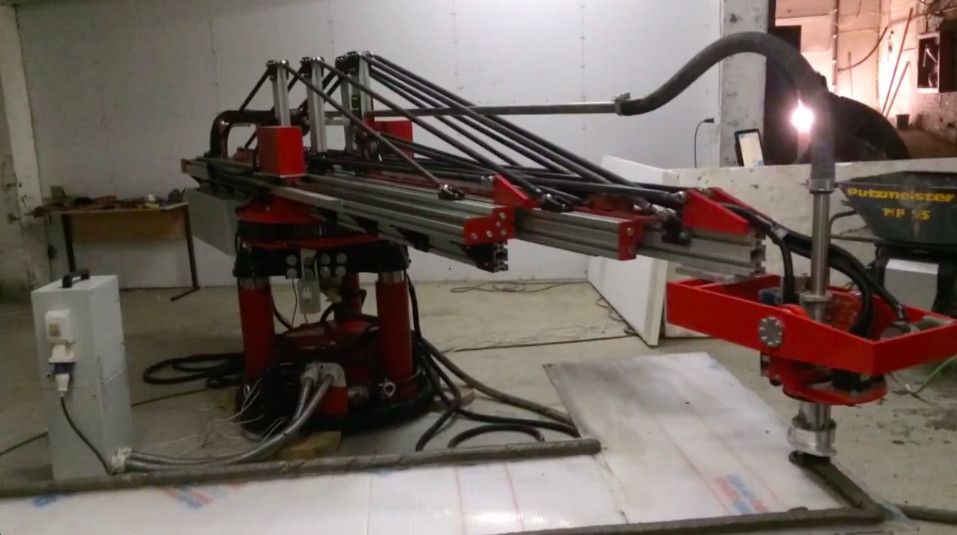
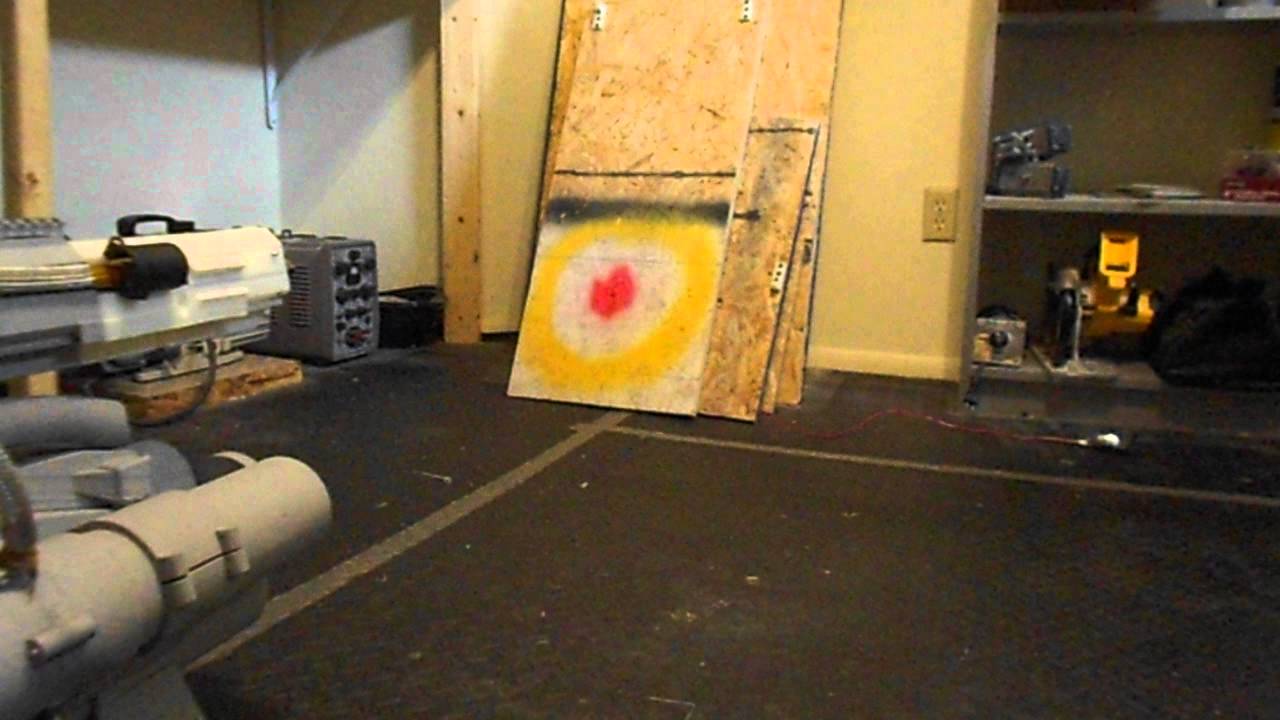If you think the image above looks frightening, you’re right. The crazy contraption pictured in the image is the first portable railgun, a futuristic projectile launcher associated most commonly with the military or NASA. The man in the image above isn’t in the military, and he’s not a NASA engineer. Instead, he’s a civilian who used some engineering smarts, some widely available parts and a 3D printer to create a functioning weapon that can fire graphite, aluminum, tungsten and even plasma projectiles at speeds of more than 560 mph.
And then there’s the best part: There are videos of this homemade railgun in action.
MUST READ: The iPhone I couldn’t live with
Little is known about Imgur user “NSA_Listbot” beyond the fact that he’s just short of being a wizard with AutoCAD and a 3D printer. The man took to Imgur over the weekend to share what may very well be one of the most amazing and terrifying DIY projects that has even been attempted. And he didn’t just attempt it, he built it.