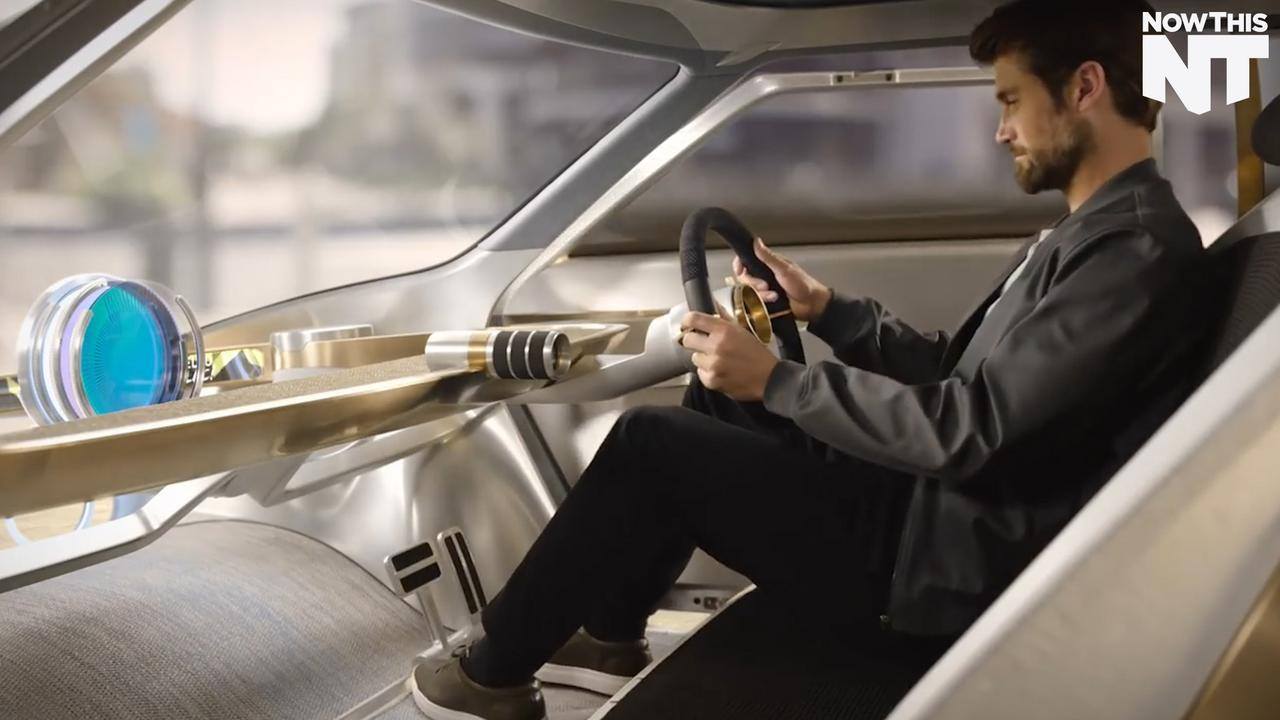
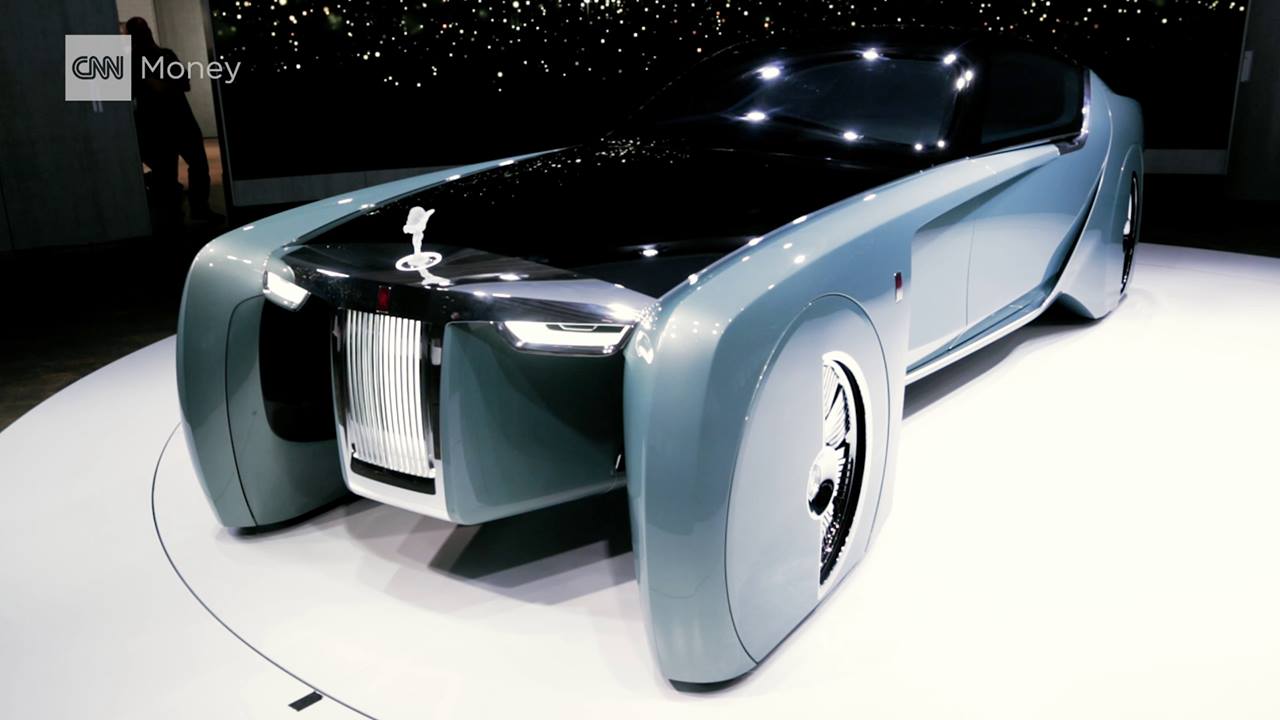
Category: transportation





Long Promised Artificial Intelligence Is Looming—and It’s Going to Be Amazing
We have been hearing predictions for decades of a takeover of the world by artificial intelligence. In 1957, Herbert A. Simon predicted that within 10 years a digital computer would be the world’s chess champion. That didn’t happen until 1996. And despite Marvin Minsky’s 1970 prediction that “in from three to eight years we will have a machine with the general intelligence of an average human being,” we still consider that a feat of science fiction.
The pioneers of artificial intelligence were surely off on the timing, but they weren’t wrong; AI is coming. It is going to be in our TV sets and driving our cars; it will be our friend and personal assistant; it will take the role of our doctor. There have been more advances in AI over the past three years than there were in the previous three decades.
Even technology leaders such as Apple have been caught off guard by the rapid evolution of machine learning, the technology that powers AI. At its recent Worldwide Developers Conference, Apple opened up its AI systems so that independent developers could help it create technologies that rival what Google and Amazon have already built. Apple is way behind.

Marrying superconductors, lasers, and Bose-Einstein condensates
Nice.
Chapman University Institute for Quantum Studies (IQS) member Yutaka Shikano, Ph.D., recently had research published in Scientific Reports. Superconductors are one of the most remarkable phenomena in physics, with amazing technological implications. Some of the technologies that would not be possible without superconductivity are extremely powerful magnets that levitate trains and MRI machines used to image the human body. The reason that superconductivity arises is now understood as a fundamentally quantum mechanical effect.
