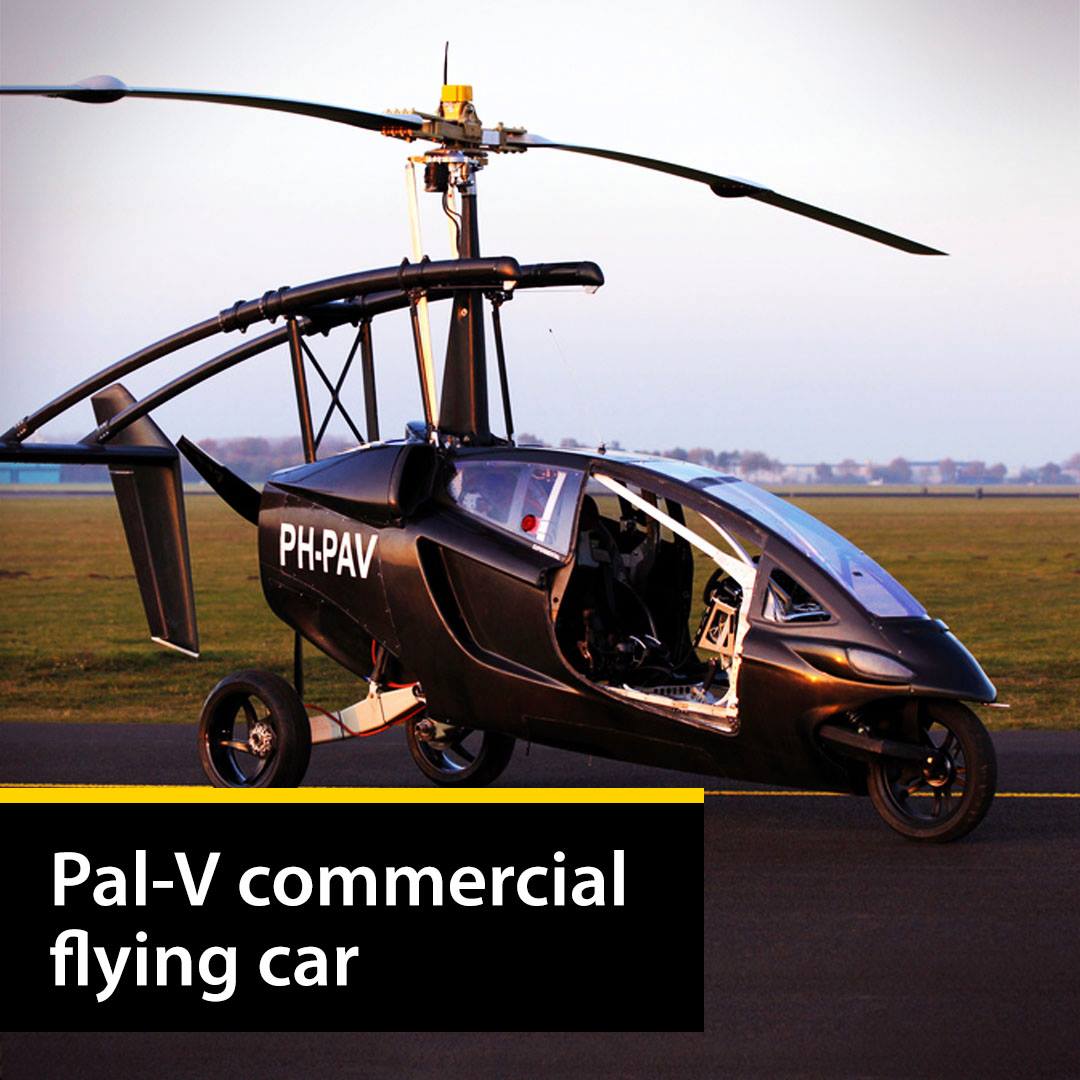
This is hands down the most impressive flying car I’ve seen to date.
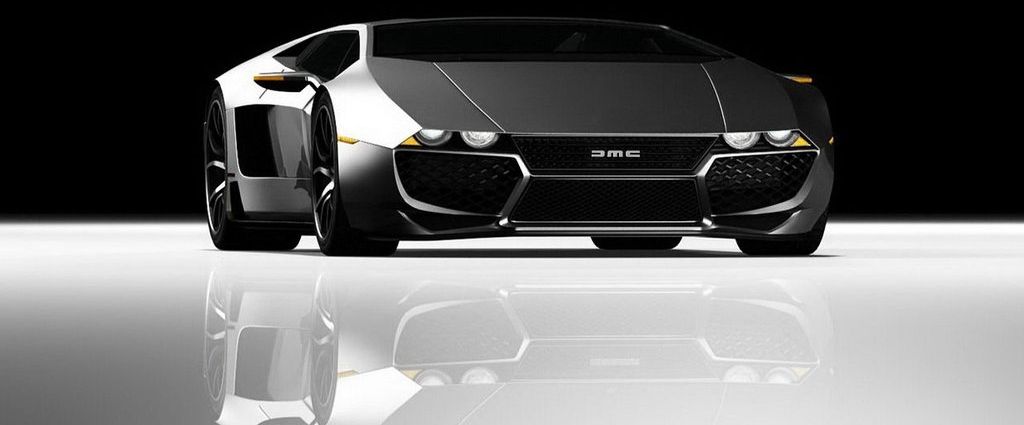




