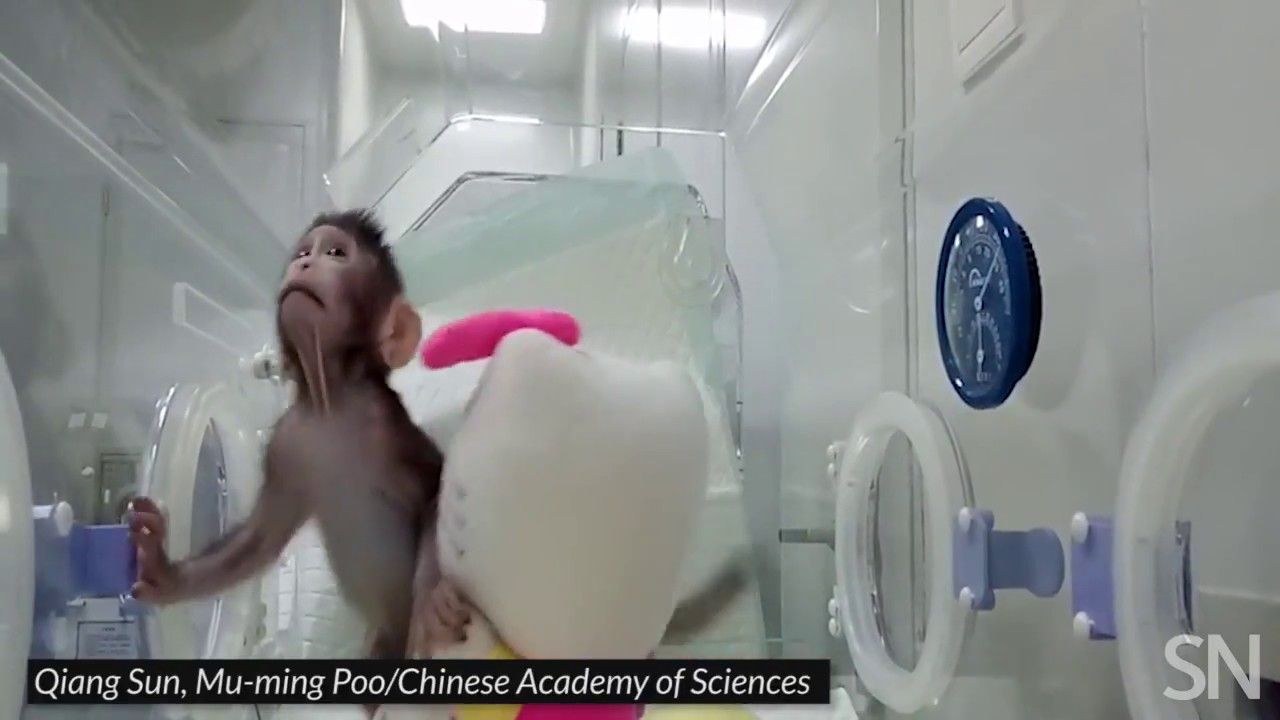
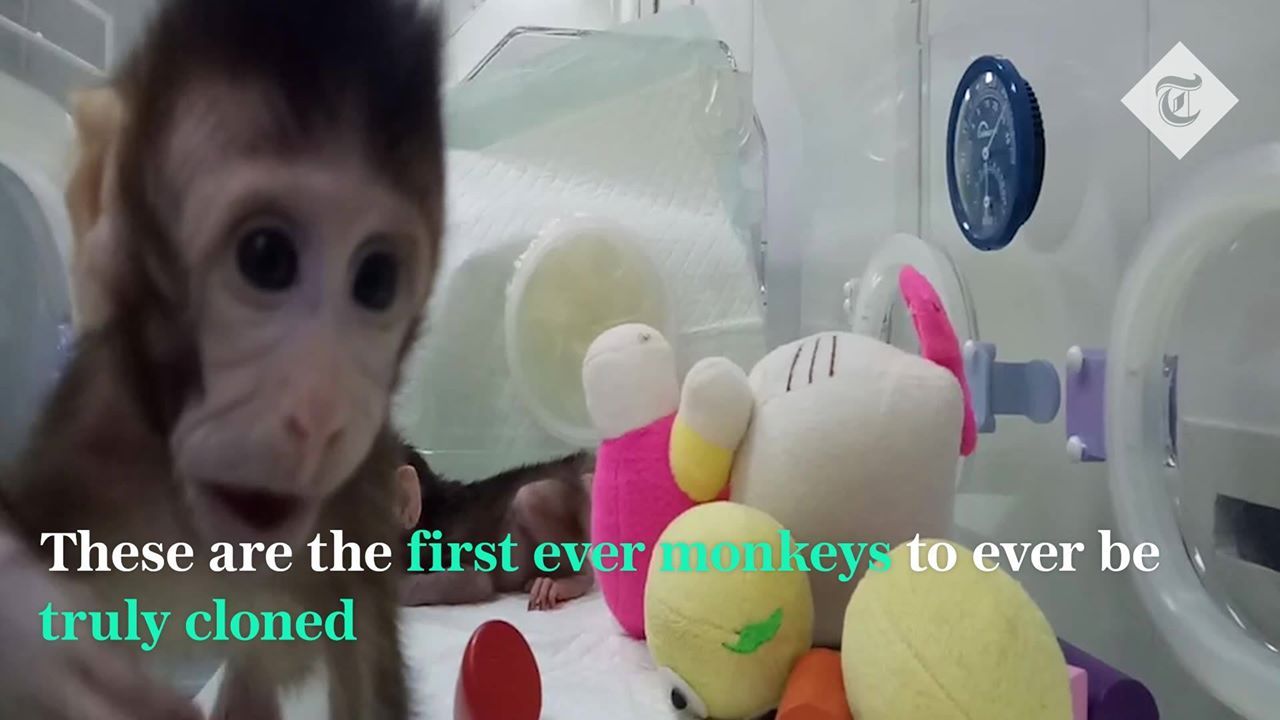
Since the birth of Dolly the sheep in 1996, scientists across the globe have used the same technique to clone nearly two dozen other animal species, including cats, dogs, rats, and cattle. Primates, however, had proven resistant to the process — until now.
In a new study published in Cell, a team of Chinese researchers led by Qiang Sun at the Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Neuroscience in Shanghai reveal that they’ve found a way to tweak the Dolly cloning technique to make it work in primates. Their efforts have resulted in the birth of two cloned female macaques: Zhong Zhong and Hua Hua.