The basic idea of quantum mechanics is that at the microscopic scale everything, including matter and light, has a wave property to it. Normally the wave nature is not noticeable as the waves are very small, and all the waves are out of synchronization with each other, so that their effects are not important. For this reason, to observe quantum mechanical behavior experiments generally have to be performed at a very low temperature, and at microscopic length scales.
Superconductors, on the other hand, have a dramatic effect in the disappearance of resistance, changing the entire property of the material. The key quantum effect that occurs is that the quantum waves become highly synchronized and occur at a macroscopic level. This is now understood to be the same basic effect as that seen in lasers. The similarity is that in a laser, all the photons making up the light are synchronized, and appear as one single coherent wave. In a superconductor the macroscopic wave is for the quantum waves of the electrons, instead of the photons, but the basic quantum feature is the same. Such macroscopic quantum waves have also been observed in Bose-Einstein condensates, where atoms cooled to nanokelvin temperatures all collapse into a single state.

Could an implant have saved the life of the toddler attacked by an alligator?
A new article considering chip implants:
Among other tragedies in Florida recently gripping America’s attention, a 2-year-old boy was snatched away from its parents by an alligator at Walt Disney World on Wednesday. I have a similar-aged toddler myself, and I followed this heartbreaking story closely. Unfortunately, it ended as horribly as it began, with the recovery of a dead child.
My presidential campaign with the Transhumanist Party is based on advocating for radical science and technology to make the world a better place for humans. As a result, for nearly two years I have been advocating for using chip implants in people to help keep them safer. Chip implants are often just the size of a grain of rice and can be injected by a needle in a nearly pain-free 60-second procedure. The implants can do a multiple array of things depending on the type. And much of the technology has been used in pets for over a decade, so it’s already been shown to be relatively safe.
