https://youtube.com/watch?v=yJ-lcdMfziw
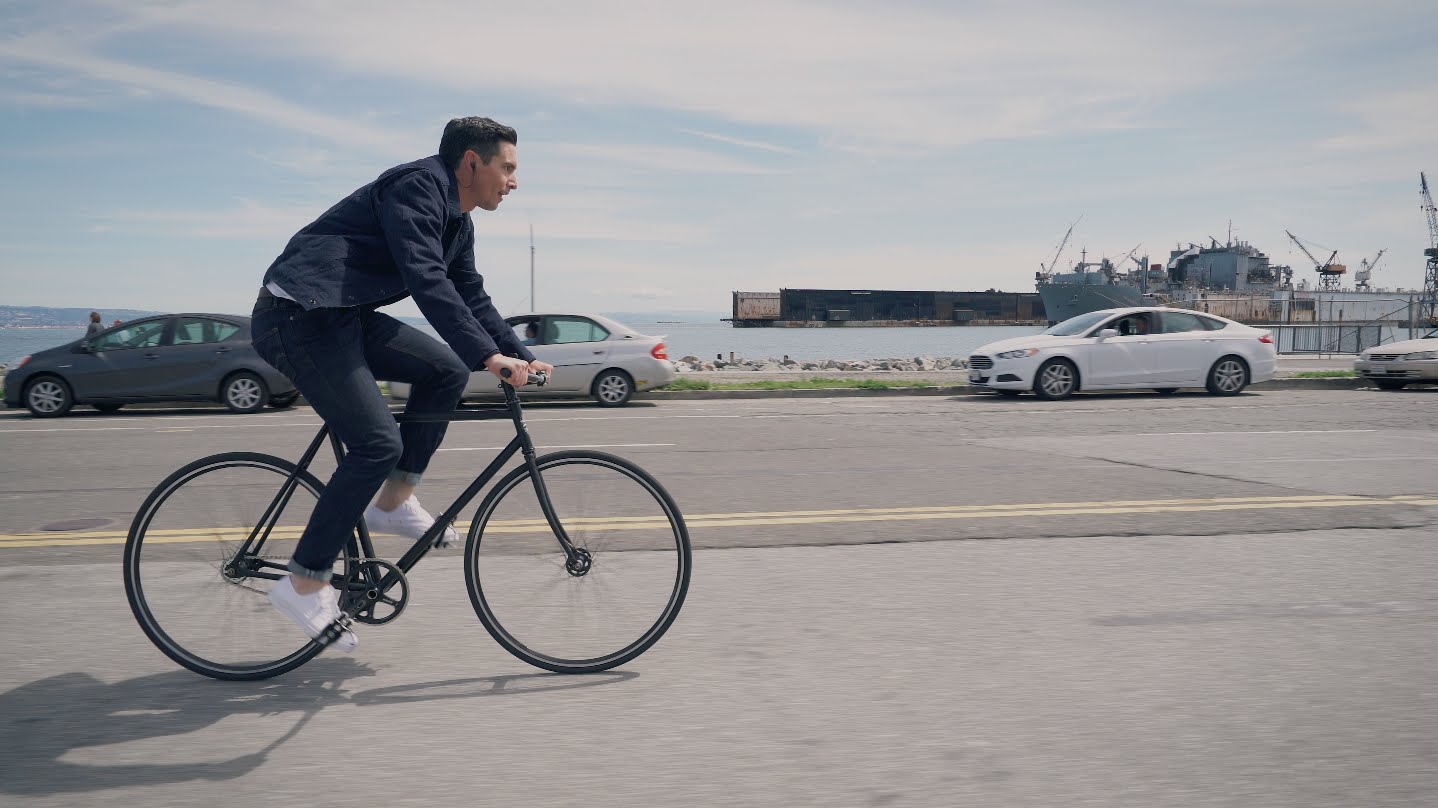
With the exception of activity trackers and smartwatches, it’s fair to say that wearable technology hasn’t really taken off just yet, but if Google and Levi’s have their way, that could soon be about to change.
The two companies are teaming up to release their first co-designed product – the world’s first ‘smart’ trucker jacket (yep, that’s a thing now). It looks for the most part like a regular Levi’s Commuter jacket, but with a conductive fabric called “interactive denim” and a Bluetooth device that attaches to the sleeve.
It was back in 2015 that Google first announced its plan to make connected clothing like this – dubbed Project Jacquard – and the Levi’s jacket will be the first garment incorporating the technology.