Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
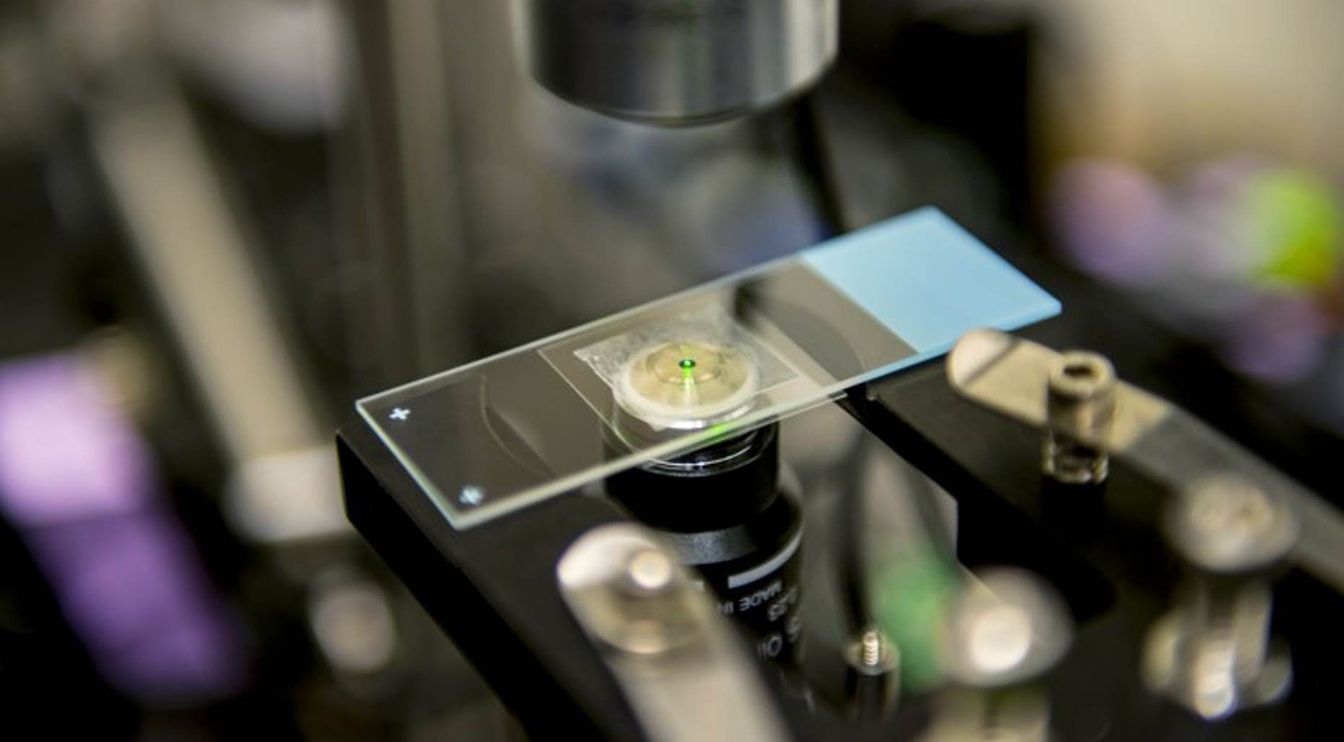

Laser ‘freeze ray’ could change cooling biology labs, computer processors
Laser cooling isn’t a new idea, but this is the first time it’s actually worked in real-world conditions.
Crazy new Tail lights
New Tail lights from Audi.
What do you think of these new Tail lights from Audi? Will they become the next big thing?
