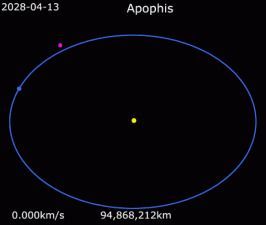
Astronomers at the University of Hawaii issued a statement on October 26, 2020, revealing critical new findings linked to the large near-Earth asteroid 99942 Apophis, which is expected to pass close to Earth in 2029, 2036 and again in 2068. Dave Tholen and collaborators announced they have now detected a Yarkovsky acceleration on asteroid Apophis, arising from a minuscule push imparted by sunlight. This force is particularly important for asteroid Apophis, the scientists in Hawaii said, because it relates to the possibility of an Earth impact in 2068.
The 2021 lunar calendars are here! Order yours before they’re gone. Makes a great gift!
Tholen and colleagues used the 323-inch (8.2-meter) Subaru Telescope at Mauna Kea, Hawaii, to make the new observations. Their work suggests that the huge space rock – whose estimated diameter is between 1,115 and 1,214 feet (340 to 370 meters) – is drifting more than 500 feet (about 170 meters) per year from its expected position in its orbit.