Those aren’t city lights.
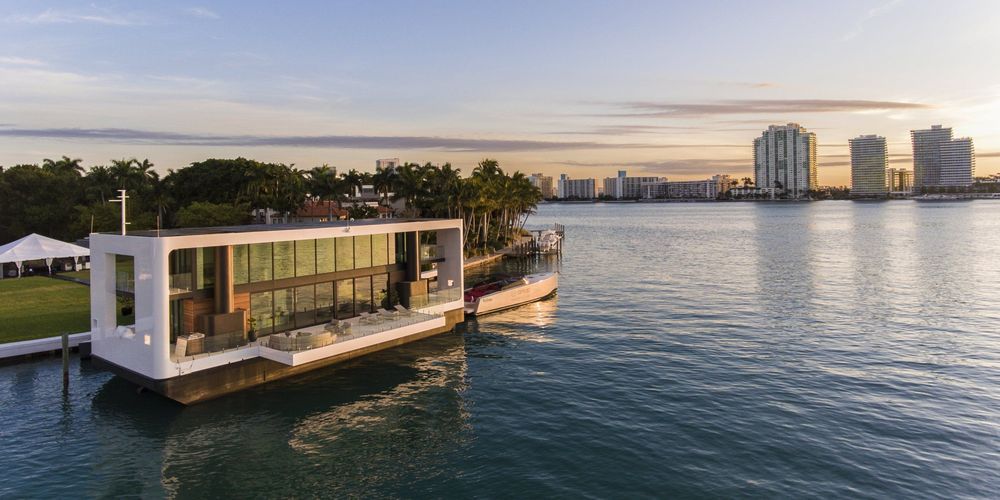


When the housing startup Arkup revealed its plan to build a floating, hurricane-proof yacht in 2017, South Florida had just witnessed the devastating effects of Hurricane Irma, a Category 4 storm that destroyed hundreds of residences.
The company’s models were designed to weather a storm of that magnitude, but it would be another two years before they became a reality.
Recently University of Glasgow developed a Graphene based E-Skin for prosthetic limbs. The research started with making a prosthetic arm that could sense even the minutest of pressure for gripping soft objects. It eventually yielded a prosthetic limb that was also self powering.
This was because of the development of Graphene based supercapacitors.
Graphene is now being explored for wearable electronics and health pathes because of its flexibility and ability to pick the smallest of signals.

Ingenius.
Researchers in China have developed a new way to remove bacteria from water that they say is both highly efficient and environmentally sound.
By shining ultraviolet light onto a two-dimensional sheet of a compound called graphitic carbon nitride, the team’s prototype can purify 10 litres (2.6 liquid gallons) of water in just one hour, killing virtually all the harmful bacteria present.
This type of technique for water cleaning is known as photocatalytic disinfection, and it is often talked about — and ardently researched — as an appealing alternative to current water filtration systems, such as chlorination or ozone disinfection, neither of which are particularly eco-friendly.
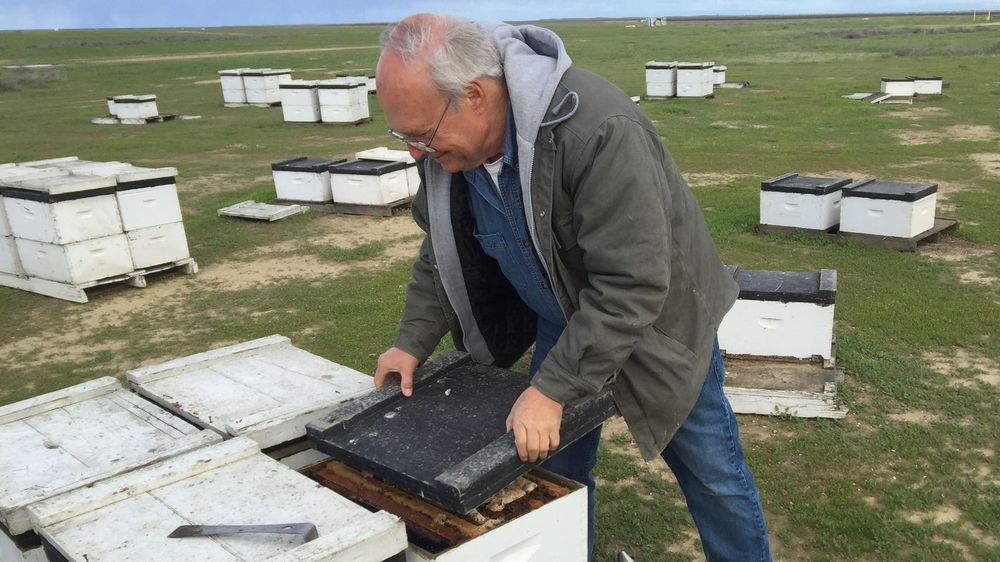