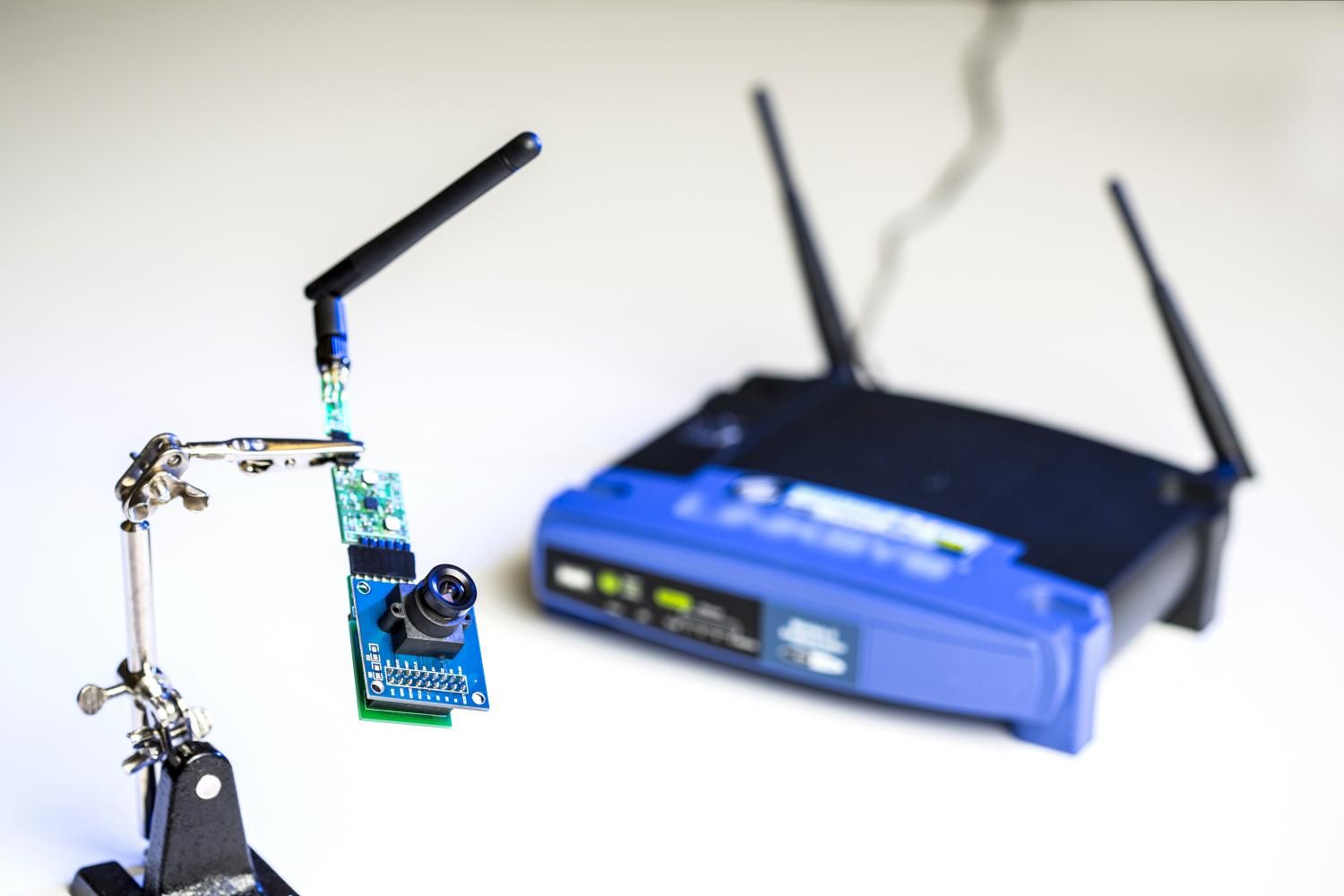

‘Power Over Wi-Fi’ named one of the year’s game-changing technologies
University of Washington engineers have developed a novel technology that uses a Wi-Fi router—a source of ubiquitous but untapped energy in indoor environments—to power devices.
The Power Over Wi-Fi (PoWiFi) system is one of the most innovative and game-changing technologies of the year, according to Popular Science, which included it in the magazine’s annual “Best of What’s New” awards announced Wednesday.
The technology attracted attention earlier this year when researchers published an online paper showing how they harvested energy from Wi-Fi signals to power a simple temperature sensor, a low-resolution grayscale camera and a charger for a Jawbone activity tracking bracelet.

