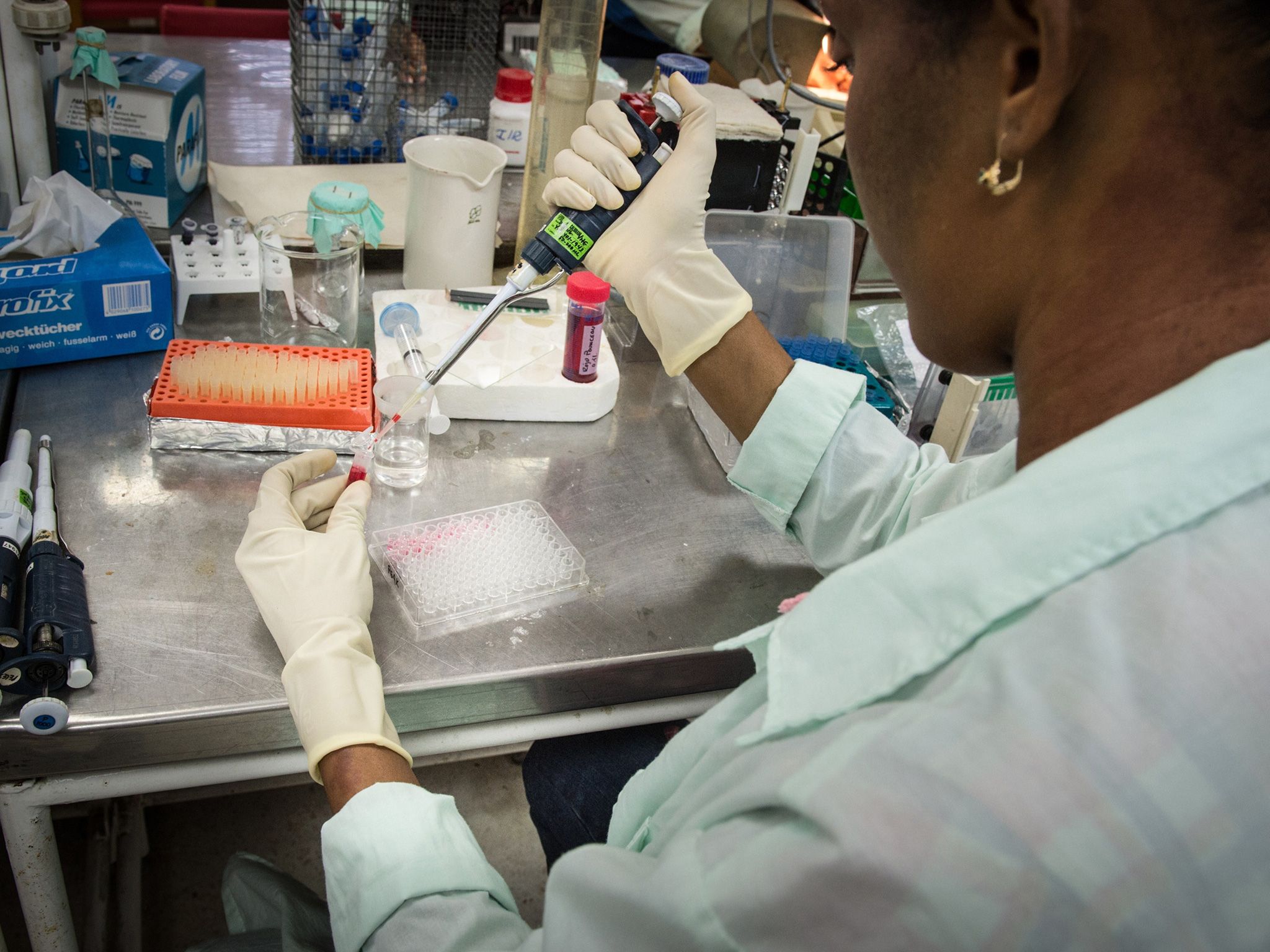
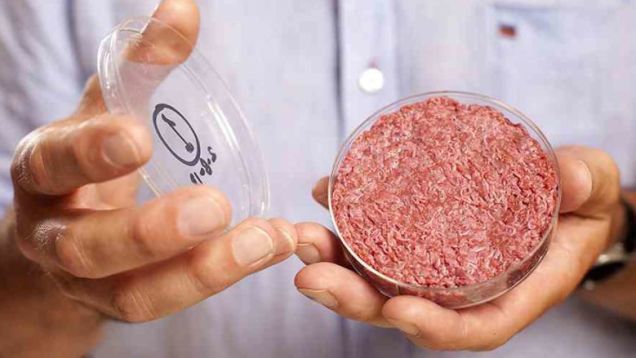
When a team of Dutch scientists unveiled the world’s first stem cell beef burger in 2013, it carried a $300,000 price tag. Worse, it was dry and tasteless. But since the initial lackluster reviews, Mark Post and his colleagues have been hard at work. Now, they say they hope to have a commercially saleable cow-less patty on the market in five years.
Until very recently, lab-grown beef sounded like science fiction. But rapid advances in molecular biology and stem cell technology have placed the futuristic concept within reach. And the arguments for removing animals from the meat equation are practically endless: The meat industry as it exists today swallows an enormous fraction of our land and natural resources, produces vast quantities of greenhouse gases, has contributed to the rise of antibiotic resistant infections, and in many cases, is downright cruel. If test tube burgers can eliminate or diminish even a fraction of these problems, then this seems like one crazy idea worth pursuing.
And pursue it scientists have. In addition to Mark Post’s stem cell burger effort, a team of Israeli researchers under the banner Future Meat are now trying to grow whole chicken breasts in the lab. Meanwhile, efforts to culture fish protein have cropped up intermittently over the years.
Read more






 Listen/View
Listen/View