Made In Space and NanoRacks have been making news lately with the announcement of partnerships to change the way objects are imagined and built off the planet, and now the companies have joined forces to provide a novel new service for CubeSat developers.
Made In Space and NanoRacks have been making news lately with the announcement of partnerships to change the way objects are imagined and built off the planet, and now the companies have joined forces to provide a novel new service for CubeSat developers.
 They call it “Stash & Deploy,” and the service will leverage the NanoRacks heritage in CubeSat deployment and the capability of Made In Space to provide 3D printing capabilities and deliver – on-demand – satellite manufacturing, assembly, and deployment in the space environment.
They call it “Stash & Deploy,” and the service will leverage the NanoRacks heritage in CubeSat deployment and the capability of Made In Space to provide 3D printing capabilities and deliver – on-demand – satellite manufacturing, assembly, and deployment in the space environment.
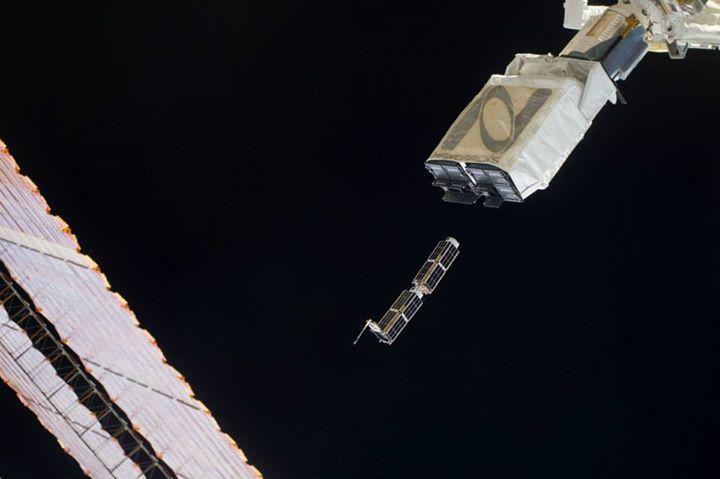
The plan calls for a variety of standard and customer-specific satellite components to be “cached” within a satellite deployment vehicle such as the International Space Station, and the components will be “stashed” for rapid manufacture of CubeSats.