The Salt Honey bees deal with many stressors: chemicals, climate change and viruses. But this year, a tiny mite has wiped out colonies, causing worry over whether there are enough bees left to do their jobs.
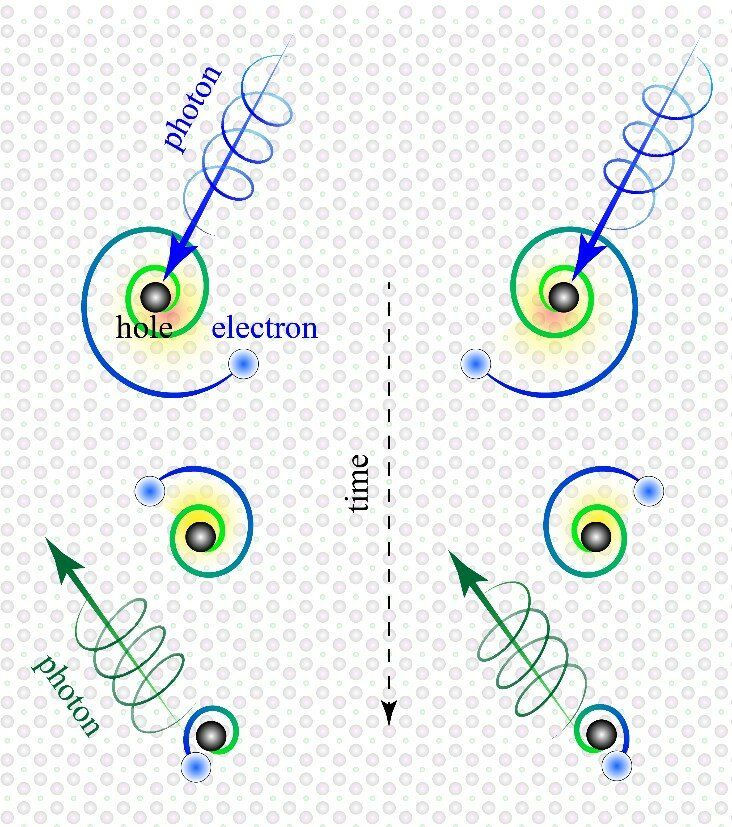
Rutgers and other physicists have discovered an exotic form of electrons that spin like planets and could lead to advances in lighting, solar cells, lasers and electronic displays.
It’s called a “chiral surface exciton,” and it consists of particles and anti-particles bound together and swirling around each other on the surface of solids, according to a study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Chiral refers to entities, like your right and left hands, that match but are asymmetrical and can’t be superimposed on their mirror image.
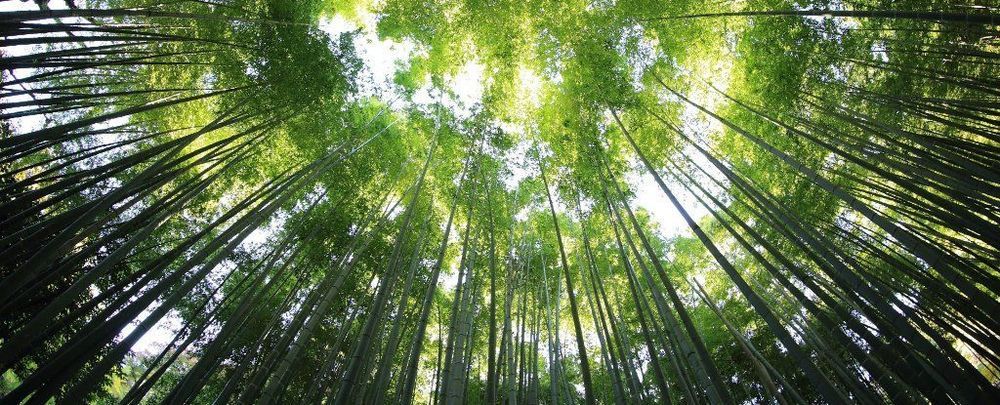