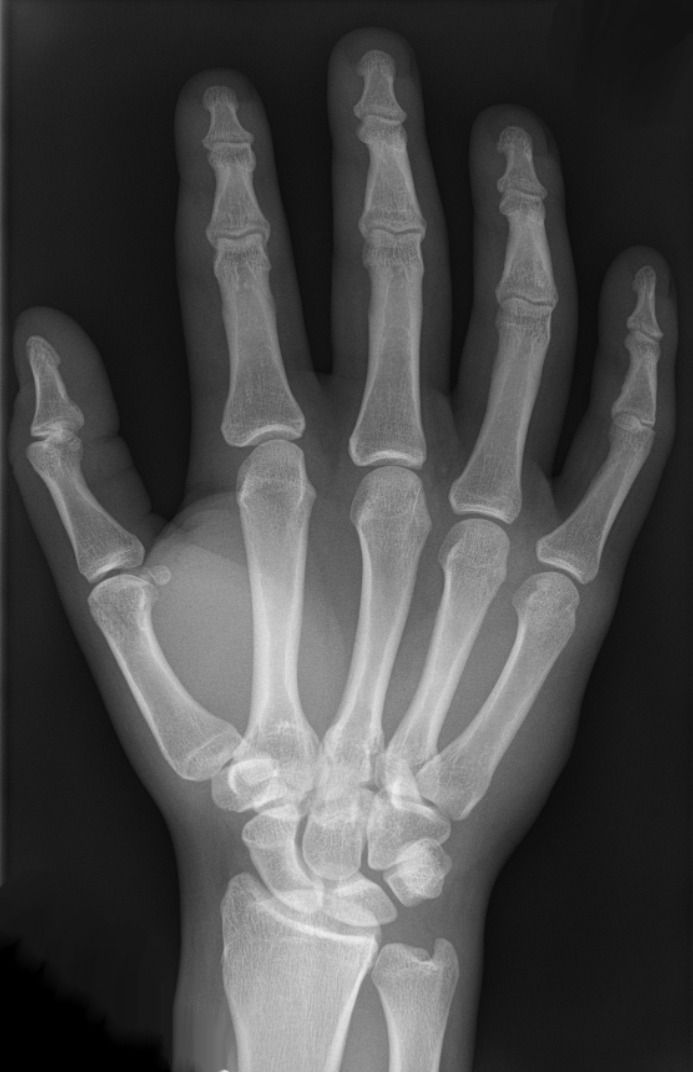
Accident Creates Bone From Stem Cells
Bone loss and frailty greatly diminish quality of life as we get older, and learning how to regrow bone across the body is a key rejuvenation target.
Stem cells are difficult to work with
We can now produce induced pluripotent stem cells from adult tissue, but differentiating them into a specific tissue is a major challenge. We’re still working on finding the exact chemical cues that create each specific cell type, and stem cells are highly sensitive. There has been progress in many areas, but we still have a way to go.

France votes to give government powers to block online communications during state of emergency — By Paul Sauers | VentureBeat
“French members of parliament (MPs) have voted to give the government extra powers to block online communications when the country is under a “state of emergency.””
