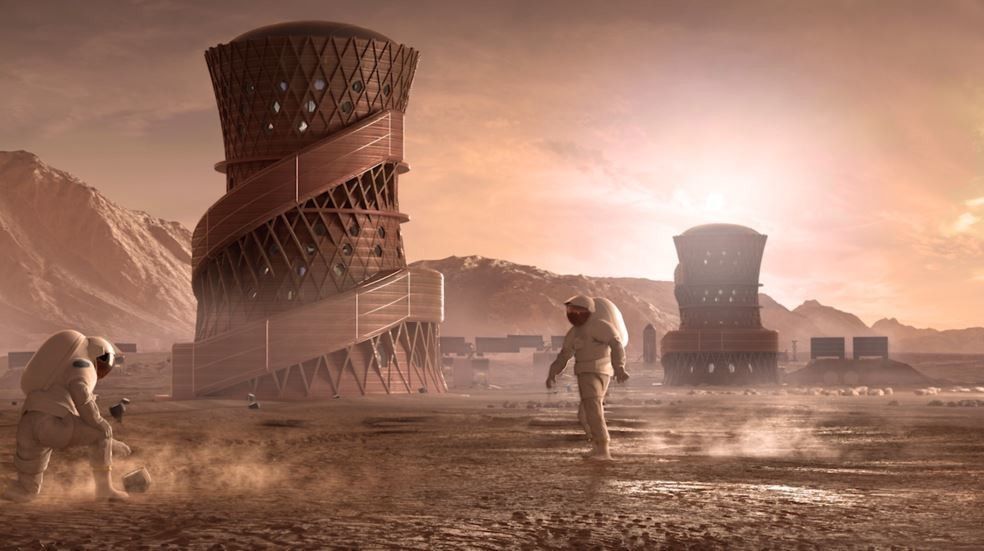
NASA has chosen the winner in its contest to design habitation for humans on Mars. It will be built on the red planet using a 3D printer and concrete made from pulverised Martian rocks.



A team of bioengineers has successfully 3D-printed tissues they believe doctors could one day implant into patients to help heal the knee, ankle, and elbow injuries that have ended the careers of countless athletes.
“I think this will be a powerful tool to help people with common sports injuries,” Rice University researcher Sean Bittner said in a press release — though the impact of the group’s work could extend far beyond the turf or pitch.

Relativity Space is working to 3D print the Terran 1 rocket in 60 days using laser printing and direct energy deposition. They will have a test flight in 2020 and will have commercial flights in 2021.
They use proprietary materials which are custom designed for printing. They are using stronger alloys designed to take advantage of Stargate’s printing physics. They have highly reliable materials for printing rocket structures and are using an in-house metallurgy and material characterization lab.
Terran 1 Baseline:

