Circa 2010
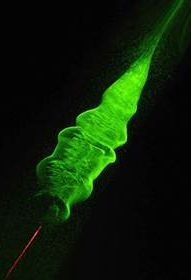
Ultra-fast pulses from a powerful laser can create droplets of water out of thin air, according to a new study. With the right conditions and large enough droplets, the researchers say, the technique could be used to make rain on demand.
Rain forms when water condenses around tiny particles in the atmosphere. Most of the time, dust or pollen do the job, but humans have long attempted to speed the process by seeding clouds with chemicals like silver iodide. Those chemicals provide the so-called “condensation nuclei” that trigger the consolidation of water into raindrops.
Unfortunately, such methods are difficult and could have environmental side effects, said Jérôme Kasparian, an optical physicist at the University of Geneva, Switzerland who was on the team that demonstrated the laser-triggered condensation. The study was published online May 2 in the journal Nature Photonics.