Waves, whether they are light waves, sound waves, or any other kind, travel in the same manner in forward and reverse directions—this is known as the principle of reciprocity. If we could route waves in one direction only—breaking reciprocity—we could transform a number of applications important in our daily lives. Breaking reciprocity would allow us to build novel “one-way” components such as circulators and isolators that enable two-way communication, which could double the data capacity of today’s wireless networks. These components are essential to quantum computers, where one wants to read a qubit without disturbing it. They are also critical to radar systems, whether in self-driving cars or those used by the military.
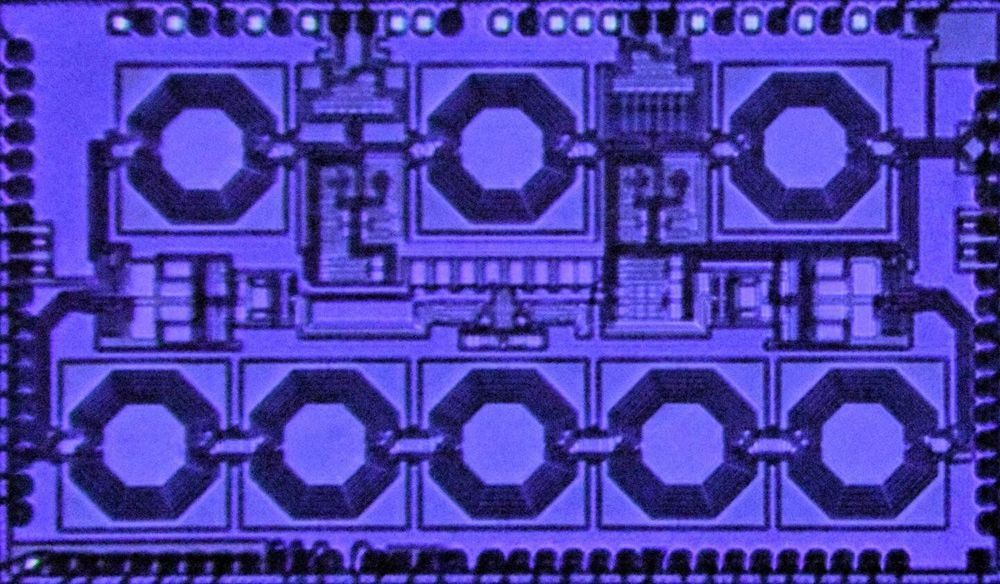
A team led by Harish Krishnaswamy, professor of electrical engineering, is the first to build a high-performance non-reciprocal device on a compact chip with a performance 25 times better than previous work. Power handling is one of the most important metrics for these circulators and Krishnaswamy’s new chip can handle several watts of power, enough for cellphone transmitters that put out a watt or so of power. The new chip was the leading performer in a DARPA SPAR (Signal Processing at RF) program to miniaturize these devices and improve performance metrics. Krishnaswamy’s group was the only one to integrate these non-reciprocal devices on a compact chip and also demonstrate performance metrics that were orders of magnitude superior to prior work. The study was presented in a paper at the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference in February 2020, and published May 4, 2020, in Nature Electronics.
“For these circulators to be used in practical applications, they need to be able to handle watts of power without breaking a sweat,” says Krishnaswamy, whose research focuses on developing integrated electronic technologies for new high-frequency wireless applications. “Our earlier work performed at a rate 25 times lower than this new one—our 2017 device was an exciting scientific curiosity but it was not ready for prime time. Now we’ve figured out how to build these one-way devices in a compact chip, thus enabling them to become small, low cost, and widespread. This will transform all kinds of electronic applications, from VR headsets to 5G cellular networks to quantum computers.”