Chemically induced pluripotent stem cells (CiPSCs) may provide an alternative and attractive source for stem cell-based therapy. Sufficient telomere lengths are critical for unlimited self-renewal and genomic stability of pluripotent stem cells. Dynamics and mechanisms of telomere reprogramming of CiPSCs remain elusive. We show that CiPSCs acquire telomere lengthening with increasing passages after clonal formation. Both telomerase activity and recombination-based mechanisms are involved in the telomere elongation. Telomere lengths strongly indicate the degree of reprogramming, pluripotency, and differentiation capacity of CiPSCs. Nevertheless, telomere damage and shortening occur at a late stage of lengthy induction, limiting CiPSC formation. We find that histone crotonylation induced by crotonic acid can activate two-cell genes, including Zscan4; maintain telomeres; and promote CiPSC generation. Crotonylation decreases the abundance of heterochromatic H3K9me3 and HP1α at subtelomeres and Zscan4 loci. Taken together, telomere rejuvenation links to reprogramming and pluripotency of CiPSCs. Crotonylation facilitates telomere maintenance and enhances chemically induced reprogramming to pluripotency.
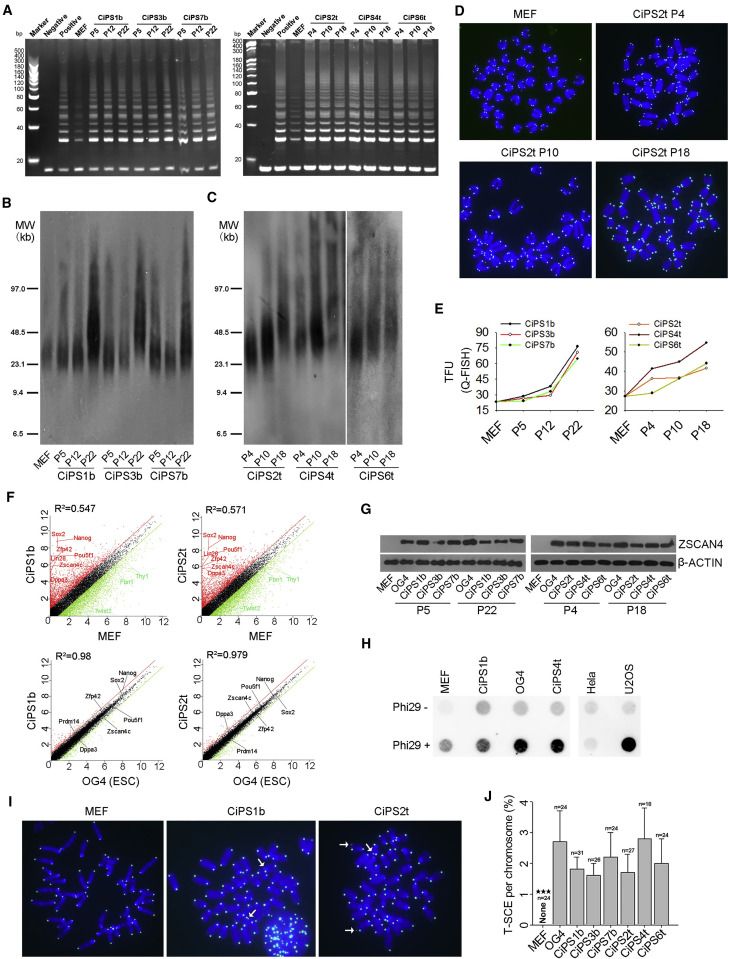
Dynamics of Telomere Rejuvenation during Chemical Induction to Pluripotent Stem Cells
Read more