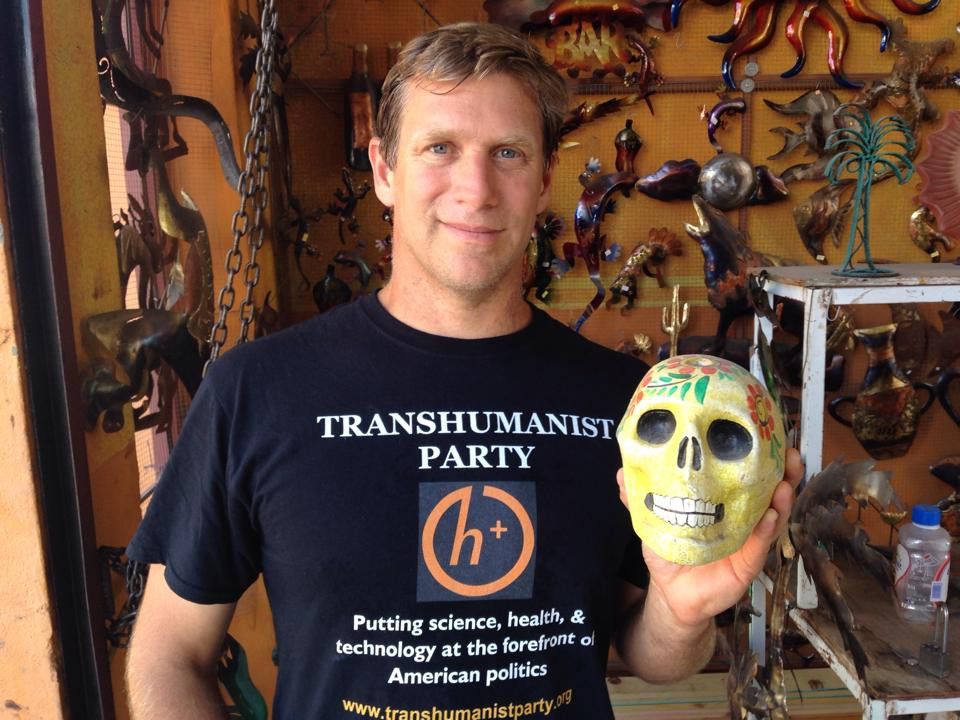

Presidential Candidate Suggests We Microchip Syrian Refugees
A new article on my campaign with a provocative headline, but most of the story is nice. I’ll be speaking in Florida on Saturday as part of the Immortality Bus tour. We visited Alabama’s largest megachurch yesterday:
His name sounds funny to Americans, but presidential candidate Zoltan Istvan says it’s totally normal in Hungary, from where his parents hail. Istvan himself was born in Los Angeles and worked for National Geographic for years — a job that led him to explore science, particularly the concept of transhumanism, which posits that people will merge with technology.
Today, Istvan continues to write for Vice, Psychology Today, Gizmod o, and more — when he’s not campaigning across the country and promoting the Transhumanist Party platform, which promises better lives — and hopefully immortality — through science. Istvan will speak this Saturday at the Church of Perpetual Life in Hollywood, which promotes the same ideals and which New Times featured in a cover story earlier this year.
Istvan says that as a journalist, he used to cover nature, until “we were in Vietnam and I had a very close call with a land mine. I thought, ‘Why don’t I write less about nature and the environment and more about science, medicine, and future uses of science to conquer death?’” After leaving Nat Geo circa 2004, when he was about 28, to take care of his ailing father, he says he made some money in real estate and in 2013, “I wrote a novel called The Transhumanist Wage r, which launched my career as a futurist.”
Now he’s onboard with the Transhumanist Party, which has been established for about 14 months, he says. “It’s an actual, organized national party,” he says, though you’re unlikely to see it on a ballot because it’s nearly impossible for small political parties to get on “unless you have almost 50 or 60 million dollars lying around.”
Quantum Computers One Step Closer After Australian Breakthrough
Engineers from the University of New South Wales, Australia, have made an important breakthrough that brings quantum computers one step closer to reality.
The team created a quantum version of a standard computer code within a silicon chip. The discovery shows that it is possible to construct realistic and reliable quantum computers.
Quantum computers have the potential to solve problems much more quickly than any computer that exists today, as they combine the rules of informatics to phenomena of quantum mechanics that are not observed in everyday life. Namely, the principle of superposition, popularized by Schrödinger’s cat being both alive and dead, and entanglement.
