Cultural inhibitions also impede the development of end-of-life care. Talking about death has long been taboo. People often feel that it is their filial duty to ensure that sick parents receive curative treatment, even when doctors advise that there is no chance of recovery and the treatment will be painful. Applications to build hospices are sometimes challenged by local residents who resent the presence of death on their doorsteps. Mr Li says neighbours’ objections have forced Songtang Hospice to move six times.
WHEN Li Songtang was 17, officials overseeing Mao’s chaotic Cultural Revolution sent him from Beijing to Inner Mongolia, a northern province where he became a “barefoot doctor”—a medical worker with rudimentary training. His patients included an academic whom the government had expelled in disgrace from the capital, and who had become terminally ill. The patient grew sicker and increasingly troubled by his political black mark. Unable to console him, Mr Li eventually lied that he had persuaded authorities to wipe the slate clean. The patient grabbed his arm with relief and gratitude, recalls Mr Li. “I can still feel it today.”
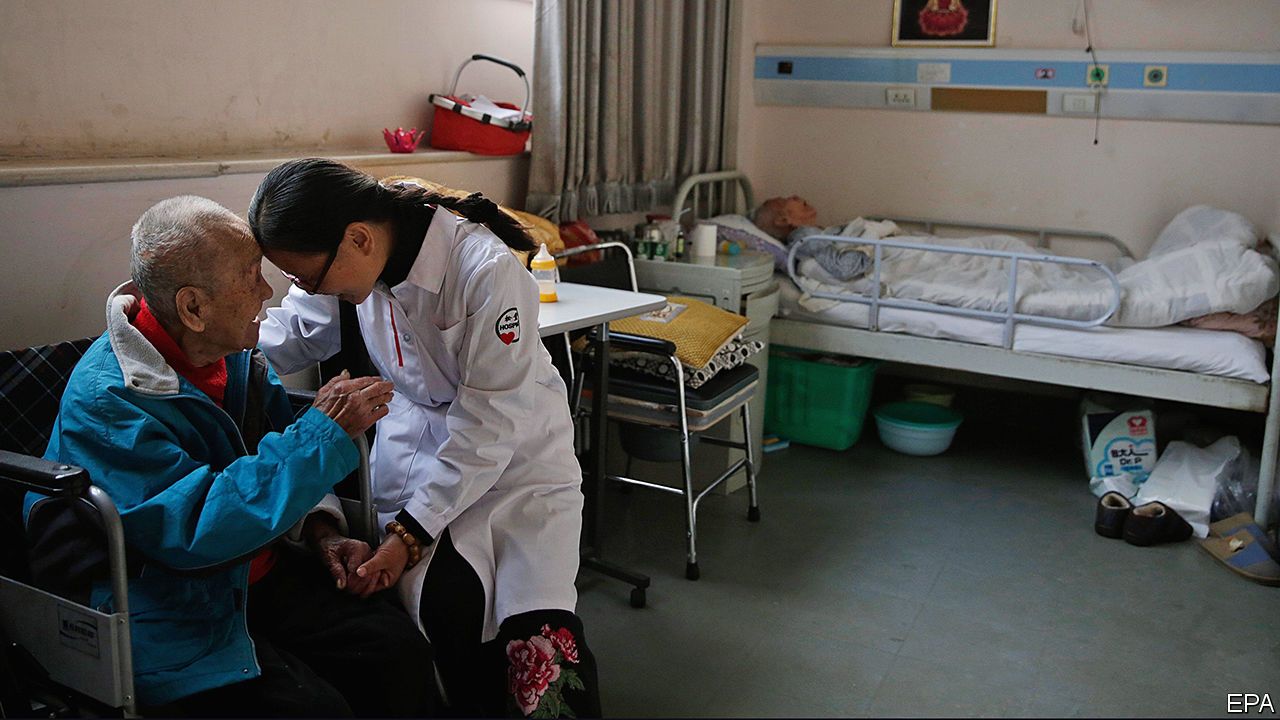
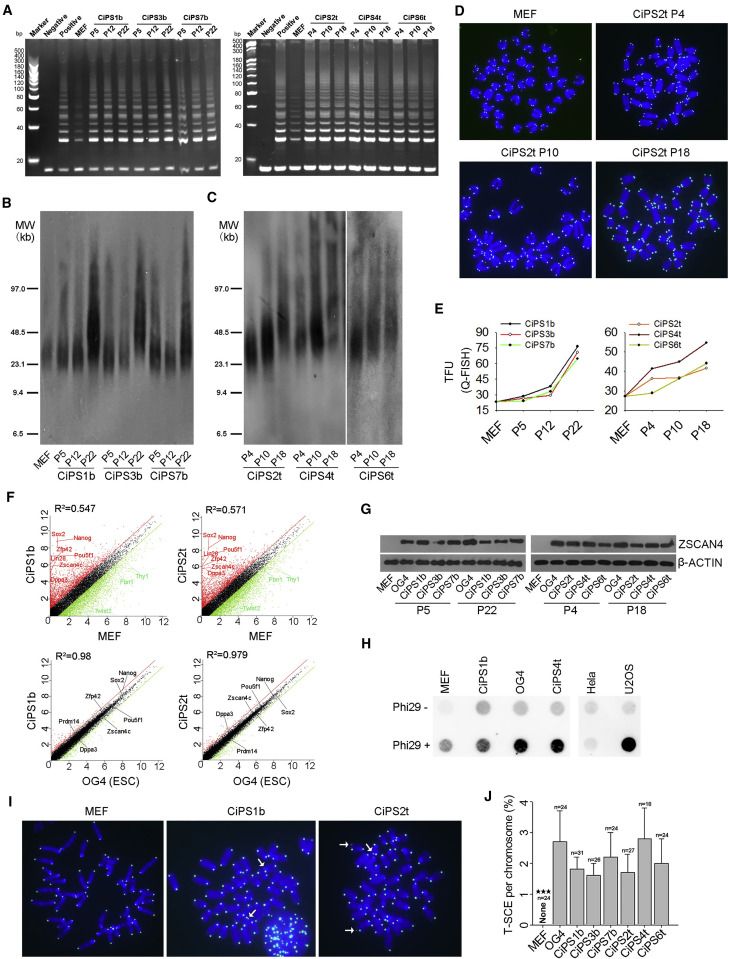
Mr Li’s experience of caring for the dying man eventually resulted in the hospice he runs in a three-storey building in Beijing’s outskirts. The facility is home to about 300 people, most of them elderly and with late-stage cancer (a patient there is pictured with a nurse). On a weekend the bright corridors are busy with volunteers who have come to chat with patients. Zhang Zhen’e, a smiley 76-year-old who shares her room with six other women, says she tries to stay cheerful because days spent worrying are “days lost”. A nearby ward for dying babies, painted green and decorated with mobiles, is less easy to visit. Eight children snooze there, asleep in mismatched wooden cots.
Get our daily newsletter
Upgrade your inbox and get our Daily Dispatch and Editor’s Picks.