Made in China motto is gaining speed in China.
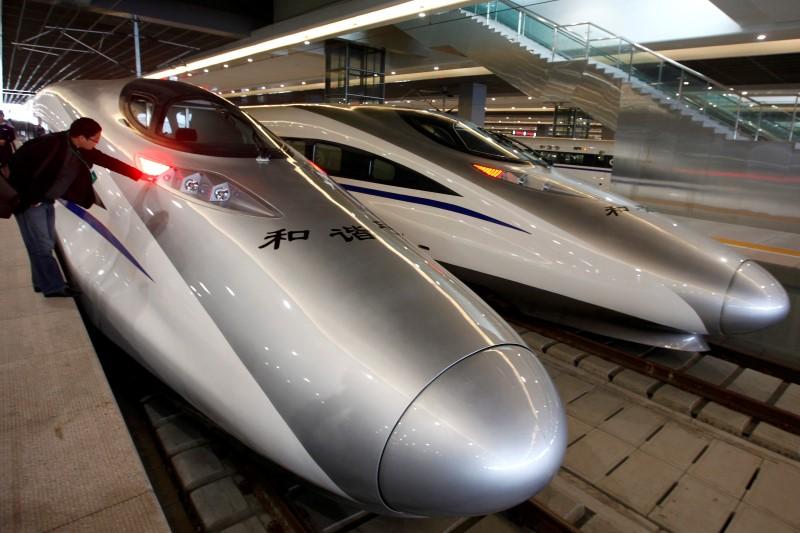
SHANGHAI Foreign firms say they are struggling to gain access to China’s vast railway market as the country, seeking to transform its domestic industry into an export powerhouse, tightens the bidding criteria on rail tenders.
The complaints echo similar concerns raised in other industries including technology and renewable energy, and highlight what some foreign companies see as an uneven playing field when operating in China.
Four rail suppliers with offshore funding said they were finding it harder to win contracts thanks to the proliferation of government-supported rivals, with at least one saying it was already experiencing discrimination.