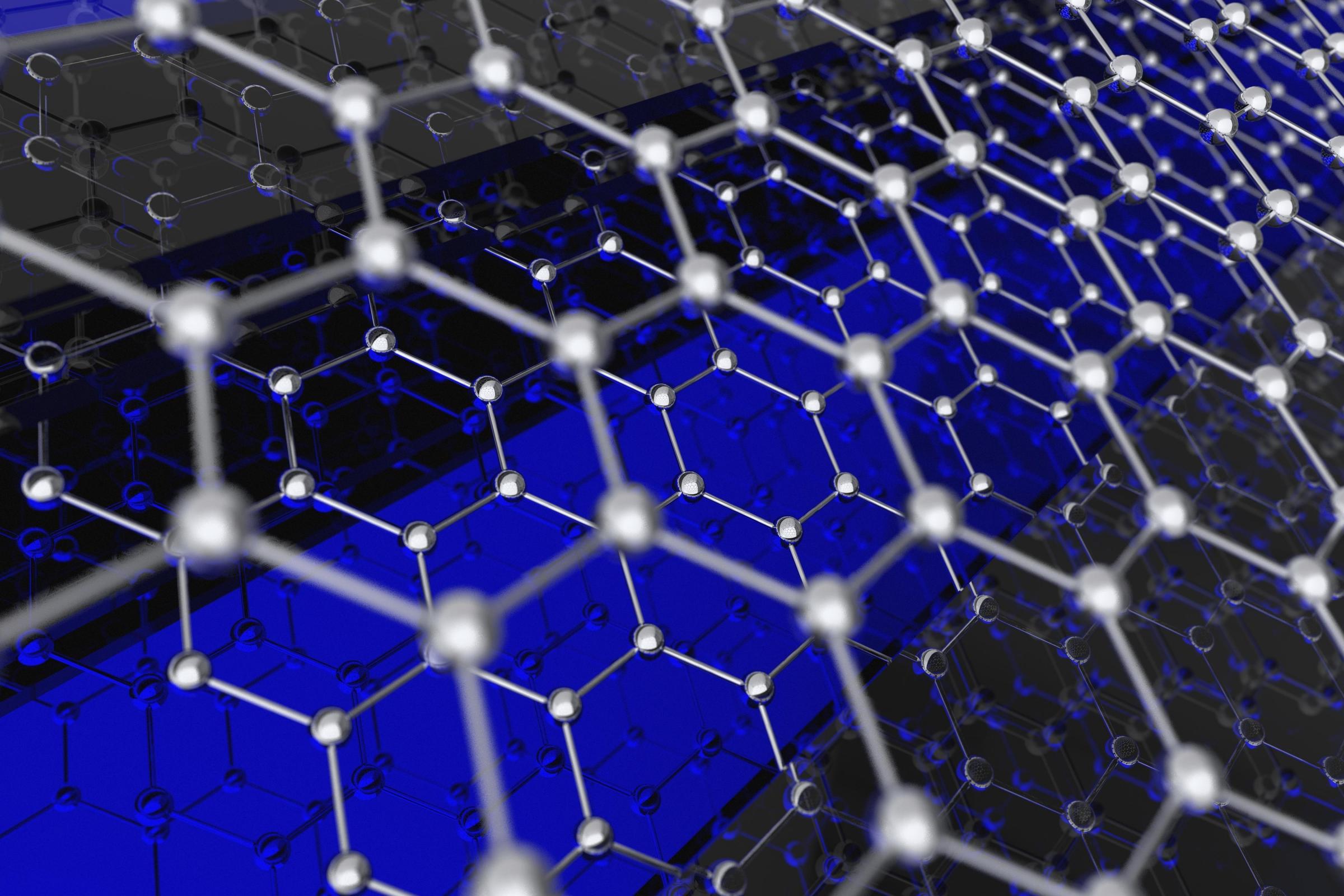
Breakthrough! Glasgow scientists discover a cheap way to produce the wonder material graphene
It has been hailed as a wonder material set to revolutionise everyday life, but graphene has always been considered too expensive for mass production – until now.
Scientists at Glasgow University have made a breakthrough discovery, allowing graphene to be produced one hundred times more cheaply than before, opening it up to an array of new applications.
First isolated in 2004, the miracle material can be used in almost anything from bendable mobile phone screens to prosthetic skin able to provide sensation.