One of the biggest factors affecting consumer adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is the amount of time required to recharge the vehicles—usually powered by lithium-ion batteries. It can take up to a few hours or overnight to fully recharge EVs, depending on the charging method and amount of charge remaining in the battery. This forces drivers to either limit travel away from their home chargers or to locate and wait at public charging stations during longer trips.
Why does it take so long to fully charge a battery, even those used to power smaller devices, such as mobile phones and laptops? The primary reason is that devices and their chargers are designed so the rechargeable lithium-ion batteries charge only at slower, controlled rates. This is a safety feature to help prevent fires, and even explosions, due to tiny, rigid tree-like structures, called dendrites, that can grow inside a lithium battery during fast charging and induce short-circuits inside the battery.
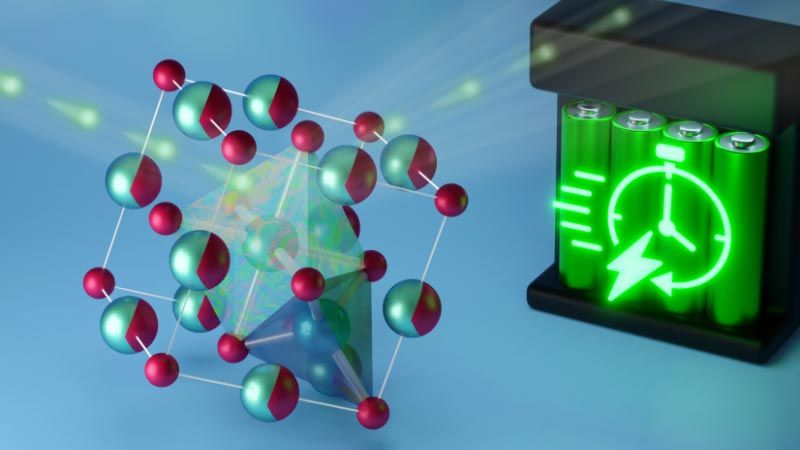
To address the need for a more practical lithium-ion battery, researchers from the University of California San Diego (UC San Diego) worked with scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) to conduct neutron scattering experiments on a new type of material that could be used to make safer, faster-charging batteries. The researchers produced samples of lithium vanadium oxide (Li3V2O5), a “disordered rock salt” similar to table salt but with a certain degree of randomness in the arrangement of its atoms. The samples were placed in a powerful neutron beam that enabled observing the activity of ions inside the material after a voltage was applied.