An ambitious new analysis of the world’s forests found that there’s space to plant 1.2 trillion new trees — a number that would absorb more carbon than human emissions.
According to the new data, ETH Zurich researcher Thomas Crowther told The Independent, trees are “our most powerful weapon in the fight against climate change.”
Crowther told The Independent that the new analysis, which he presented at a conference this weekend, suggests that a worldwide tree-planting spree would have a greater impact on the planet’s environment than building wind turbines or vegetarian diets — an effort, he says, that could cancel a decade of greenhouse emissions.
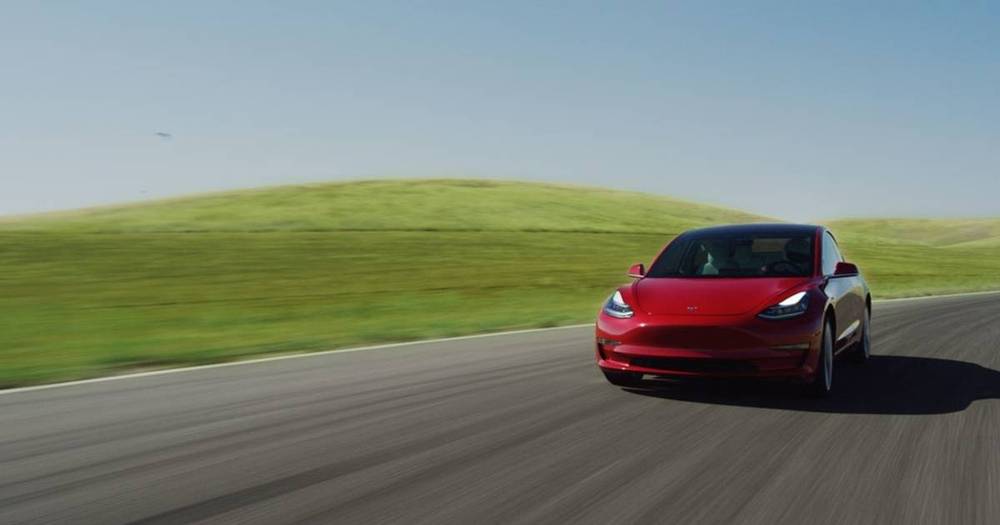

To make a regular car go faster on the track, you can add go-fast components like a turbocharger or better fuel, or improve handling components like brakes and tires. Carmakers can also make a dizzying amount of software tweaks to everything from the stability and traction control systems to throttle mapping and how much fuel gets into the engine.
But with an electric car, the software is the star of the show. Code controls everything. That’s why Tesla can introduce Track Mode to the Model 3 with a software download, unlocking new features designed to get the electric sports sedan around a track faster than before.
On something like the BMW M5, putting the car in Sport Mode adjusts a dizzying array of settings for throttle response, transmission, chassis, steering, stability control, and whether the car operates in all- or rear-wheel drive.

Electric cars could be charged at any time and any place.
It could reliably supply energy 99 per cent of the time, at six-times the intensity of solar farms on earth, he said.
Chinese scientists first plan to build and launch small to medium-sized solar power stations to be launched into the stratosphere to generate electricity, between 2021 and 2025.

Unlike high tech solutions to climate change like carbon capture systems, Crowther argued, trees are nice because anyone can plant one.
“It’s a beautiful thing because everyone can get involved,” he told The Independent. “Trees literally just make people happier in urban environments, they improve air quality, water quality, food quality, ecosystem service, it’s such an easy, tangible thing.”
READ MORE: Massive restoration of world’s forests would cancel out a decade of CO2 emissions, analysis suggests [The Independent].