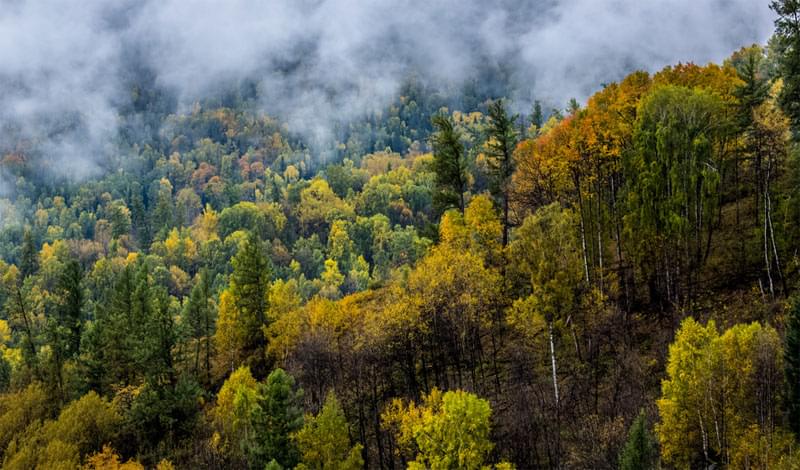
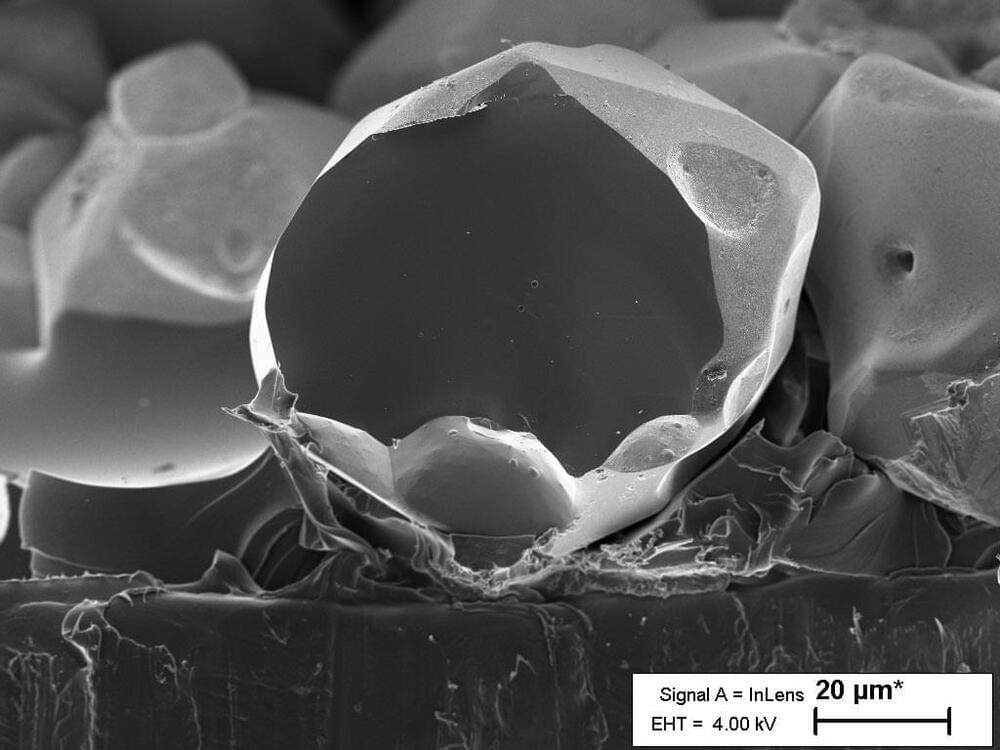
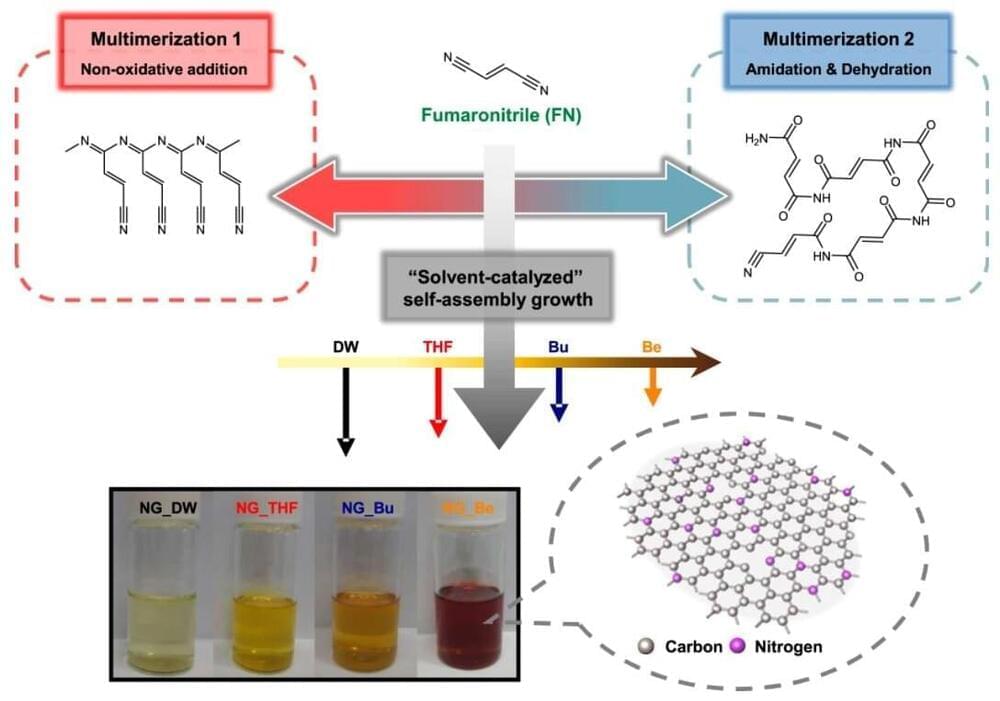
Graphene consists of a planar structure, with carbon atoms connected in a hexagonal shape that resembles a beehive. When graphene is reduced to several nanometers (nm) in size, it becomes a graphene quantum dot that exhibits fluorescent and semiconductor properties. Graphene quantum dots can be used in various applications as a novel material, including display screens, solar cells, secondary batteries, bioimaging, lighting, photocatalysis, and sensors. Interest in graphene quantum dots is growing, because recent research has demonstrated that controlling the proportion of heteroatoms (such as nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorous) within the carbon structures of certain materials enhances their optical, electrical, and catalytic properties.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok-Jin Yoon) reported that the research team led by Dr. Byung-Joon Moon and Dr. Sukang Bae of the Functional Composite Materials Research Center have developed a technique to precisely control the bonding structure of single heteroatoms in the graphene quantum dot, which is a zero-dimensional carbon nanomaterial, through simple chemical reaction control; and that they identified the relevant reaction mechanisms.
With the aim of controlling heteroatom incorporation within the graphene quantum dot, researchers have previously investigated using additives that introduce the heteroatom into the dot after the dot itself has already been synthesized. The dot then had to be purified further, so this method added several steps to the overall fabrication process. Another method that was studied involved the simultaneous use of multiple organic precursors (which are the main ingredients for dot synthesis), along with the additives that contain the heteroatom. However, these methods had significant disadvantages, including reduced crystallinity in the final product and lower overall reaction yield, since several additional purification steps had to be implemented. Furthermore, in order to obtain quantum dots with the chemical compositions desired by manufacturers, various reaction conditions, such as the proportion of additives, would have to be optimized.