A new section: Bitcoin ATM business model
has been added. Jump to “2019 Update”
The good news is that building a Bitcoin ATM is easy and less expensive than you might expect. But, offering or operating them engulfs the assembler in a regulatory minefield! It might just be worth sticking to selling bitcoin on PayPal (visit this website for more information on that). You might also wish to rethink your business model —especially user-demand. That’s the topic of our 2019 update at the bottom of this article.
A photo of various Bitcoin ATMs appears at the bottom of this article. My employer, Cryptocurrency Standards Association, shared start-up space at a New York incubator with the maker of a small, wall mounted ATM, like the models shown at top left.
What is Inside a Cryptocurrency ATM?
You could cobble together a Bitcoin ATM with just a cheap Android tablet, a camera, an internet connection, and [optional]: a secure cash drawer with a mechanism to count and dispense currency).* A receipt printer that can also generate a QR code is a nice touch, but you don’t really need one. You can use your screen for the coin transfer and email for a receipt.
Of course your programming and user interface makes all the difference in the world. And your ATM must interface with an exchange—yours or a 3rd party exchange.
If your plan is to sell Bitcoin and not exchange it for cash, then you don’t need a currency dispensing component at all. You only need a credit card swipe-reader and an RFI tap reader. Some models are smaller than a cookie and sell for under $30. They can be attractively embedded into your machine. In fact, some bank card processors offer them without cost.
I Have Built a Prototype. Now What?
Once you have a working prototype, you will need to test it with focus groups (alpha test) and at prospective public sites (beta test). You must also harden the production model against tamper and theft and find paying businesses or property owners, so that you can achieve economies of scale. (A reasonable business model requires that you produce dozens of devices each month).
Parts Cost: Bill of Materials
At scale, you can achieve a unit production cost of less than $200. But that’s for a desktop unit that does not accept or dispense cash. A high-quality and attractive machine that accepts cash and is free standing or ready for outdoor installation into a building exterior might cost you $650. You could sell these for $2,500 plus recurring fees to the property owner, depending on venue, or you might simply lease them, just as Xerox did in the early days of office copiers. (In a hotly competitive market, such as Las Vegas, you may need to pay a portion of your profits to the site, rather than profiting from ‘renting’ the ATM).
Regulations: A Threat to Your Business

But wait! Before you run off and create an ATM venture of your own, with visions of a 350% profit margin, all is not as easy as it seems!…
Cryptocurrency ATMs intersect with a minefield of regulatory licensing and compliance standards. In many regions, they are not even legal for placement in a public area.
In most countries (including all of USA), you must be a registered Money Transmitter. You will need separate state licensing and—since you are moving cash in or out of the banking system—you must be partnered with a federally chartered bank. You will also need to post a hefty insurance bond—perhaps even for each machine and each municipality in which it is placed! These laws convey liability to both your client (a property owner) and to you. Many courts will hold the manufacturer of financial or medical products accountable for ensuring that their customers are licensed and compliant with regulations. That is, you may not be able to legally sell your ATM to organizations that have not demonstrated that they qualify to operate one.
Why is There a Camera in my ATM?
In all cases, you must capture photographs of your user and their state-issued ID, because you are required to know your customer and adhere to a slew of anti-money laundering practices. For example, with transactions larger than $2,000 (from anyone who is not known to you and a regular client), you must generate a Suspicious Activity Report. For transactions larger than $10,000, you must comply with RICO (Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act). This requires a camera, interview, and reporting process. You will be generating forms with data supplied by your user and possibly even a real-time verification of the facts they provide.
If you wonder why you needn’t do these things this when buying or selling your own cryptocurrency, it is because: (a) You are trading your own assets and are not the custodian of customer accounts; and (b) You are a consumer. It is likely that the exchange is required to do all of these things.
With Regulations, Can Bitcoin ATMs Generate Profit?
For the reasons described above, the operational cost of deploying and operating an ATM network (or your equipment for sale or rent) is significantly higher than the up front hardware cost. When you add the need to protect your venture from legal claims arising from process glitches or users that claim they lost cash or Bitcoin, you may arrive at an operational cost that makes your business model unworkable.
Of course, Bitcoin ATMs are profitable in some cases. I have consulted with a few start ups that operate them successfully in Las Vegas casinos, a few airports and race tracks, and at large outdoor fairs. But, for everyday use, the heyday of ATMs is most likely 5 or 10 years off. Before this happens, we need a more uniform and functional regulatory & insurance framework, and a higher volume of users per ATM.
Check out various Bitcoin ATM models below. Few manufacturers turn a profit. In the end, it boils down to location (high volume sites with the right people) and location (legal jurisdiction).
* One ATM startup found inexpensive hardware for dispensing currency by recycling mechanisms from bill-change machines used in game arcades or in hotels next to vending machines. These machines are being discarded, because newer vending machines accept credit cards and smart phone payment. But again, if you only plan to accept a credit or debit instrument for Bitcoin, then you don’t need a cash counter or dispenser.
2019 UPDATE: ATM Business Model Requires Urgency
The economics of Bitcoin ATMs is thoroughly uncompelling, unless you own or administer a public area with high foot traffic. Even with lots of traffic, the business model has a problem…
Bitcoin is easily acquired and exchanged online—both legally and illegally. Often, I urgently need to find a bank ATM, especially when travelling. But, despite being an avid proponent and adopter of cryptocurrency, I can’t imagine needing a crypto ATM. Needing virtual exchange is rarely urgent, and there are better alternatives than standing in front of a machine. After all, we each have a better machine in our pockets.

