Tesla may be one of the first automakers to use Ultra-wideband (UWB) technology in their vehicles. According to documents filed with the Federal Communications Commission, the manufacturer has submitted new products that support UWB.
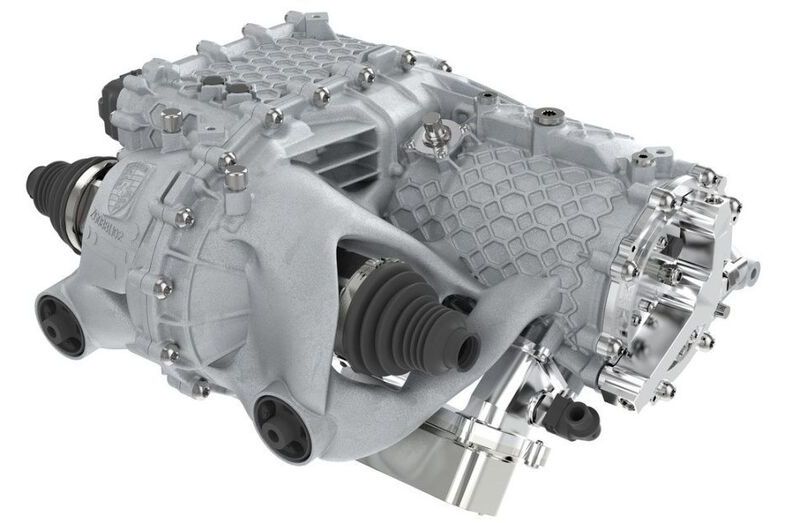




In December, Porsche announced that it had been 3D printing prototype housings for electric drives that were stronger, lighter, and much quicker to manufacture. The engine-gearbox units produced using this method were even able to pass all of the company’s quality and stress tests without issue.
Porsche manufactures the housings using a 3D printing method called laser metal fusion, which entails a laser beam heating and melting a powder surface depending on the desired contours. This method allows Porsche to produce an engine gearbox that is both 10% lighter and 100% stronger because of the inherent lattice structures.
Another significant upside to manufacturing parts this way is the ease and speed of creating new components or making changes to existing ones. For example, an entirely new part can be designed and then physically printed very quickly with no need to do things such as create new tooling to manufacture the part.

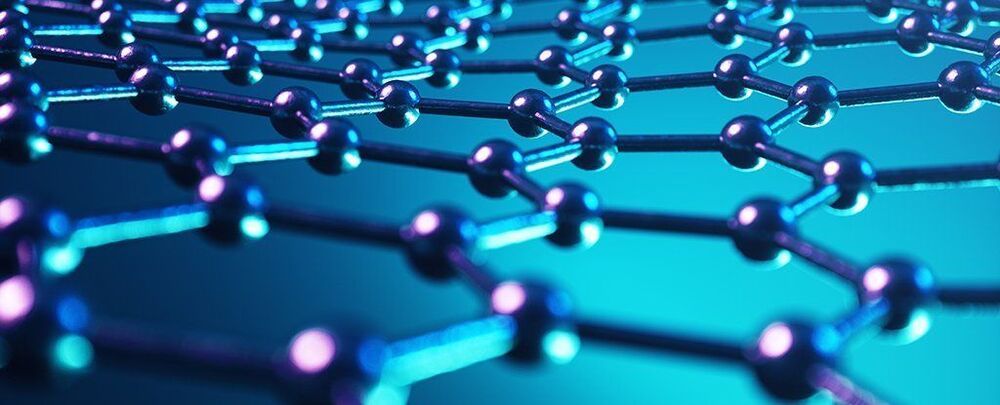
Graphene continues to dazzle us with its strength and its versatility – exciting new applications are being discovered for it all the time, and now scientists have found a way of manipulating the wonder material so that it can better filter impurities out of water.
The two-dimensional material comprised of carbon atoms has been studied as a way of cleaning up water before, but the new method could offer the most promising approach yet. It’s all down to the exploitation of what are known as van der Waals gaps: the tiny spaces that appear between 2D nanomaterials when they’re layered on top of each other.
These nanochannels can be used in a variety of ways, which scientists are now exploring, but the thinness of graphene causes a problem for filtration: liquid has to spend much of its time travelling along the horizontal plane, rather than the vertical one, which would be much quicker.

