I told folks this; I see another one from Google has joined the QC less than 10 year club. My guess is more likely less than 7 years.
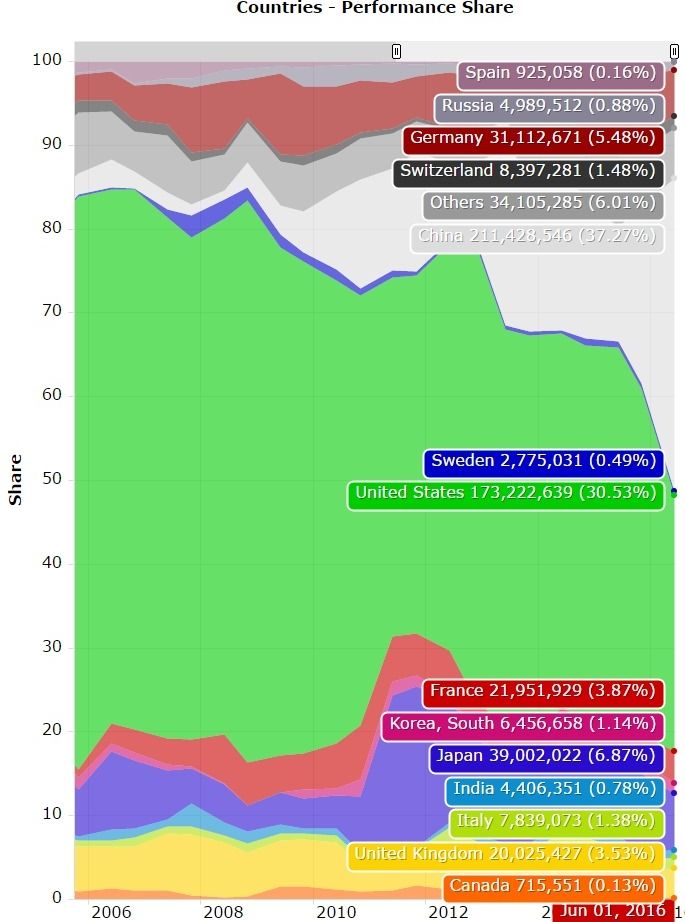
A seminal moment in the quantum technology field just happened: Google’s team of scientists have simulated a hydrogen molecule from its quantum computers, a breakthrough that suggests it could “simulate even larger chemical systems,” writes one of Google Quantum’s engineers, Ryan Rabbush. The search engine’s achievement underscores the technology’s potential as Rabbush posits it can “revolutionize the design of solar cells, industrial catalysts, batteries, flexible electronics, medicines, materials and more.”
As advances in such supercomputers continue, investment and research in this field gathers greater momentum as Google, Alibaba, Baidu, Amazon and other tech giants and governments too are racing to develop this technology. Recently, the European Commission allocated €1 billion to research, incubate and invest in quantum technologies. Meanwhile Google last month made headlines about testing its quantum security to shield its Chrome browser.
“It is a technology that is developing very rapidly,” explains Serguei Beloussov, CEO and founder of data security firm Acronis, adding that industries related to “creativity and human ingenuity” are more difficult to predict and that is the case with this fast-developing field. “Quantum computing at the moment [particularly] quantum metrology and quantum security are things that are dependent on science so [development] can be very slow or rapid. If this technology actually appears, it will be such a huge change that companies like Amazon, Alibaba, Google want to be in front of that change and that is why they are investing,” says this tech expert who is also executive chairman of tech company, Parallels.
Read more