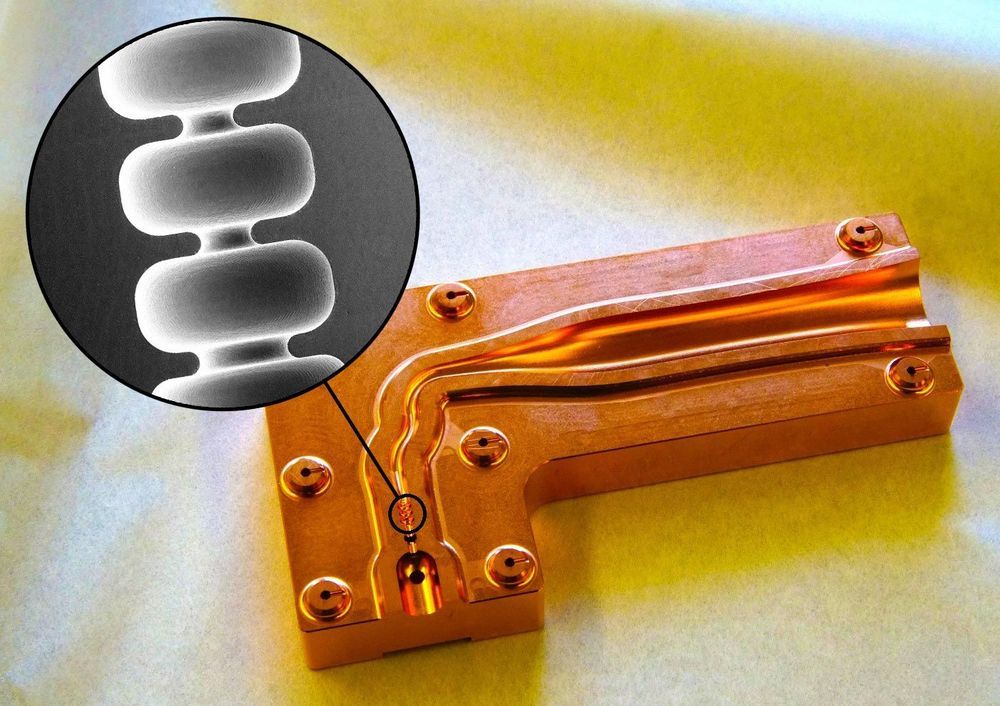
SLAC invention uses terahertz radiation to power a miniscule copper accelerator structure.
Particle accelerators generate high-energy beams of electrons, protons and ions for a wide range of applications, including particle colliders that shed light on nature’s subatomic components, X-ray lasers that film atoms and molecules during chemical reactions and medical devices for treating cancer.
As a rule of thumb, the longer the accelerator, the more powerful it is. Now, a team led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory has invented a new type of accelerator structure that delivers a 10 times larger energy gain over a given distance than conventional ones. This could make accelerators used for a given application 10 times shorter.