WOODS HOLE, Mass. — The dialogue between neurons is of critical importance for all nervous system activities, from breathing to sensing, thinking to running. Yet neuronal communication is so fast, and at such a small scale, that it is exceedingly difficult to explain precisely how it occurs. A preliminary observation in the Neurobiology course at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), enabled by a custom imaging system, has led to a clear understanding of how neurons communicate with each other by modulating the “tone” of their signal, which previously had eluded the field. The report, led by Grant F. Kusick and Shigeki Watanabe of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, is published this week in Nature Neuroscience.
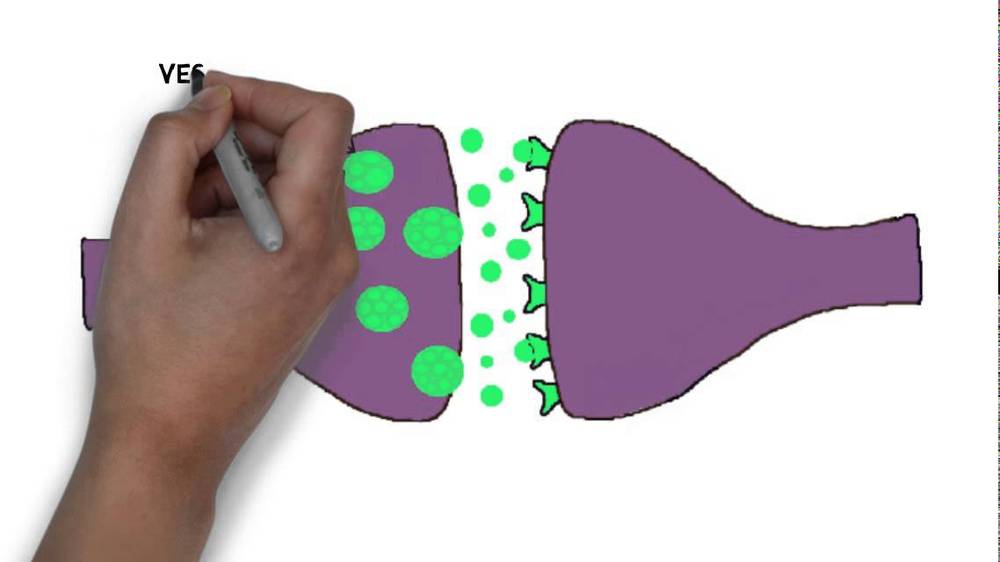
In 2016 Watanabe, then on the Neurobiology course faculty, introduced students to the debate over how many synaptic vesicles can fuse in response to one action potential (see this 2-minute video for a quick brush-up on neurotransmission). To probe this controversy, they used a “zap-and-freeze” imaging technology conceived by co-authors M. Wayne Davis, Watanabe and Erik Jorgensen, and built by Leica for testing in the Neurobiology course. They zapped a neuron with electricity to induce an action potential, then quickly froze the neuron and took an image. They saw multiple vesicles fusing at once at many synapses, the first novel finding of this Nature Neuroscience report.
But there was more. Back at Johns Hopkins, Kusick and Watanabe decided to walk through the neurotransmission process with zap-and-freeze, taking images every 3 milliseconds after the action potential. That’s when they found an answer to an even larger question — how do neurons change the tone of their neurotransmission signal?