Good for the environment and the economy.





In 1965, I. J. Good described for the first time the notion of “intelligence explosion”, as it relates to artificial intelligence (AI):
Let an ultraintelligent machine be defined as a machine that can far surpass all the intellectual activities of any man however clever. Since the design of machines is one of these intellectual activities, an ultraintelligent machine could design even better machines; there would then unquestionably be an “intelligence explosion,” and the intelligence of man would be left far behind. Thus the first ultraintelligent machine is the last invention that man need ever make, provided that the machine is docile enough to tell us how to keep it under control.
Decades later, the concept of an “intelligence explosion” — leading to the sudden rise of “superintelligence” and the accidental end of the human race — has taken hold in the AI community. Famous business leaders are casting it as a major risk, greater than nuclear war or climate change. Average graduate students in machine learning are endorsing it. In a 2015 email survey targeting AI researchers, 29% of respondents answered that intelligence explosion was “likely” or “highly likely”. A further 21% considered it a serious possibility.

SSPI approach: • Enabling technologies developed at Caltech • Ultra-light deployable space structures • High efficiency ultra-light photovoltaic (PV) • Phased Array and Power Transmission • Integration of concentrating PV, radiators, MW power conversion and antennas in single cell unit • Localized electronics and control for system robustness, electronic beam steering • Identical spacecraft flying in formation • Target is specific power over 2000 Watts per kilogram. This would cost competitive with ground-based power.

Sure, it’ll be great when a drone can drop off your Amazon Prime goodies or 7-Eleven snacks just minutes after you order them… but it’ll be even better when they help regrow millions of trees.
That’s what U.K.-based BioCarbon Engineering has set out to do. The company has been developing a high-tech system that uses drones to replant deforested areas — even in areas where planting wouldn’t be feasible using older methods.
BioCarbon’s system utilizes drones for two separate stages of the process. First, they’re sent into the target area to create a detailed, three-dimensional map. Once they’ve completed that step, the planting drones return to the site to do their thing.

It is often not the lack of a cure, but the lack of will. Many great strides have been made with diabetes, when people stopped trying to develop medicines, and instead focused on how to enable the body to produce insulin.
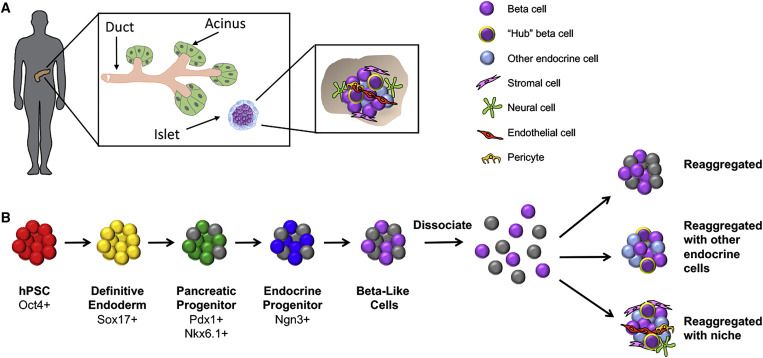
Restoration of insulin independence and normoglycemia has been the overarching goal in diabetes research and therapy. While whole-organ and islet transplantation have become gold-standard procedures in achieving glucose control in diabetic patients, the profound lack of suitable donor tissues severely hampers the broad application of these therapies. Here, we describe current efforts aimed at generating a sustainable source of functional human stem cell-derived insulin-producing islet cells for cell transplantation and present state-of-the-art efforts to protect such cells via immune modulation and encapsulation strategies.

My colleague Conor Sen recently made a bold prediction: Government will be the driver of the U.S. economy in coming decades. The era of Silicon Valley will end, supplanted by the imperatives of fighting climate change and competing with China.
This would be a momentous change. The biggest tech companies — Amazon.com, Apple Inc., Facebook Inc., Google (Alphabet Inc.) and (a bit surprisingly) Microsoft Corp. — have increasingly dominated both the headlines and the U.S. stock market: