There is absolutely NO need to code
Recently, I spoke at VRTO2018 in Toronto, Canada—which gave me a chance to see some of the bleeding edge tech in VR, AR, and Mixed Reality. Of all the VR tech I encountered there, it was Psychic VR Lab’s creation Styly that captured my imagination most of all.
Terrence McKenna once described virtual reality as a “technology that will help us show each other our dreams.” He discussed this angle at length, finding that VR’s potential to share our subjective experiences with each other on an embodiment-based medium, to have vast consequences for our species. “In the cyberdelic future, artists will rule because the world will be made of art.” McKenna further speculated that he saw VR as a potential next step in the evolution of language itself. When and how and with what technology this will be achieved has been an open question. Yet, with the arrival of Tokyo-based company Psychic VR Lab and their new tool Styly, we seem within closer striking distance to McKenna’s dream of “inhabiting” the imagination more than ever before.
Psychic VR Lab made a splash in 2015 by providing a website that hosted and processed images using Google’s phantasmagoric Deep Dream. Their new project Styly is a hyper-user-friendly platform for creating shareable VR worlds. The browser-based interface consists of just a few buttons. Model content can be browsed and imported from a variety of pre-existing libraries like Sketchfab, 3D Warehouse, Unity’s asset store, and Google Poly. This means you do not need to make your own models from scratch — they can be imported in. Images can be uploaded from Instagram, videos from YouTube (including 360 videos), and music from Soundcloud are all a single click away. Mp3s and image files can be imported from you desktop, and it also supports Unity, SketchUp, Blender, Tilt Brush, Blocks, Maya, and Mixamo.
For me, the Styly interface had about a 12-minute learning curve — And I have not played with a modeling or animation program for about 15 years. The first thing I created was a Gigeresque nightmare world, and it took less than half an hour to build.
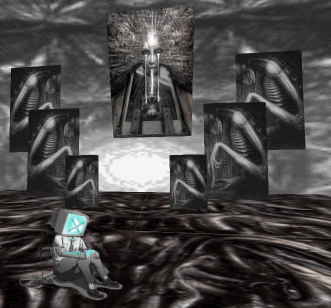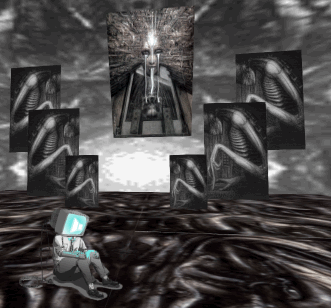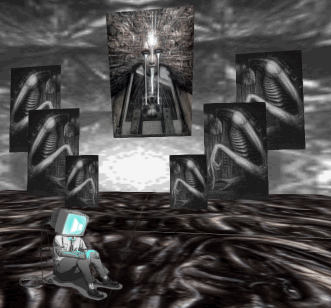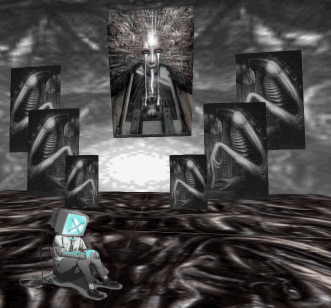
Though still a fresh tech, what Styly made vividly clear to me was that one of the big winners in the ongoing race for VR supremacy is going to be whoever develops the first VR Instagram. Instagram was an easy-to-use streamlining of several kinds of image editing software. It ended up becoming the most successful prosumable photograph tech since the Polaroid — and far outstripping it.

Another wonderful feature of Psychic VR Lab’s Styly tool is a gallery for users to share their own VR worlds with each other. This gallery feature, along with their easy-to-use VR world builder, is McKenna’s VR philosophy in full effect. McKenna pointed out throughout his career: whoever democratizes VR world building and sharing for user-producers, prosumers, call them what you will — artists — whatever company or tech that enables the spirit of the artist in us, just as Instagram has, is the one that is by definition going to be the most overwhelming novel, interesting, and important. The alternative VRs are going to be who has the best sandbox community, the best market-researched Whateverworld, the most addictive Blockchain Casino, the most useful listen-to-me-talk speakerspace, and so on. All that is inevitable. Nevertheless, it is whoever enables the artists that is worthy of attention; because whoever enables the artists enables the future.

The easy-to-use prosumer angle is one that will likely be the most interesting and the most ethically and spiritually important when it comes to the VR question. As McKenna said:
“The importance of virtual reality, as I see it, is that it is a technology that will allow us to show each other our dreams. We will be able to build structures in the imagination that we cannot now share with each other. I imagine a world where children begin to build their virtual realities when they are five, six, seven. By the time they are twenty these virtual realities might be, practically speaking, the size of Manhattan. Well, then what real intimacy will mean is saying to someone ”Would you like to visit my world?” My world with my visions, my values, my dreams, my fears. In a sense, what virtual reality is, is a strategy to let us turn ourselves inside out. So that we see each other’s minds […] But virtual reality is going to allow us to share much much more of ourselves. After all my reality is not how I look. My reality is who I am. And the only way I could give that to you is by inviting you inside.”
Groups like Psychic VR Lab and tools like Styly are helping to make McKenna’s cyberdelic vision a reality.
Enjoy 8 hours of McKenna discussing VR and the Future.
Originally published at Medium





 by allowing people to see their avatar with their own personal measurements in various outfits. This doesn’t have to be limited to at-home experiences though. Dan suggests that instead of walking into the boutique changing room, you walk into one with mirrors connected to VR software. Your reflection ‘tries on’ different virtual outfits before you pull your favorite one off the store rack.
by allowing people to see their avatar with their own personal measurements in various outfits. This doesn’t have to be limited to at-home experiences though. Dan suggests that instead of walking into the boutique changing room, you walk into one with mirrors connected to VR software. Your reflection ‘tries on’ different virtual outfits before you pull your favorite one off the store rack. together.”
together.”