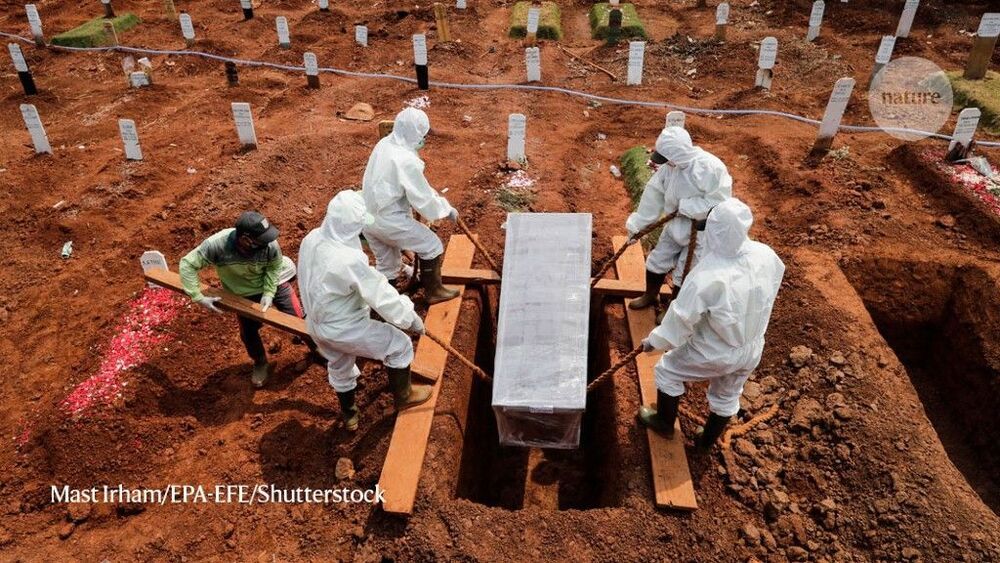
Viruses are tiny invaders that cause a wide range of diseases, from rabies to tomato spotted wilt virus and, most recently, COVID-19 in humans. But viruses can do more than elicit sickness — and not all viruses are tiny.
Large viruses, especially those in the nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA virus family, can integrate their genome into that of their host — dramatically changing the genetic makeup of that organism. This family of DNA viruses, otherwise known as “giant” viruses, has been known within scientific circles for quite some time, but the extent to which they affect eukaryotic organisms has been shrouded in mystery — until now.
“Viruses play a central role in the evolution of life on Earth. One way that they shape the evolution of cellular life is through a process called endogenization, where they introduce new genomic material into their hosts. When a giant virus endogenizes into the genome of a host algae, it creates an enormous amount of raw material for evolution to work with,” said Frank Aylward, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences in the Virginia Tech College of Science and an affiliate of the Global Change Center housed in the Fralin Life Sciences Institute.