In aerospace, parts are complicated, and manufacturing them can be very expensive and time consuming. When rocket engine parts can take up to a year to make, it is very difficult to start a new rocket company and for aerospace companies to be cost effective, innovative and nimble.
These barriers to entry are why you don’t see many start-up space companies and why the industry has relied on the same basic engine designs as those built during the Apollo program.
3D printing is changing all that. At Virgin Orbit, we are building a rocket system that will send small satellites into orbit. We aim to open access to space for small satellites to improve life on earth through services such as internet connectivity to the under connected and data for planning, production, disaster mitigation etc.




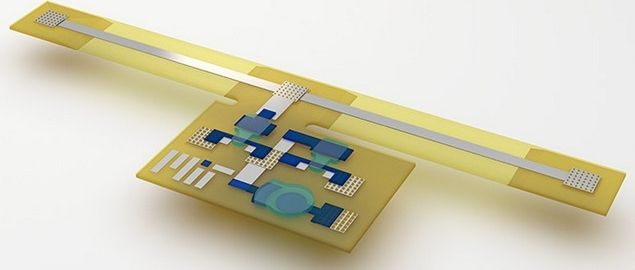
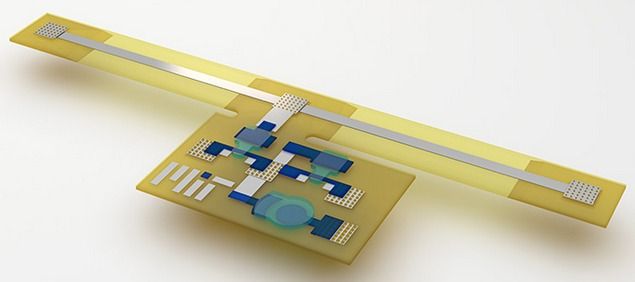 Illustration of 3D-printed sensory composite (credit: Subramanian Sundaram)
Illustration of 3D-printed sensory composite (credit: Subramanian Sundaram)

