The global low-carbon revolution could be at risk unless new international agreements and governance mechanisms are put in place to ensure a sustainable supply of rare minerals and metals, a new academic study has warned.
The amount of cobalt, copper, lithium, cadmium, and rare earth elements needed for solar photovoltaics, batteries, electric vehicle (EV) motors, wind turbines, fuel cells, and nuclear reactors will likely grow at a rapid pace in the upcoming years. Even if alternatives are found for one metal, there will be reliance on another as the scope of possibilities is inherently limited by physical and chemical properties of elements.
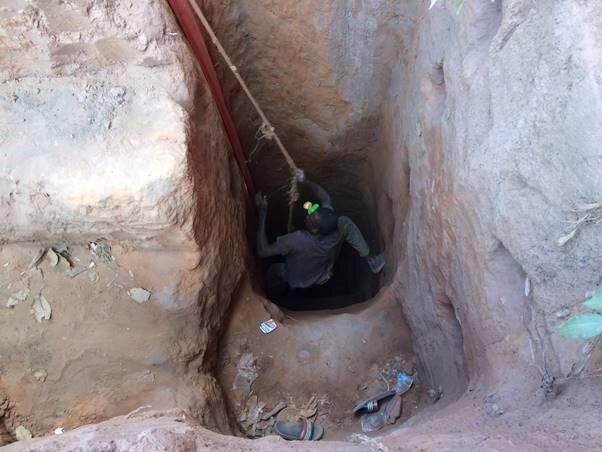
However, with global supplies often heavily monopolized by a single country, confronted by social and environmental conflict, or concentrated in poorly functioning markets, there is a real possibility that a shortage of minerals could hold back the urgent need for a rapid upscaling of low-carbon technologies. In some cases, markets are providing misleading signals to investors that can lead to poor decisions. In other cases, the countries or regions supplying minerals are politically unstable.