it safe to browse the internet or pay for things online.

First ever blueprint unveiled to construct a large scale quantum computer
A blueprint for QC larger servers mass production. The question is; is it the right blueprint for everyone? Not sure.
An international team, led by a scientist from the University of Sussex, have today unveiled the first practical blueprint for how to build a quantum computer, the most powerful computer on Earth.
This huge leap forward towards creating a universal quantum computer is published today (1 February 2017) in the influential journal Science Advances. It has long been known that such a computer would revolutionise industry, science and commerce on a similar scale as the invention of ordinary computers. But this new work features the actual industrial blueprint to construct such a large-scale machine, more powerful in solving certain problems than any computer ever constructed before.
Once built, the computer’s capabilities mean it would have the potential to answer many questions in science; create new, lifesaving medicines; solve the most mind-boggling scientific problems; unravel the yet unknown mysteries of the furthest reaches of deepest space; and solve some problems that an ordinary computer would take billions of years to compute.

Blueprint for a microwave trapped ion quantum computer
More detailed write up on QC Blueprint introduced this week. It does seem to try to address scalability; however, the real test is when we test a smart device and a small server with the blueprint.
The availability of a universal quantum computer may have a fundamental impact on a vast number of research fields and on society as a whole. An increasingly large scientific and industrial community is working toward the realization of such a device. An arbitrarily large quantum computer may best be constructed using a modular approach. We present a blueprint for a trapped ion–based scalable quantum computer module, making it possible to create a scalable quantum computer architecture based on long-wavelength radiation quantum gates. The modules control all operations as stand-alone units, are constructed using silicon microfabrication techniques, and are within reach of current technology. To perform the required quantum computations, the modules make use of long-wavelength radiation–based quantum gate technology. To scale this microwave quantum computer architecture to a large size, we present a fully scalable design that makes use of ion transport between different modules, thereby allowing arbitrarily many modules to be connected to construct a large-scale device. A high error–threshold surface error correction code can be implemented in the proposed architecture to execute fault-tolerant operations. With appropriate adjustments, the proposed modules are also suitable for alternative trapped ion quantum computer architectures, such as schemes using photonic interconnects.

Black holes on an electronic chip
Watch out for the black holes in those QC chips.
Eindhoven professor Rembert Duine has proposed a way to simulate black holes on an electronic chip. This makes it possible to study fundamental aspects of black holes in a laboratory on earth. Additionally, the underlying research may be useful for quantum technologies. Duine (also working at Utrecht University) and colleagues from Chile published their results today in Physical Review Letters.
“Right now, it’s purely theoretical,” says Duine, “but all the ingredients already exist. This could be happening in a lab one or two years from now.” One possibility is in the group of Physics of Nanostructures in the Department of Applied Physics. According to Duine, in these labs experiments are being done that are necessary to create this type of black holes.
Event horizon
Black holes in space are so dense that nothing can escape their gravitational pull once it passes a point of no return called the event horizon. The researchers have now found a way to make such points of no return for spin waves, fluctuations that propagate in magnetic materials. When an electric current runs through the material, the electrons drag these waves along.