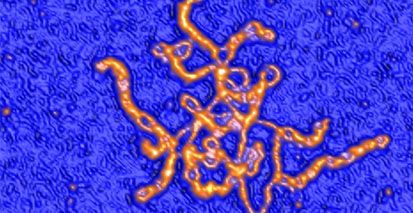
Chromatin proteins have expanded the mammalian synthetic biology toolbox by enabling control of active and silenced states at endogenous genes. Others have reported synthetic proteins that bind DNA and regulate genes by altering chromatin marks, such as histone modifications. Previously we reported the first synthetic transcriptional activator, the “Polycomb-based transcription factor” (PcTF), that reads histone modifications through a protein-protein interaction between the PCD motif and trimethylated lysine 27 of histone H3 (H3K27me3). Here, we describe the genome-wide behavior of PcTF. Transcriptome and chromatin profiling revealed PcTF-sensitive promoter regions marked by proximal PcTF and distal H3K27me3 binding. These results illuminate a mechanism in which PcTF interactions bridge epigenetic marks with the transcription initiation complex. In three cancer-derived human cell lines tested here, many PcTF-sensitive genes encode developmental regulators and tumor suppressors. Thus, PcTF represents a powerful new fusion-protein-based method for cancer research and treatment where silencing marks are translated into direct gene activation.
Category: biotech/medical
“Fifty years after the show aired, Star Trek’s fictional tricorder is far from becoming a reality. But a $10 million prize from the XPRIZE Foundation is hoping to motivate inventors to create one quickly.”
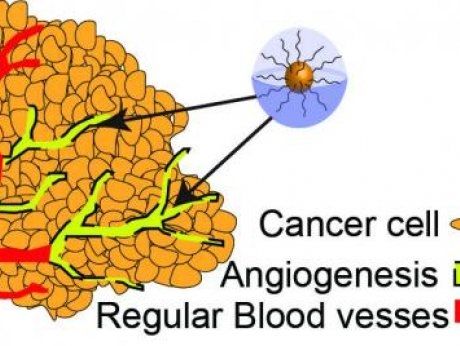
Cancer thrives when mutated cells undergo frequent division. Most anti-cancer drugs work by inserting themselves in between the DNA base pairs that encode our genetic information. This process is known as intercalation, and it can result in subtle changes to the DNA molecule’s geometric shape or tertiary structure. These structural changes interfere with the DNA’s transcription and a cell’s replication process, ultimately resulting in cell death.
While intercalating agents used in chemotherapy drugs are highly effective in fighting cancer, they also may kill important cells in the body and lead to other complications such as heart failure. Therefore, researchers are always searching for faster, cheaper and more accurate tools to aid in the design of next-generation anti-cancer drugs with reduced side effects.
A paper published in ACS Nano, one of the top nanotechnology journals in the world, explores this topic. “Modeling and Analysis of Intercalant Effects on Circular DNA Conformation,” (LINK TO http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.6b04876) focuses on the effect of the intercalating agent ethidium bromide (a mimic for many chemotherapy drugs) on the tertiary structure of DNA.
Luv this article because it hits a very important topic of how will things change with BMI/ mind control technology in general. For example with BMI will we need wearable devices? if so, what type and why? Also, how will banking, healthcare, businesses, hospitality, transportation, media and entertainment, communications, government, etc. in general will change with BMI and AI together? And, don’t forget cell circuitry, and DNA storage and processing capabilities that have been proven to date and advancing.
When you take into account what we are doing with synthetic biology, BMI, AI, and QC; we are definitely going to see some very amazing things just within the next 10 years alone.
Neuroscientists have just demonstrated that we can control drones with our minds. Find out how this shapes the future of digital marketing.
A very old story and one that myself and others have raised many times. However, worth repeating due to the current advancements in BMI.
A vulnerability of brain implants to cyber-security attacks could make “brainjacking”, which has been discussed in science fiction for decades, a reality, say researchers from the University of Oxford. Writing in The Conversation, an Australia-based non-profit media, Laurie Pycroft discussed brain implants as a new frontier of security threat.