Online trading is easier and safer than via ATM. Even user anonymity is better online than standing in a public place and using a kiosk equipped with a camera.
Therefore, an ATM placement business needs clients with urgent needs. In the internet era, urgency and expert installation are the values that support the bottom line. But again, there is a problem…
The problem with using urgency to build a local delivery model for ATMs, is that Bitcoin is a virtual product. Even a seller or exchange in China can deliver an online money exchange instantly.
Consider this reverse analogy…
Suppose that you are responsible for setting up a video projector in a hotel ball-room. The conference is already in progress and hundreds of people are looking toward a blank movie screen. You suddenly discover that your video cable is defective and wireless options will not work . You need an HDMI cable and a thunderbolt adapter immediately. It must be at least 18 feet long and be a recent model to support the audio channels and resolution of your presentation.

The local Best Buy store has the cable in stock. It’s $89.99 and the store can have it at the front desk in the next 10 minutes. Your frugal partner finds the same cable online for $29.99 (2-day delivery) or $9.50 shipped from China (about 2 weeks).
Which do you choose? Is it just a cable that you need? No! The value that you require is a compatible cable in your hands within minutes — preferably from a local and experienced vendor, in case there is an installation or application problem.
In almost any scenario—even catering to impulse buyers—a Bitcoin ATM can’t match the value of someone delivering a compatible cable instantly. If it is a commodity that you are selling (Bitcoin is a commodity), then a profitable business model requires that you sell speed, convenience or privacy. Cryptocurrency ATMs lose on all three fronts.
That last paragraph above is my freebie to the next ATM vendor who seeks consulting services. Test your model, before seeking help in penetrating a market that is tough to define and defend.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, hosts the Bitcoin Event and is keynote speaker at Cryptocurrency Conferences. He is a top writer at Quora.


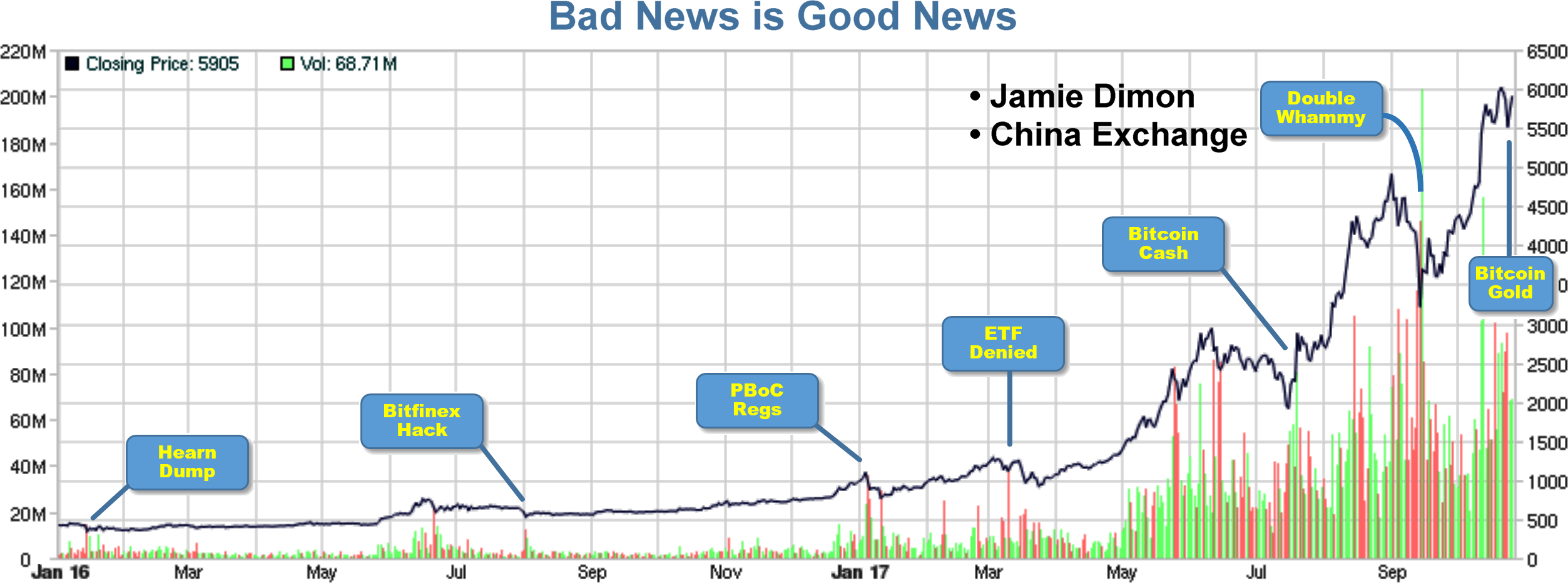
 On each date highlighted above, there was a damning piece of information that should cause early adopters to reconsider their enthusiasm for Bitcoin. In fact, the
On each date highlighted above, there was a damning piece of information that should cause early adopters to reconsider their enthusiasm for Bitcoin. In fact, the  red herring—they present a buying opportunity. If I were allowed to give investor advice (I am not; and I don’t), I would express my opinion with more verve and obvious conviction.
red herring—they present a buying opportunity. If I were allowed to give investor advice (I am not; and I don’t), I would express my opinion with more verve and obvious conviction.