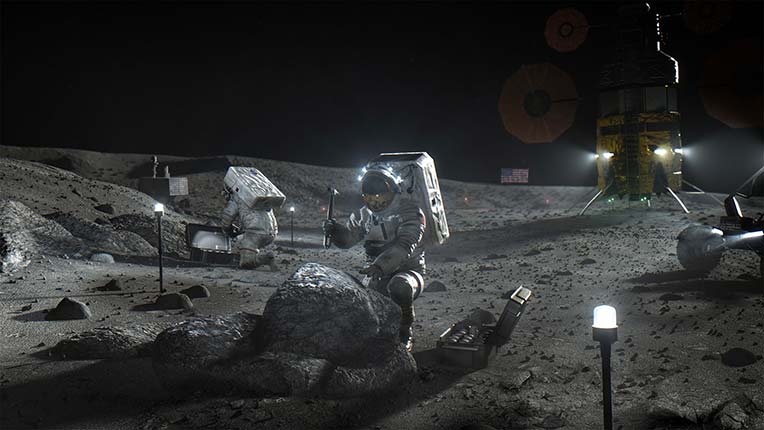
Here’s a riddle: What do the Moon, nuclear weapons, clean energy of the future, terrorism, and lung disease all have in common?
The answer is helium-3, a gas that’s extremely rare on Earth but 100 million times more abundant on the Moon.
The capability to show anatomic details of the lungs and airways, and the ability to display functional imaging as a patient breathes, makes helium-3 MRI far better than the standard method of testing lung function. Called spirometry, this method tells physicians how the lungs function overall, but does not home in on particular areas that may be causing a problem. Plus, spirometry requires patients to follow instructions and hold their breath, so it is not great for testing young children with pulmonary disease.
Over the past several years, researchers have been developing MRI for lung testing using other hyperpolarized gases. The main alternative to helium-3 is xenon-129. Over the years, researchers have learned to overcome certain disadvantages of the latter, such as its potential to put patients to sleep. Since helium-3 provides the strongest signal, though, it is still the best gas for MRI studies in many lung conditions.
But the supply of helium-3 on Earth has been decreasing in recent years, due to the declining rate of dismantling of warheads, just as the Department of Homeland Security has required more and more of the gas for neutron detection. As a result, the cost of the gas has skyrocketed. Less is available now for medical uses–unless, of course, we begin mining it on the moon.