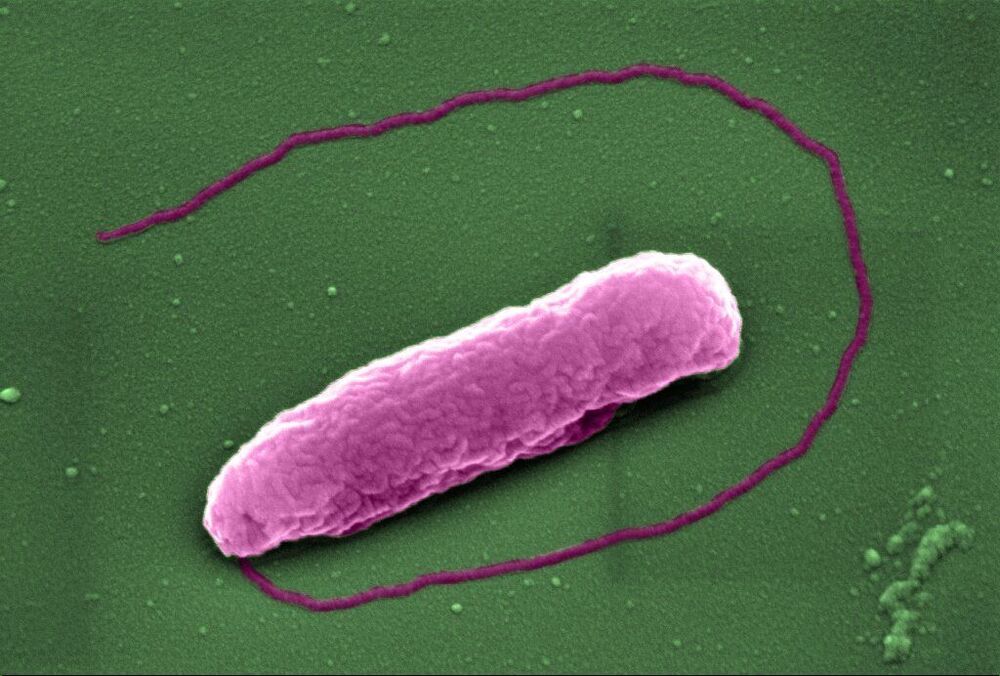
Now, researchers have revealed that colistin punches holes in bacteria, causing them to pop like balloons. The work, funded by the Medical Research Council and Wellcome Trust, and published in the journal eLife, also identified a way of making the antibiotic more effective at killing bacteria.
Scientists have revealed how an antibiotic of ‘last resort’ kills bacteria.
The findings, from Imperial College London and the University of Texas, may also reveal a potential way to make the antibiotic more powerful.
The antibiotic colistin has become a last resort treatment for infections caused by some of the world’s nastiest superbugs. However, despite being discovered over 70 years ago, the process by which this antibiotic kills bacteria has, until now, been something of a mystery.