The most common type of brain implant is the deep brain stimulation (DBS) system. It consists of implanted electrodes positioned deep inside the brain connected to wires running under the skin, which carry signals from an implanted stimulator.
The stimulator consists of a battery, a small processor, and a wireless communication antenna that allows doctors to programme it. In essence, it functions much like a cardiac pacemaker, with the main distinction being that it directly interfaces with the brain, Pycroft explained.
Never under estimate people you never know who may be the next Bill Gates.
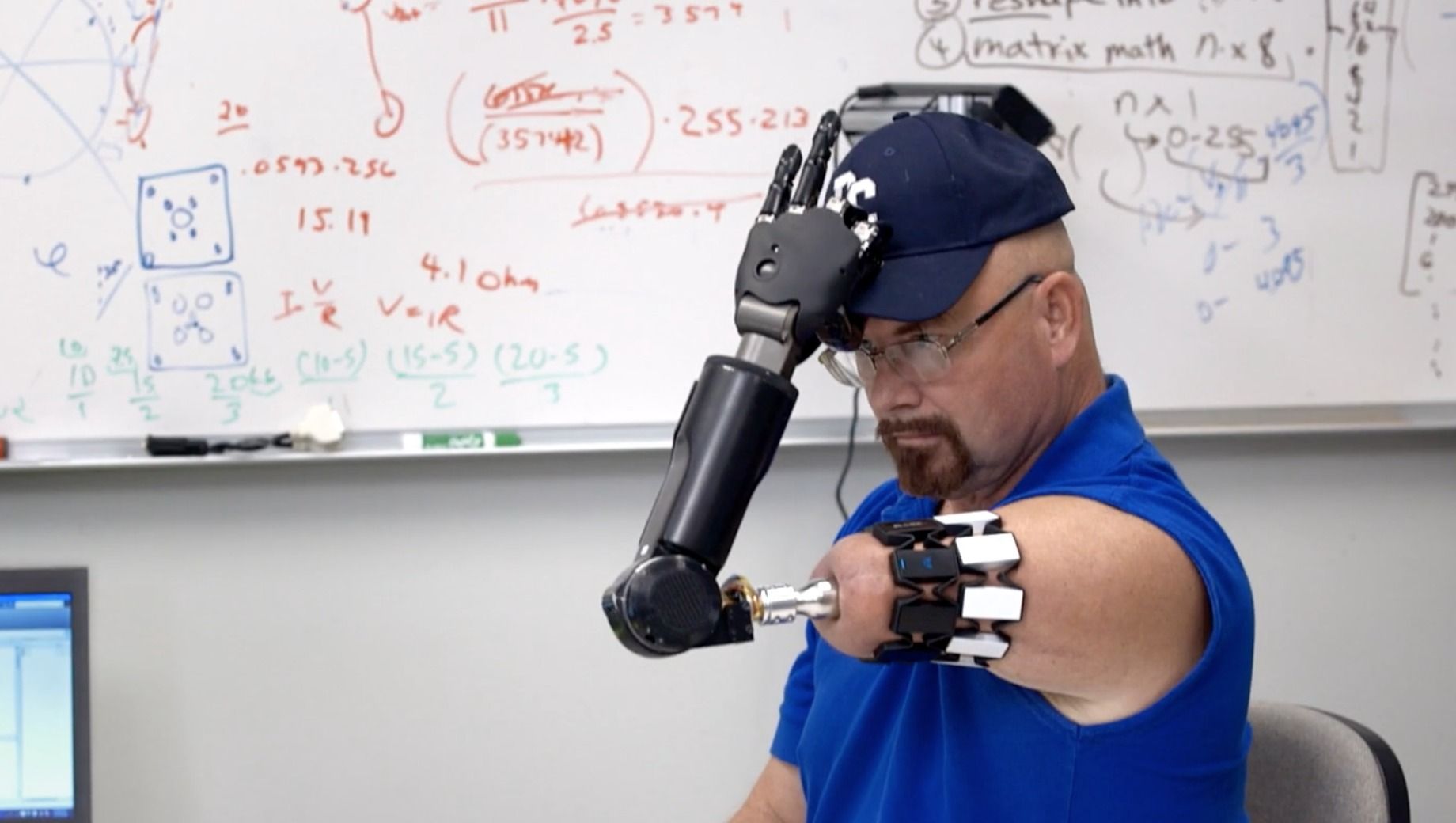
After losing his left arm to cancer in 2008, Jonny Matheny’s life changed radically. The self-styled West Virginia hillbilly, formerly a retail bread sales and delivery man, started traveling to medical research facilities around the country to volunteer as a test-subject for advanced prosthetics and experimental surgeries. Today, Matheny is something of a Model T for cyborgs, wielding one of the most advanced mind-controlled prosthetics ever built.
