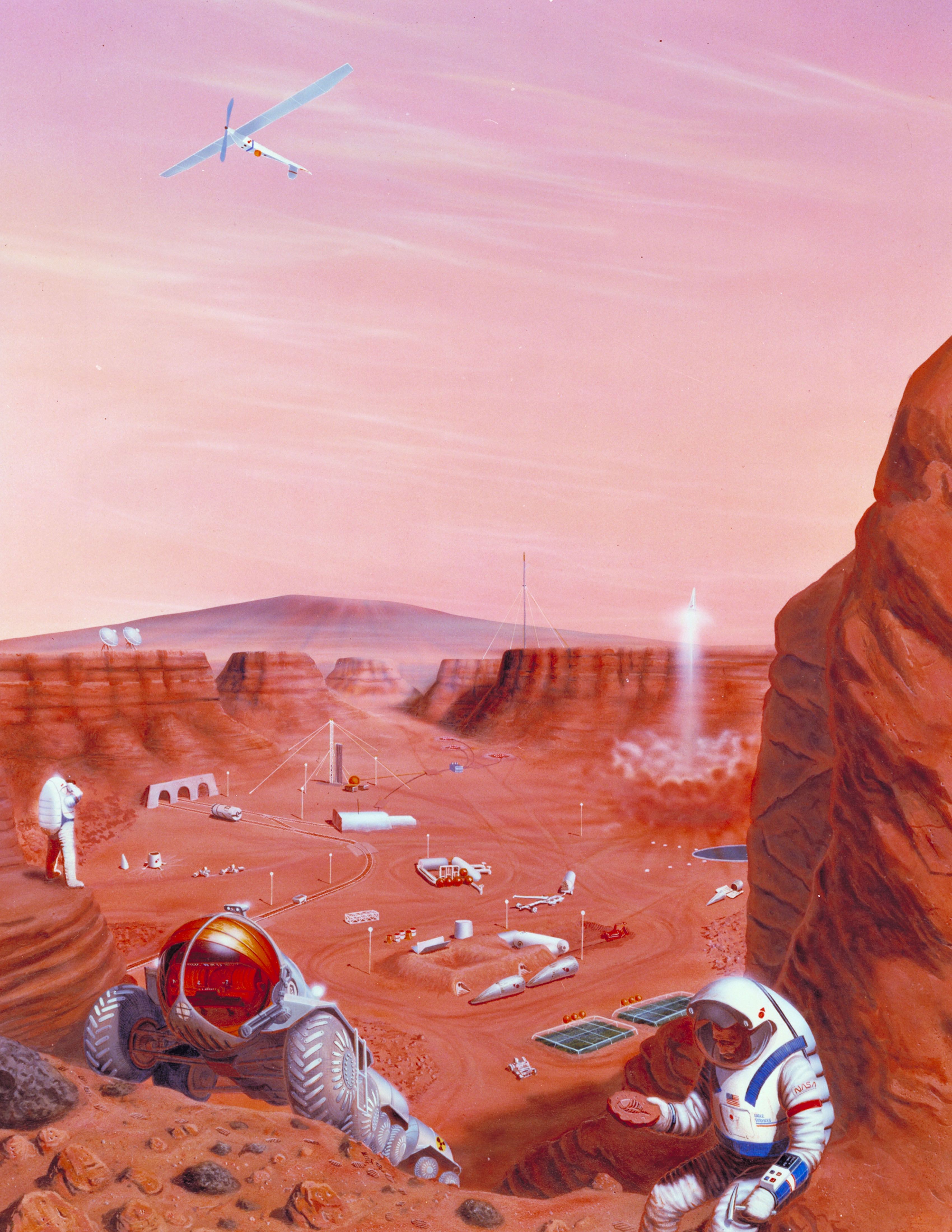
And it will change how we think about construction here on Earth.
