“Computational design tool transforms flat materials into 3D shapes” — I could use this many times over.
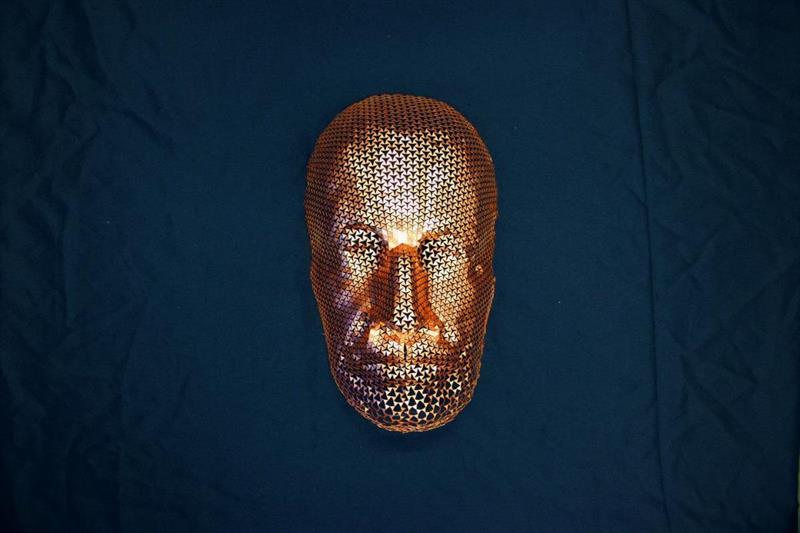
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne, Switzerland (EPFL) have developed a new computational design tool can turn a flat sheet of plastic or metal into complex 3D shapes. They say the tool enables designers to fully and creatively exploit an unusual quality of certain materials — the ability to expand uniformly in two dimensions.
In this case, the researchers were making hexagonal cuts into flexible, but not normally stretchable plastic and metal sheets to give them the ability to expand uniformly, up to a point. But the design tool could be useful for a variety of synthetic materials, known as auxetic materials that share this same distinctive quality.
Origami-style folding techniques have already helped produce devices such as cardiac stents, which must be maneuvered into the narrowed artery of a heart patient and then expanded to hold the artery open, and solar arrays that unfold after being launched into space. Auxetic materials could be used in similar ways, while also exploiting their additional capabilities.