When I met Matheny at a DARPA technology expo earlier this year, I was astounded by the flexibility and responsiveness of his Modular Prosthetic Limb, the latest in a series of mind-controlled prosthetics developed at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. But nothing drives home the revolutionary potential of a device like this than seeing it used to perform mundane tasks: effortlessly putting on a hat or stirring a pot, for instance.
A new video by Freethink gives us a behind-the-scenes look at Matheny’s journey to become the world’s most sophisticated bionic man. Honestly, more than reading any detailed scientific primer, watching a guy serve salad with a carbon-fiber arm that takes cues from his brain convinced me that the future is going be full of cyborgs, and that the rest of us will be be jealous.
Interesting perspective on cancer.
A lot of the focus in the medical approach to cancer focuses on destroying it, but what if it was treated cancer like long-term diseases such as diabetes? Researchers have explored the concept of a method to control cancer with a drug delivery system that keeps the cells from multiplying.
The method, which researchers have called the “metronomic dosage regimen,” involves giving the patient lower doses of chemotherapy more frequently to create an environment where cancer cells cannot grow.
“This new system takes some existing cancer therapy drugs for ovarian cancer, delivers both of them at the same time and allows them to work synergistically,” said Adam Alani, an associate professor in the Oregon State University/Oregon Health & Science University College of Pharmacy, and lead author on the study published in the journal Chemistry of Materials. “Imagine if we could manage cancer on a long-term basis as a chronic condition, like we now do high blood pressure or diabetes. This could be a huge leap forward.”
A nice story out on transhumanism:
An idea that has frequently been used by science fiction is now starting to gain widespread attention by futurists, scientists, philosophers, and even the general public; the idea that the human species needs to use either artificial augmentations or gene manipulation to usher in the next stage of evolution. That idea is transhumanism.
 But why would humans want to willingly accelerate or initiate the next step in evolution? The positives of transhumanism are lofty goals that mankind has sought after for years, goals such as a world without diseases, ignorance, or even death. The only question, and an extremely important one, is how much is humanity willing to modify itself to attain those goals, and could the end result still be considered human? Some sources even suggest that in order to discuss individuals who are radically different from modern-day humans, the term “posthuman” must be used. Transhumanists who alter or augment themselves would theoretically at some point become a posthuman.
But why would humans want to willingly accelerate or initiate the next step in evolution? The positives of transhumanism are lofty goals that mankind has sought after for years, goals such as a world without diseases, ignorance, or even death. The only question, and an extremely important one, is how much is humanity willing to modify itself to attain those goals, and could the end result still be considered human? Some sources even suggest that in order to discuss individuals who are radically different from modern-day humans, the term “posthuman” must be used. Transhumanists who alter or augment themselves would theoretically at some point become a posthuman.
There are some examples that could be considered related to transhumanism. For example, vaccinations, laser eye surgery, and hearing aids are all technological innovations used to help improve the human body in some way. However, transhumanism suggests that humans in their current stage have not reached the end of their evolution, and that transhumanism itself, the modification of our bodies, would be the culmination of our evolution. However, transhumanism emphasizes that the next stage of evolution should be directed by humans rather than left to environmental or outside factors.
A number of different organizations have arisen that espouse the principles of transhumanism, such as Humanity+ which was originally founded as the World Transhumanist Association (WTA). In 2002, Humanity+ issued the “Transhumanist Declaration” which is a series of eight points that outlines the goals of transhumanism, such as the believe that humanity has not yet realized its potential, that humans should have the freedom to choose how they advance themselves, recognizing the sentience of human, animal and artificial intelligence, etc.