The space bomber will shoot nuclear bombs from space!



In December of last year, scientists at the Large Hadron Collider in Europe announced startling results hinting at the existence of an undiscovered subatomic particle—one with a mass six times heavier than the Higgs boson, the particle that made headlines in 2012.
The evidence is still thin, but if more data confirm the finding, it could sharpen humankind’s understanding of the building blocks of the universe.
“This was a very surprising announcement and a puzzle at the same time, because the lifetime and mass of the particle could reveal something else beyond simply one extra particle, if it turns out to be a real signal,” said Kyoungchul “K.C.” Kong, associate professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Kansas. “Yet we do not claim this as a discovery, and we need more data.”

A Russian rocket engine company, with the assistance of a major research and development institute, will work on a project to create a powerful electrodeless plasma rocket engine, Russia’s Roscosmos space corporation said Wednesday.
The project will be developed by the Kurchatov Institute, Russia’s leading research and development institution in the field of nuclear energy, and the Chemical Automatics Design Bureau (CADB).
“The project involves the development of a new-generation electrodeless plasma engine. It is a high-power engine using fuel in a plasma state. It has a high energy efficiency, an ability to use almost any kind of rocket fuel… and its maximum engine power is limited only by the power supply of a high-frequency generator,” Roscosmos said in a statement.
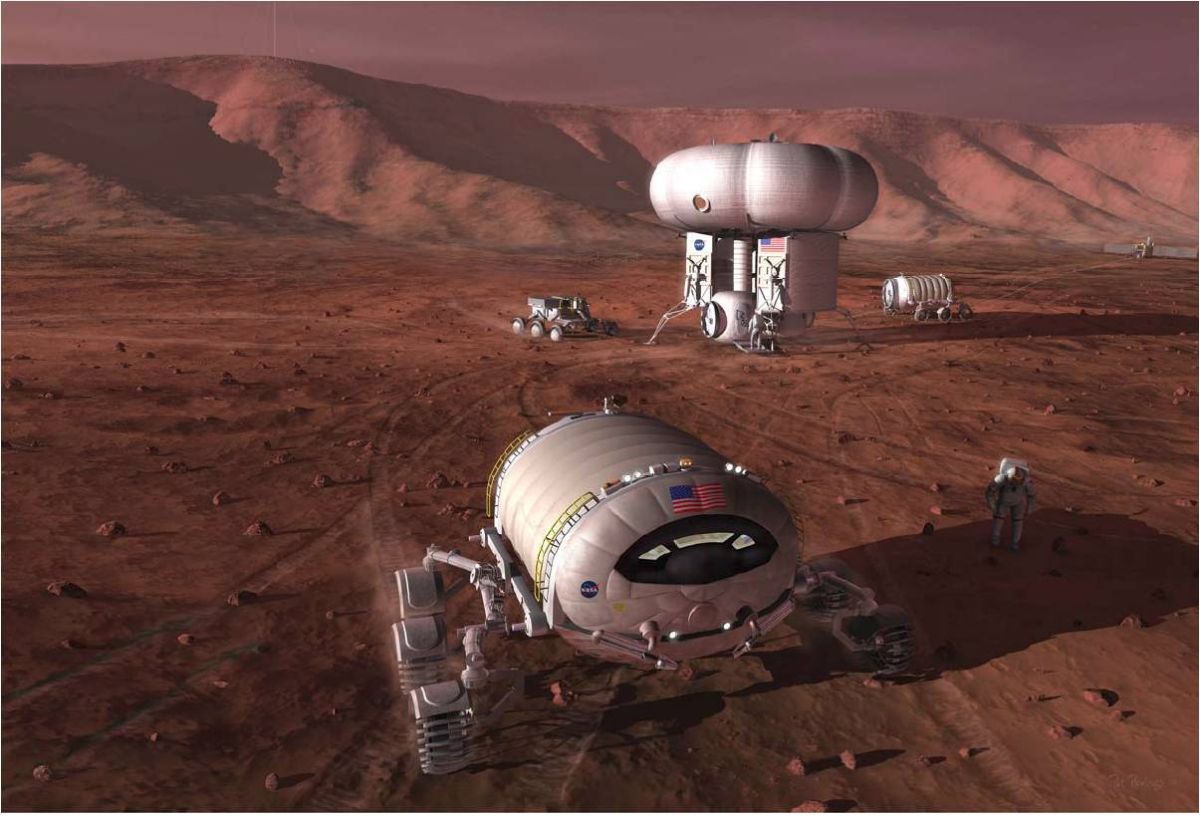


Long-term human colonization of Mars is feasible, as long as Red Planet pioneers “live off the land,” a recent NASA report concludes.
“There are massive resources on Mars obtainable from the atmosphere and extracted from the regolith which are capable of supporting human colonization,” write the authors of the report, which is called “Frontier In-Situ Resource Utilization for Enabling Sustained Human Presence on Mars.”
Using Martian resources, existing technologies could supply water, oxygen, fuel and building materials, the report adds, “to relax the dependence on Earth during the buildup of a colony on Mars.” [Red Planet or Bust: 5 Crewed Mars Mission Ideas].