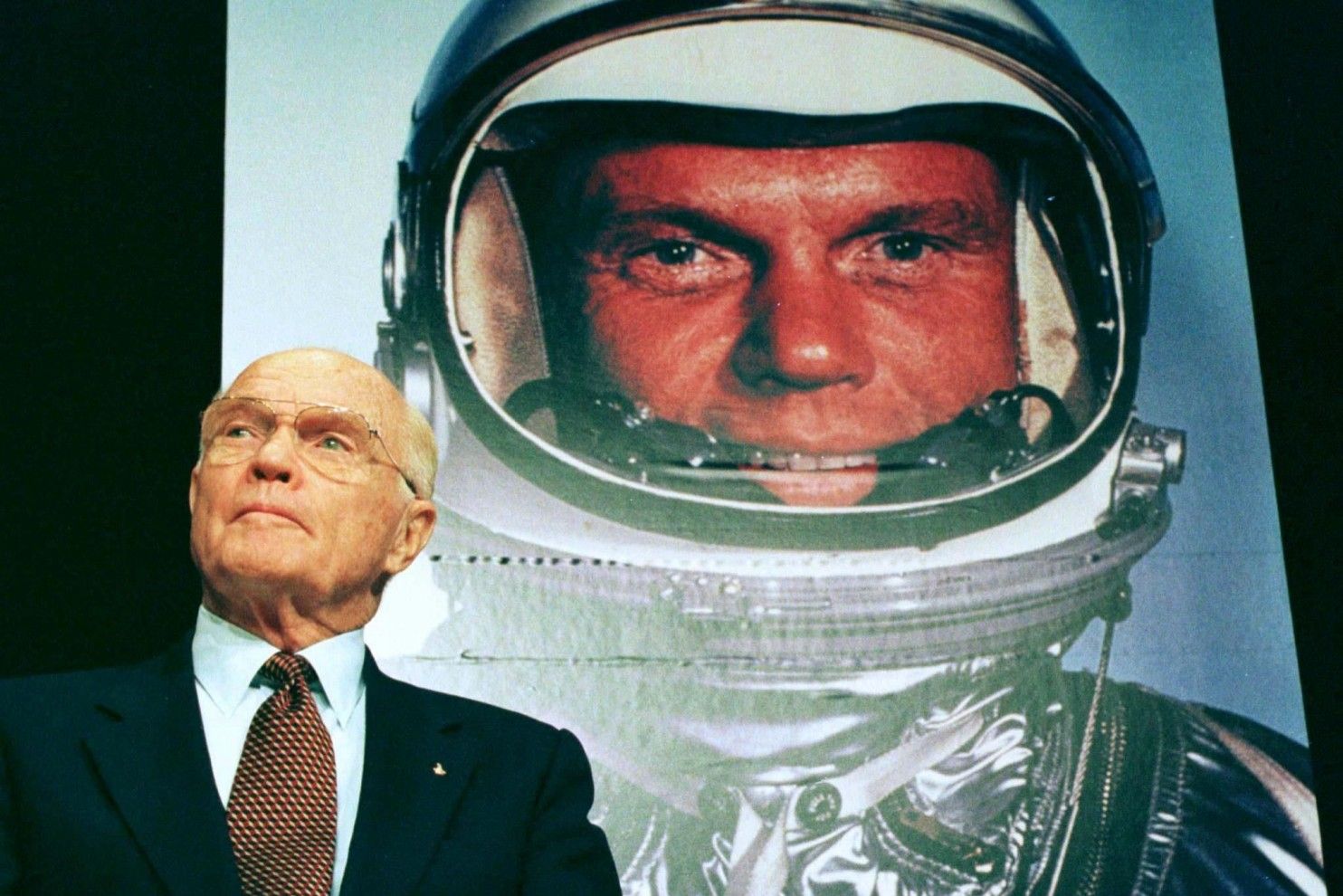





John Glenn, who captured the nation’s attention in 1962 as the first American to orbit the Earth during a tense time when the United States sought supremacy over the Soviet Union in the space race, and who rocketed back into space 36 years later, becoming the oldest astronaut in history, died Dec. 8 at a hospital in Columbus, Ohio. Mr. Glenn, who in his post-NASA career served four terms as a U.S. senator from Ohio, was 95.