Hydrogen. In theory, it’s the perfect fuel. Run it through a fuel cell and you get electricity, water vapor, and heat. Doesn’t get any more Earth friendly than that, does it? There is theory and then there is reality, starting with where one gets the hydrogen in the first place. It is one of the most abundant elements on Earth — every molecule of water has two hydrogen atoms and there is a lot of water in the world.
Then there is the whole universe of hydrocarbons from gasoline to plastics. By definition, there are hydrogen atoms in all of them and that’s the problem. Hydrogen is so reactive it bonds with everything. Getting pure hydrogen means breaking the chemical bonds that bind to other elements. Keeping it sequestered in its pure state is a whole other conundrum.
Assuming all those challenges are overcome, then comes the question of how to distribute it so it can be used to power the fuel cells in vehicles. A DC fast charging installation might cost $300000 but a hydrogen refueling station can cost $3 million. Compressing it, trucking it, and storing it all present additional hurdles to consider.
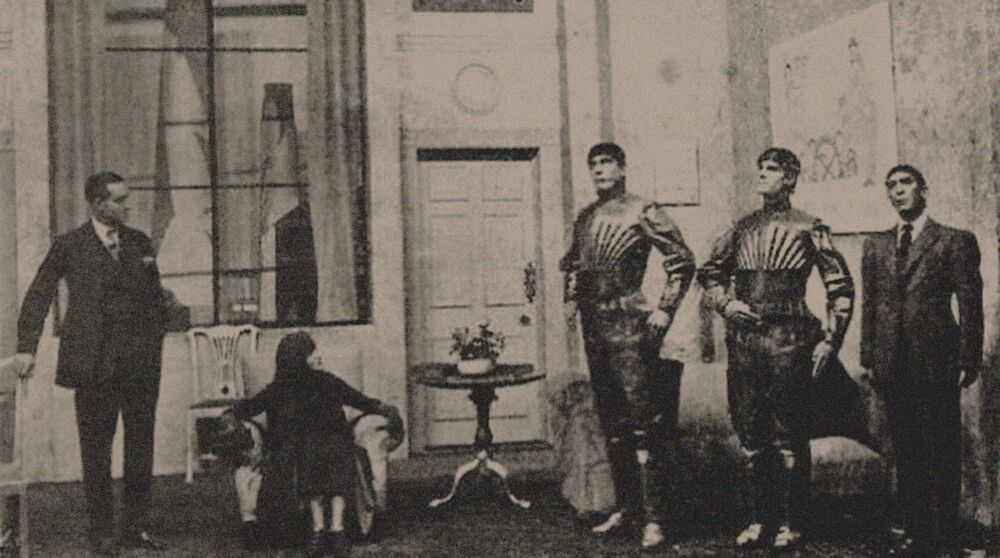
Exactly one hundred years ago, a play premiered that introduced a significant new word to the world – robot. When the first production of Karel Čapek’s R.U.R. opened on January 251921, at the National Theater in what is now the Czech Republic, it not only gave a name to the cybernetic machines that were just beginning to emerge, it also shaped people’s perceptions of what a robot is and the potential dangers they pose.
R.U.R., which stands for Rossum’s Universal Robots, came along at the perfect moment. The period between 1880 and 1930 saw the fastest rate of change in human history, with more fundamental advances in half a century than in the previous 2000 years.
It was the age of the machine, which had intruded so thoroughly into modern society that artists had to come up with whole new forms of expression to include it and portray it. It was also the age of Henry Ford, with his assembly line churning out thousands of uniform black motor cars by the thousands at a price that the average worker could afford. The telephone, wireless telegraphy, radio, the first televisions, radium, airplanes, plastic … the world was awash with new technology.


