An Israeli startup is planning on bringing its fast charging batteries to electric cars.


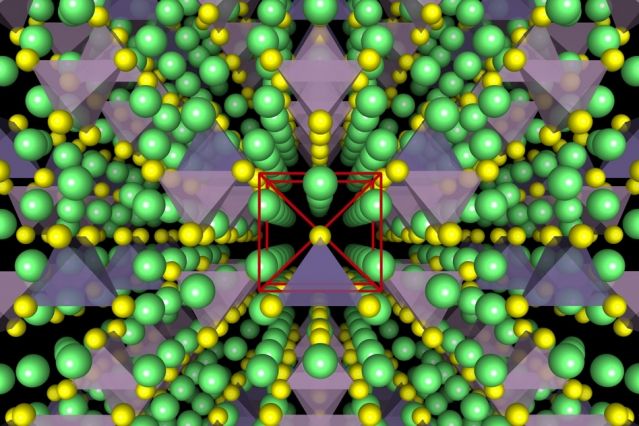
If you pry open one of today’s ubiquitous high-tech devices—whether a cellphone, a laptop, or an electric car—you’ll find that batteries take up most of the space inside. Indeed, the recent evolution of batteries has made it possible to pack ample power in small places.
But people still always want their devices to last even longer, or go further on a charge, so researchers work night and day to boost the power a given size battery can hold. Rare, but widely publicized, incidents of overheating or combustion in lithium-ion batteries have also highlighted the importance of safety in battery technology.
Now researchers at MIT and Samsung, and in California and Maryland, have developed a new approach to one of the three basic components of batteries, the electrolyte. The new findings are based on the idea that a solid electrolyte, rather than the liquid used in today’s most common rechargeables, could greatly improve both device lifetime and safety—while providing a significant boost in the amount of power stored in a given space.

Apple is definitely working on a self-driving car project, and according to some new documents, Project Titan appears to be further along than anyone thought.
Rumors of Apple’s car project first starting surfacing at the beginning of this year, with an announcement not expected until 2020 at the earliest, but the Guardian reports that Apple is already trying to secure a super-secret Bay Area test facility for the electric car.

Highways England are embarking on a trial to see if electric charging technology can be installed underneath roads across the country.
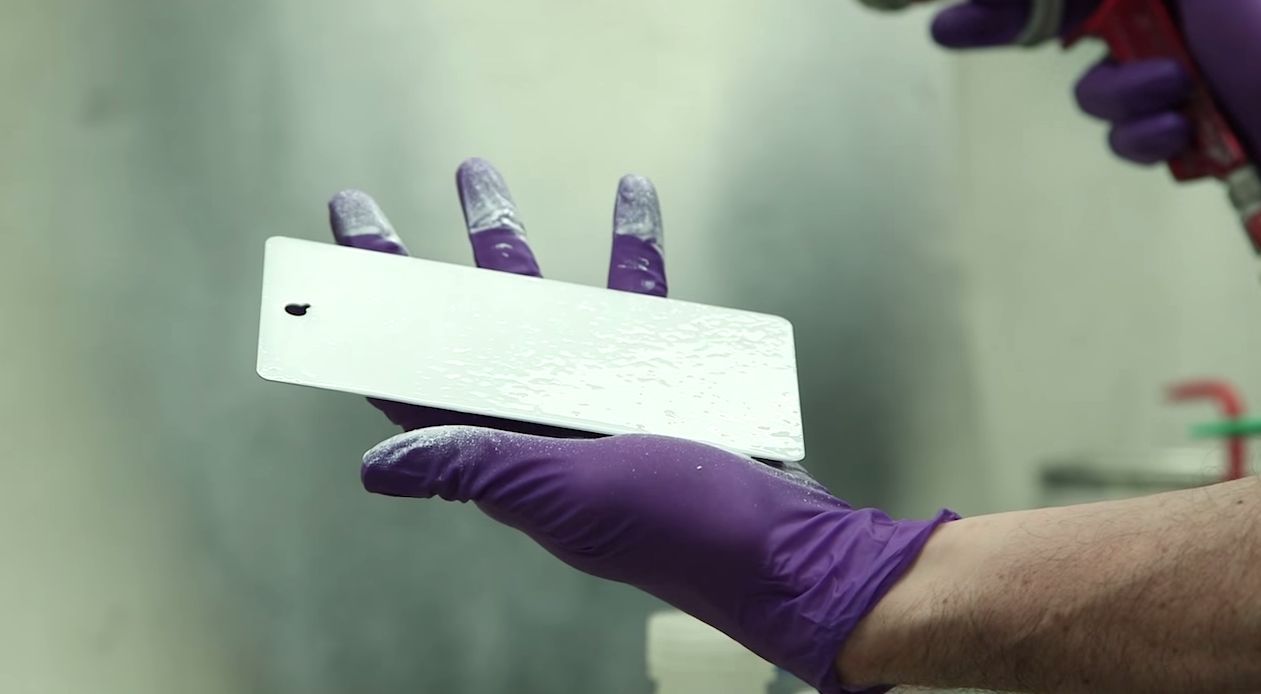

Sunlight can be brutal. It wears down even the strongest structures, including rooftops and naval ships, and it heats up metal slides and bleachers until they’re too hot to use. To fend off damage and heat from the sun’s harsh rays, scientists have developed a new, environmentally friendly paint out of glass that bounces sunlight off metal surfaces—keeping them cool and durable.
The researchers present their work today at the 250th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
“Most paints you use on your car or house are based on polymers, which degrade in the ultraviolet light rays of the sun,” says Jason J. Benkoski, Ph.D. “So over time you’ll have chalking and yellowing. Polymers also tend to give off volatile organic compounds, which can harm the environment. That’s why I wanted to move away from traditional polymer coatings to inorganic glass ones.”

The UK government has announced it’s set to trial a new type of highway that wirelessly charges hybrid and electric cars that drive on it.
The supercharged highways would juice up hybrid or electric cars that would normally need to stop, using a straight line charging path between A and B.
The results of this off road trial, based on this feasibility test, will be published and could lead to real motorway trials in the next few years, if successful. But it will come at a cost.
Amazing! Back to the Future 2 eat your heart out….
The Lexus SLIDE hoverboard isn’t just hype. It really works, and we sent racer and Jalopnik contributor Robb Holland to ride it. And crash. Drive free or die!

Tesla Motors Inc. Chief Executive Elon Musk said Friday the company is “almost ready” to make its cars go driverless on highways and parallel-park themselves
The much-awaited software update that would make Tesla TSLA, -0.24% vehicles able to steer themselves safely down the road has one more thing to sort out, Musk said in a tweet. Read more

What happens when you combine a Tesla Model S with KITT from the TV show Knight Rider? The Youxia X.
Elon Musk has made it official: his electric car company, Tesla Motors, is planning to debut an unnamed new Roadster in four years, and it won’t be based on the Lotus like the last one.
But Musk isn’t done with the old cars yet. The electric tech mogul held a press conference on Friday to tell reporters how fast his old car goes with its new upgrade: zero to 60 miles per hour in 2.8 seconds, which would put the four-door sedan in a league with high-end sports cars like the most recent Lamborghini Murciélago. Read more