A new network of 3D-printed gun advocates is growing in America – and this time things are different. Unlike previous attempts to popularise 3D-printed guns, this operation is entirely decentralised. There’s no headquarters, no trademarks, and no real leader. The people behind it reckon that this means they can’t be stopped by governments.
A decentralised network of gun-printing advocates is mobilising online, they’re anonymously sharing blueprints, advice and building a community. There’s no easy way they can be halted.
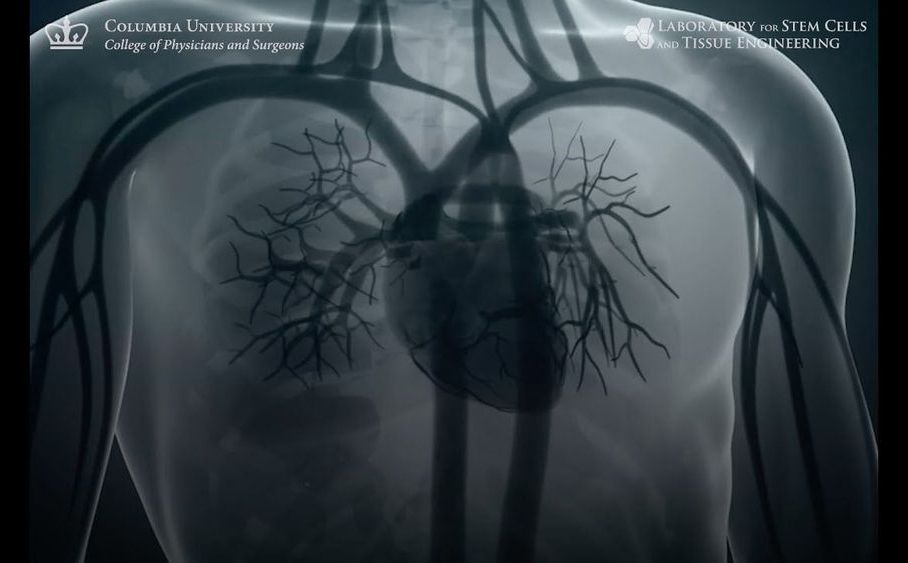
Regenerative medicine and stem cells are often uttered within the same breath, for good reason.
In animal models, stem cells have reliably reversed brain damage from Parkinson’s disease, repaired severed spinal cords, or restored damaged tissue from diabetes, stroke, blood cancers, heart disease, or aging-related tissue damage. With the discovery of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), in which skin and other tissue can be reversed into a stem cell-like state, the cells have further been adapted into bio-ink for 3D printing brand new organs.
Yet stem cells are hard to procure, manufacture, and grow. And unless they’re made from the patient’s own cell supply—massively upping production costs—they’re at risk of immune rejection or turning cancerous inside their new hosts.
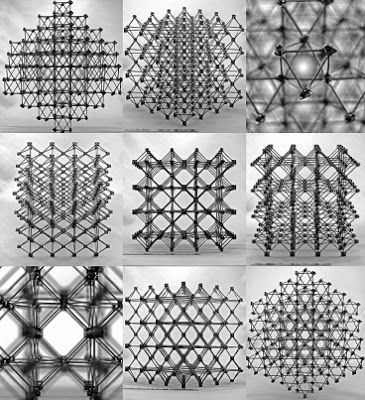
Researchers invent a new approach to assembling big structures — even airplanes and bridges — out of small interlocking composite components. MIT researchers have developed a lightweight structure whose tiny blocks can be snapped together much like the bricks of a child’s construction toy. The new material, the researchers say, could revolutionize the assembly of airplanes, spacecraft, and even larger structures, such as dikes and levees.
NBF – This is huge. It boosts what is possible with additive manufacturing and 3D printing. This will revolutionize manufacturing and construction.
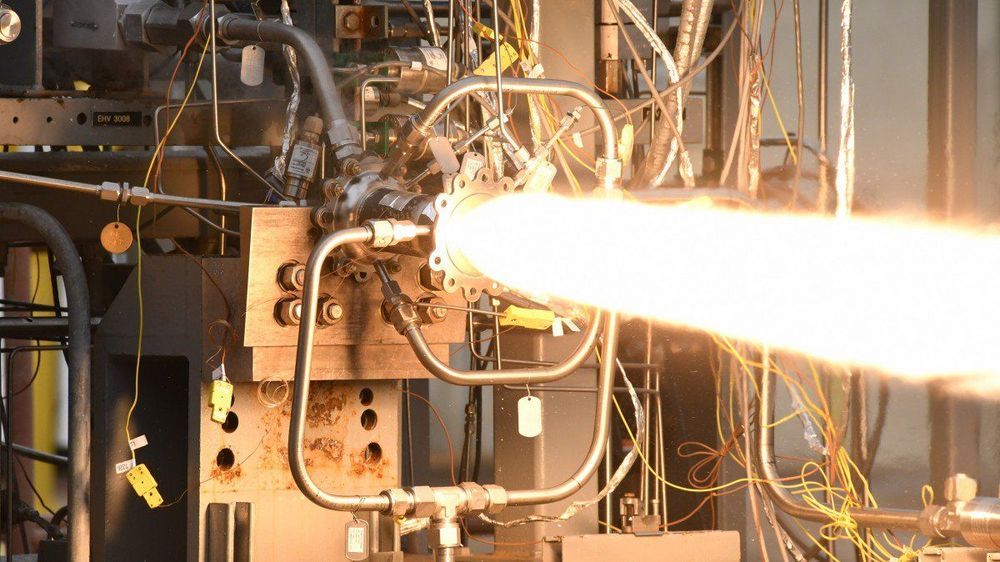

They have successfully test-fired 3D-printed combustion chambers made from multiple materials.
The news: By combining their manufacturing and testing capabilities, small-satellite launcher Virgin Orbit and NASA created a rocket combustion chamber that was 3D-printed from multiple metals. A combustion chamber is the container where all the propellants get mixed up and ignite—so it must be able to cope with extreme heat and force. The test part that used the chamber generated more than 2,000 pounds of thrust in a series of 60-second test fires. You can watch a video of the test firing here.
Why are chambers a challenge? Because it has to withstand so much, it must be designed to a very high standard, meaning the part is expensive and time consuming to make.

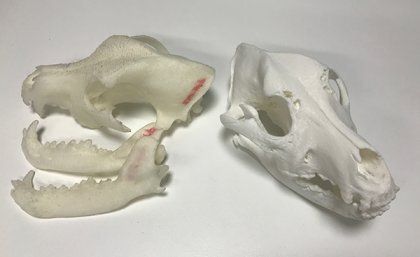
3D printed models of dog skulls are helping University of Queensland vets to save animals and educate tomorrow’s veterinary students.
The models, showcased at the World Science Festival, were the result of a collaboration between UQ Library’s Digital Scholars Hub and the School of Veterinary Science.
UQ veterinarian and Associate Professor Rachel Allavena used the skulls to help children understand how dogs with short noses can suffer from the condition brachycephalia.