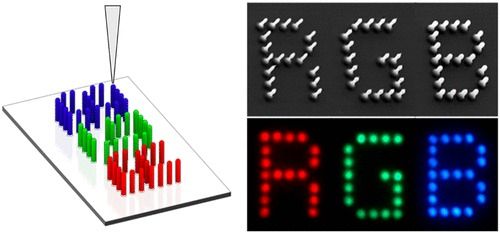
In Korea, scientists are turning to better ways for improving our screen time, and this means 3D printing something most of us know little about: quantum dots. Focusing on refining the wonders of virtual reality and other electronic displays even further, researchers from the Nano Hybrid Technology Research Center of Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI), a government-funded research institute under National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST) of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), have created nanophotonic 3D printing technology for screens. Meant to be used with virtual reality, as well as TVs, smartphones, and wearables, high resolution is achieved due to a 3D layout expanding the density and quality of the pixels.
Led by Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo and Dr. Seung Kwon Seol, the team has published the results of their research and development in “3D-Printed Quantum Dot Nanopixels.” While pixels are produced to represent data in many electronics, conventionally they are created with 2D patterning. To overcome limitations in brightness and resolution, the scientists elevated this previously strained technology to the next level with 3D printed quantum dots to be contained within polymer nanowires.