Looks like living cells may have a lot more surprises to offer.
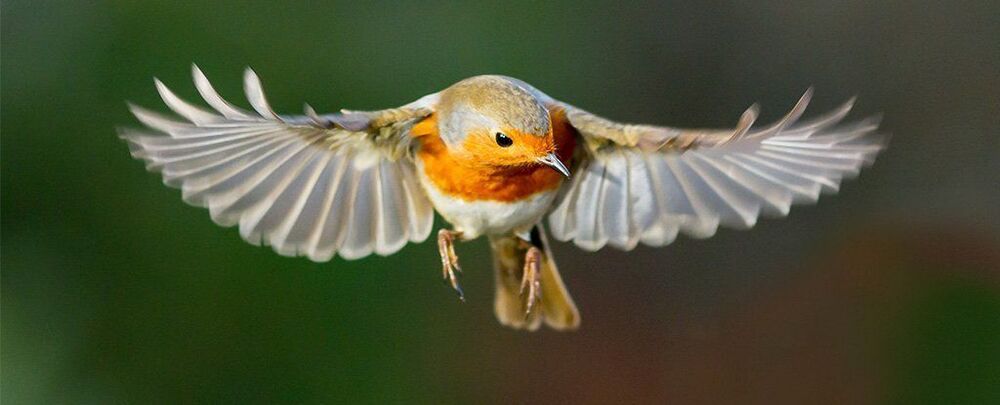
Seeing our world through the eyes of a migratory bird would be a rather spooky experience. Something about their visual system allows them to ‘see’ our planet’s magnetic field, a clever trick of quantum physics and biochemistry that helps them navigate vast distances.
Now, for the first time ever, scientists from the University of Tokyo have directly observed a key reaction hypothesised to be behind birds’, and many other creatures’, talents for sensing the direction of the planet’s poles.
Importantly, this is evidence of quantum physics directly affecting a biochemical reaction in a cell — something we’ve long hypothesised but haven’t seen in action before.