Other NASA officials have said they have plans to speak with Congressional staffers about ARM and assuage concerns the agency is wasting valuable time and resources on something impractical.
A successful ARM mission would be the craziest thing NASA has ever done, but would also hit on pretty much every big agency objective. ARM would basically kill a dozen space birds with one space rock.
Photos via Screenshot from NASA webcast., NASA.
Nice.
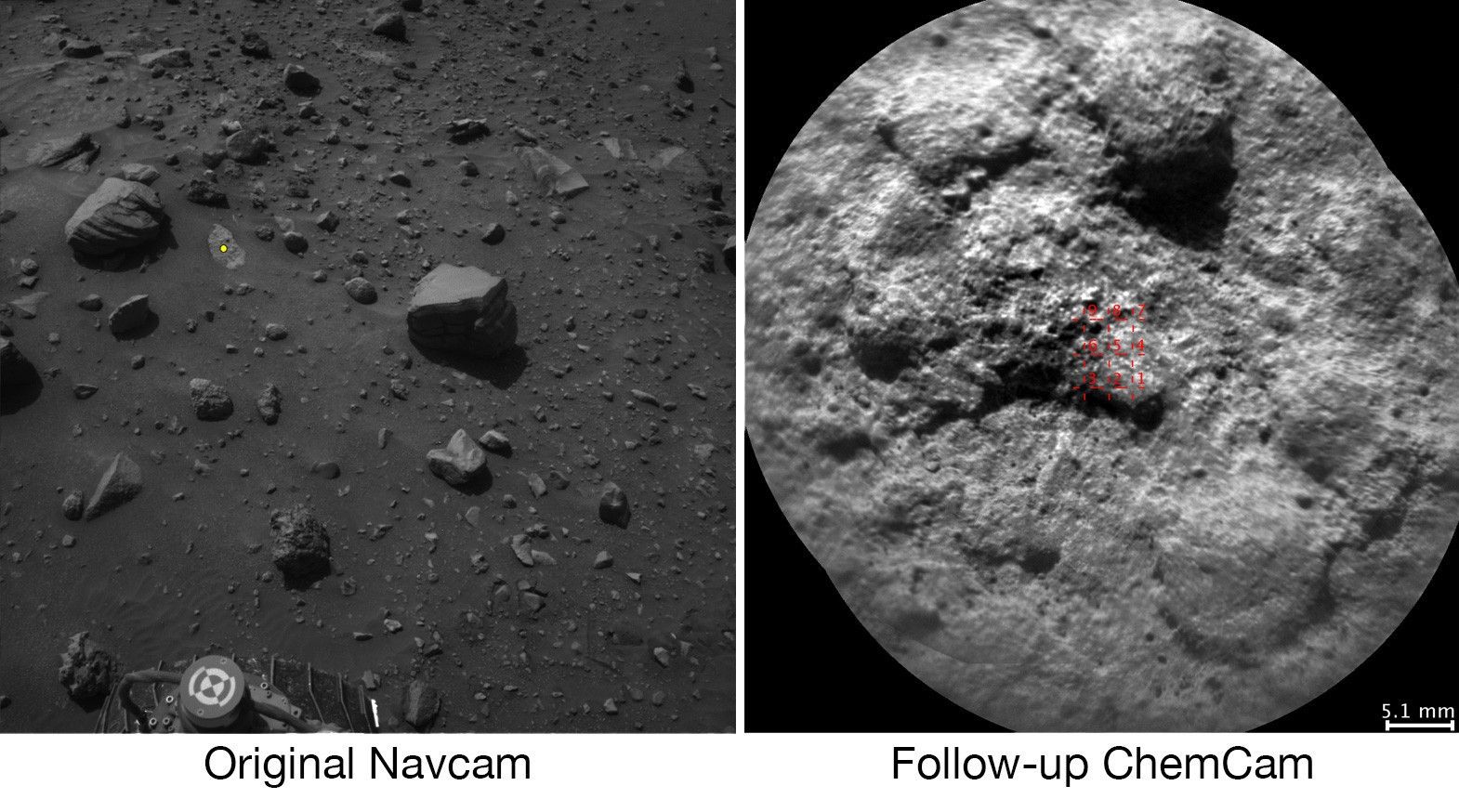
Who’s calling the shots now? After nearly four years on the job, NASA’s Curiosity rover is finally making certain scientific decisions on its own. The Martian explorer now picks some of the rock targets to blast with the laser on its ChemCam instrument.
A software upgrade known as AEGIS allows the rover to make key decisions when Mars is out of sync with Curiosity’s handlers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, delivering more data in less time. It’s the first time a robot has been able to choose such science targets autonomously on any planetary mission.
“Time on Mars is valuable and we get more data this way and we get the data much faster,” said AEGIS team member Raymond Francis, a scientific applications software engineer at JPL.

Want to build stuff for Space; well you may need to move from earth to a spacelab. I can see the job ads “want to see and experience other planetary worlds; live for adventure, see space; sleep near Mars, etc.”
Any robust future in space will almost certainly require a way to build there — and that future might not be as far out as you think!

The idea of a space elevator to lift us into orbit is one of the oldest concepts in sci-fi, but thanks to the efforts of scientists in Japan, we might soon be seeing this fantastic feat of engineering become a reality at last.
A mini satellite called STARS-C (Space Tethered Autonomous Robotic Satellite-Cube) is heading to the International Space Station in the coming months and is a prototype design that could form the basis of a future space elevator.
Once STARS-C has been delivered – on some to-be-determined date after the Northern Hemisphere’s summer – its makers at Shizuoka University will put it to the test: the orbiter will split into two 10-cm (3.94-inch) cubes and spool out a thin 100-metre tether made of Kevlar between them.

X literally marks the spot in the center of the Milky Way, a phenomenon that offers clues about the galaxy’s formation.