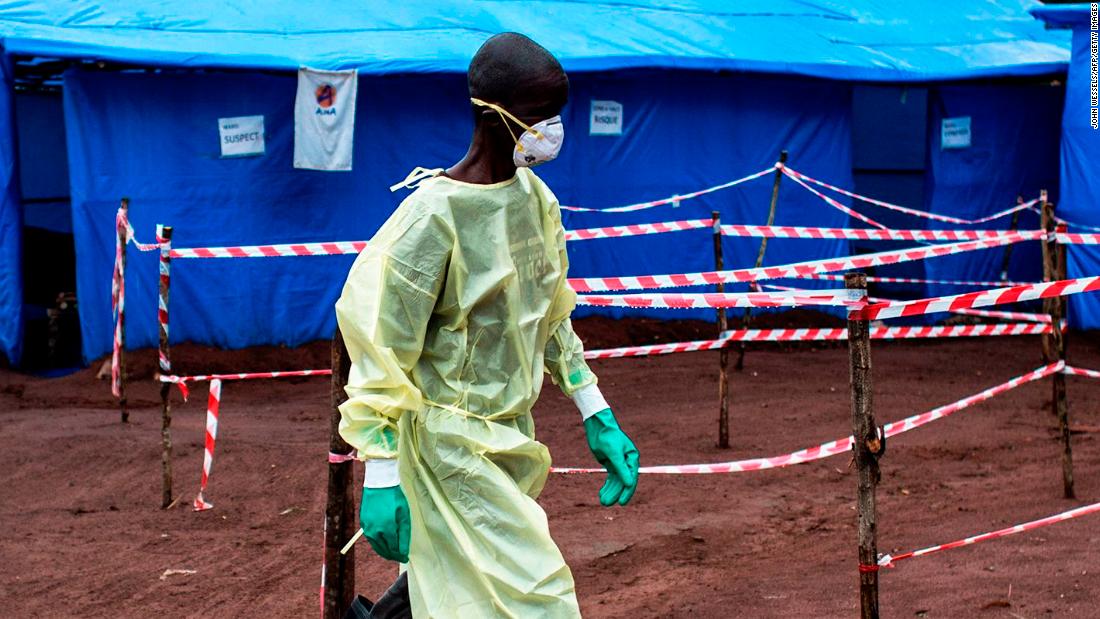
The government of the Democratic Republic of Congo declared an outbreak of Ebola hemorrhagic fever, a rare and deadly disease, on Tuesday, the World Health Organization reported. The declaration came after laboratory results confirmed two cases of the disease in the province of Bikoro in the northwestern part of the country.
Ebola virus disease, which most commonly affects people and nonhuman primates (monkeys, gorillas and chimpanzees), is caused by one of five Ebola viruses. The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission. The average case fatality rate is around 50%.
A government statement released Tuesday states that the Ministry of Health has “taken all necessary measures to respond promptly and effectively to this new epidemic of Ebola in the DRC’s national territory”.