The first prototype of DeLorean appeared in October 1976, and production officially began in 1981 in Dunmurry, a suburb of south west Belfast, Northern Ireland (with the first DMC-12 rolling off the production line on January 21). The car features gull-wing doors and an innovative fiberglass chassis and underbody structure, along with a brushed stainless steel body.
DMC became famous for its appearance and was modified as a time machine in the Back to the Future film trilogy. A little more than 8,500 DMC-12s left DeLorean’s factory in Northern Ireland between 1981 and 1983, until its founder John DeLorean’s was arrested by the FBI on charges of drug trafficking.
Actually, it is quite impressing that Texas-based DeLorean Motor Company could soon initiate again its production thanks to a new law which exempts small volume car manufacturers from the safety requirements applied to the newly cars. On January 27, 2016, in Humble, Texas location, the car maker announced that production will resume and “new” DMC-12’s will be rolling off the assembly line in early 2017.

Driving a motor vehicle requires making tough choices in the heat of the moment. Whether slamming on the brakes in traffic or speeding up before a light turns red, split-second decisions are often a choice between the lesser of two evils. Sometimes, a choice could lead to bodily injury or even a loss of life.
As more self-driving cars reach the road, life-and-death decisions once made by humans alone will increasingly shift to machines. Yet the idea of giving that responsibility over to a computer may be unsettling to some.
Self-driving cars have the potential to significantly reduce the tens of thousands of auto fatalities occurring yearly—but a reduction isn’t the same as elimination. In fact, some deaths will inevitably happen at the hands of computer algorithms once they make those decisions for us.

SINGAPORE (AP) — The world’s first self-driving taxis will be picking up passengers in Singapore starting Thursday.
Select members of the public will be able to hail a free ride through their smartphones in taxis operated by nuTonomy, an autonomous vehicle software startup. While multiple companies, including Google and Volvo, have been testing self-driving cars on public roads for several years, nuTonomy says it will be the first to offer rides to the public. It will beat ride-hailing service Uber, which plans to offer rides in autonomous cars in Pittsburgh, by a few weeks.
The service will start small — six cars now, growing to a dozen by the end of the year. The ultimate goal, say nuTonomy officials, is to have a fully self-driving taxi fleet in Singapore by 2018, which will help sharply cut the number of cars on Singapore’s congested roads. Eventually, the model could be adopted in cities around the world, nuTonomy says.

I never get tired of reading about the glass energy solutions.
Harnessing Big Data Power Promises Greater Rewards for Environment & Businesses
‘Ideal’ energy storage material for electric vehicles developed.
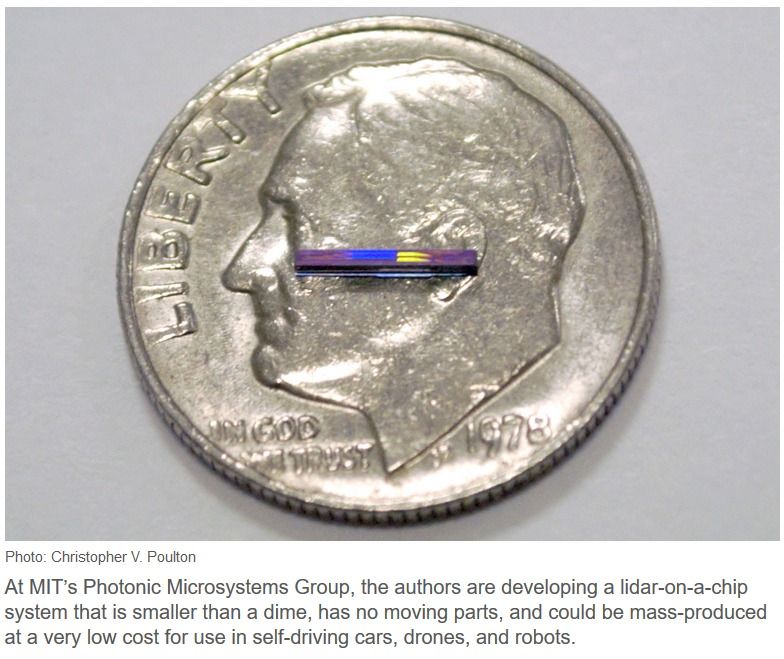
The Lidar (Light detection and ranging) systems on self-driving vehicles are big and generally expensive. MIT has a Lidar-on-a-chip solution that will fit on a dime and cost about $10 to manufacture.
Please consider the IEEE Spectrum article MIT and DARPA Pack Lidar Sensor Onto Single Chip.

Ride-hailing giant Uber announced on Thursday that is has acquired Otto for approximately $680 million.
All of Otto’s team, which includes ex-leader of Google’s self-driving project, Anthony Levandowski, will move to Uber. They will work on the company’s self-driving project and report directly to CEO Travis Kalanick.
See also: Self-driving tech startup Otto wants truckers to keep on…napping.