The death was confirmed by Hank Wilson, communications director at the John Glenn College of Public Affairs at Ohio State University. Mr. Glenn had a stroke after heart-valve replacement surgery in 2014, but the immediate cause was not announced.
Mr. Glenn was one of the seven original astronauts in NASA’s Mercury program, which was a conspicuous symbol of the country’s military and technological might at the height of the Cold War. He was not the first American in space — two of his fellow astronauts preceded him — but his three-orbit circumnavigation of the globe captured the imagination of his countrymen like few events before or since. Mr. Glenn was the last survivor of the Mercury Seven.
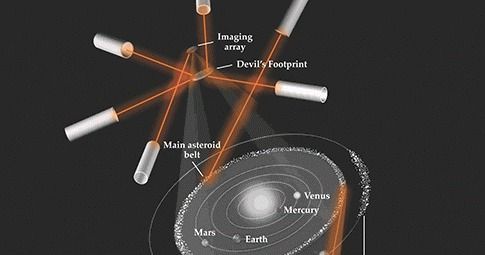
Physics Today has a speculative article that proposes that laser light be used to shape and polish an asteroid to high optical standards. This could create an Asteroid Belt Astronomical Telescope (ABAT).
The Asteroid Belt Astronomical Telescope (ABAT) focuses light from laser-polished asteroids onto dual imaging arrays above and below the solar system; other intense laser pulses maneuver the arrays to different locations, thus allowing ABAT to point at multiple celestial targets. Asteroid ablation residue corralled into a pair of Devil’s Footprints shields the focal regions from solar illumination. (Courtesy of Laura Kim.)
Imagined 10 meter resolution imaging of exoplanet.
Why is warp drive R&D so important for the future of mankind?
–> Primarily, because without “warp bubble” (warp drive) technology any random object that is “drifting” in space will easily be able to decommission/neutralize even the most robust spacecraft.
–> Without mankind first developing warp drive (“warp bubble”) technology, we will never reach places like Earth 2.0 (presumably in the Proxima Centauri star system).

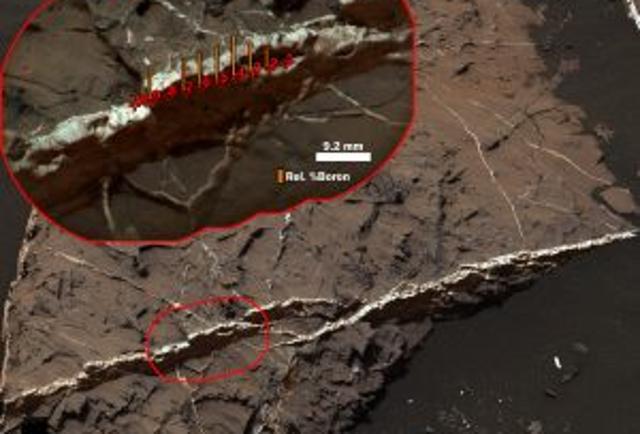
Despite having a setup that has been pretty much operating for years, how many data points are in the paper? Eighteen. Now, if this were a really time-consuming experiment, I wouldn’t let that bother me. Hell, some synchrotron experiments have only a single data point. But this is clearly not a time-limited experiment.

In Brief
Senator Ted Cruz opened up last Wednesday’s hearing by the US Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness with a description of the changing landscape of technology: “Whether we recognize it or not, artificial intelligence is already seeping into our daily lives.”
Senator Cruz explained that scientists are predicting how investments in AI will increase by more than 300 percent in the next few years, which means AI will have a more prominent role in society. With that in mind, the subcommittee’s hearing focused on the impact AI has in various sectors of US society, and how to best ensure US leadership in AI development.