I have a RFID NFC chip in my hand that is programmed to send a text saying “Win in 2016” to people who have the right type of phone. To get the text, all you have to do is put your phone by my hand. My chip can also start a car with the right software, hand out a business card electronically, or give out my medical information.
But the future of implants—as well as other wearable tech—may end up being most useful for the safety it provides.
Aggressive, sparkplug-free gasoline auto engines with high efficiency
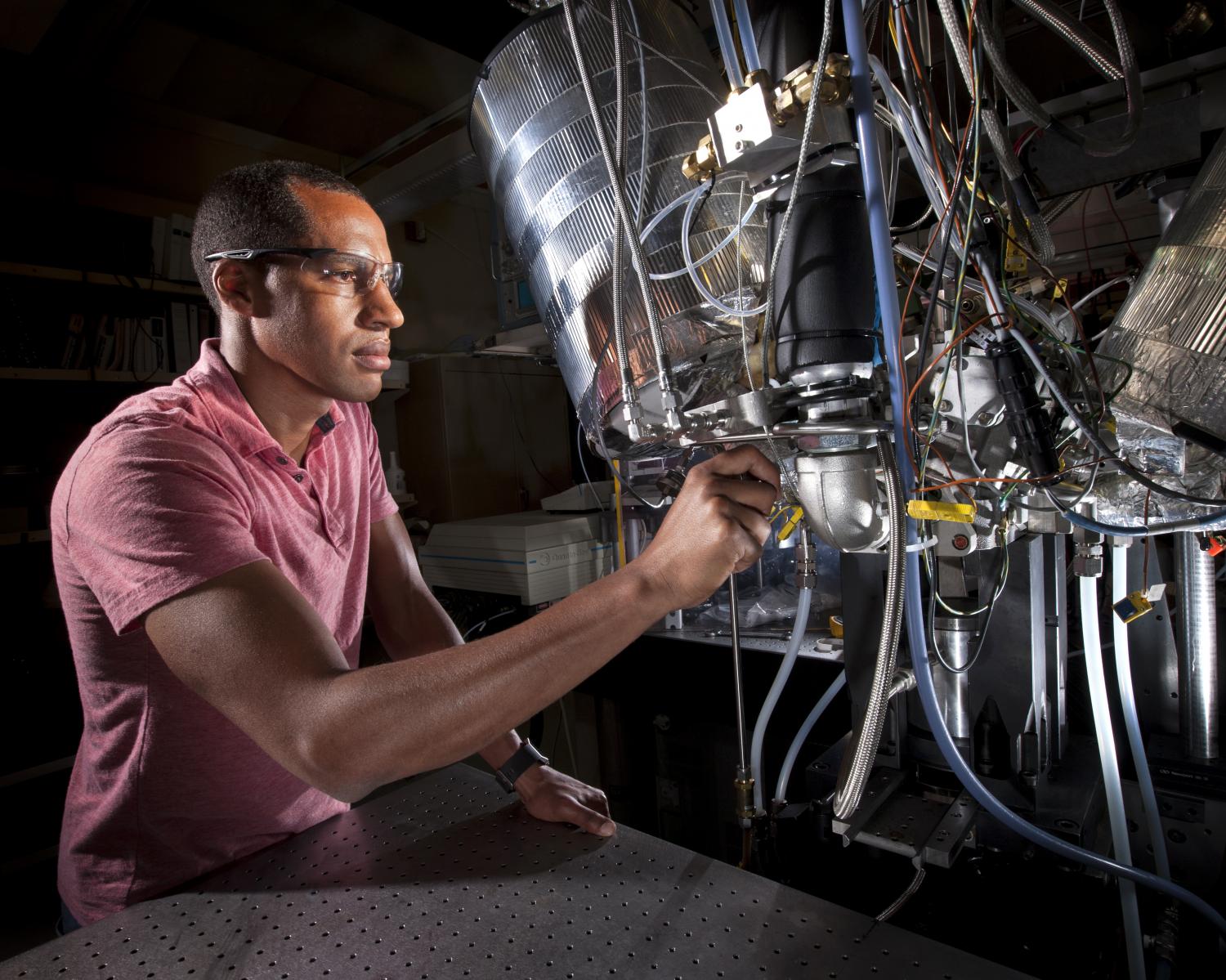
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories’ Combustion Research Facility are helping to develop sparkplug-free engines that will help meet ambitious automotive fuel economy targets of 54.5 miles per gallon by 2025.
They are working on low-temperature gasoline combustion (LTGC) operating strategies for affordable, high-efficiency engines that will meet stringent air-quality standards.
Sandia researchers Isaac Ekoto and Benjamin Wolk said the goal of the LTGC project is an engine in which chemically controlled ignition initiates the combustion of dilute charge mixtures.

