A NEW laser is being built that is powerful enough to rip apart empty space.
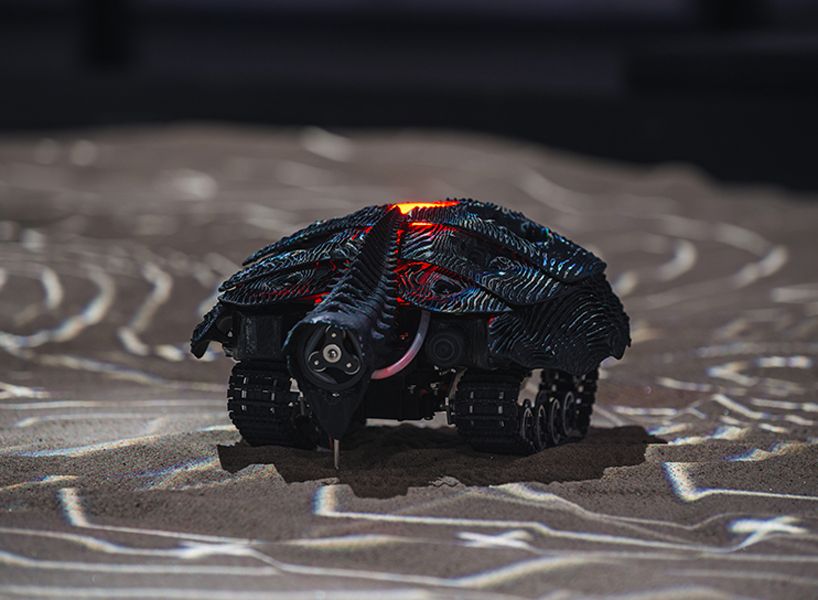



for the 2017 tallinn architecture biennale, noumena has presented its installation based on the future of robots and its adaptability with the environment. deep learning has paved the way for machines to expand beyond narrow capabilities to soon achieving human-level performance on intellectual tasks. however, as artificial intelligence — A.I. — establishes its place within humans, society will need to develop a framework for both to thrive. a new form of artificial life will emerge, finding space at the peripheries of humanity in order to not compete for human-dominated resources. A.I. will attempt to improve its operating surroundings to not just survive but be self-sustaining, forming the basis of a civilization constrained at the intersection of nature and technology.
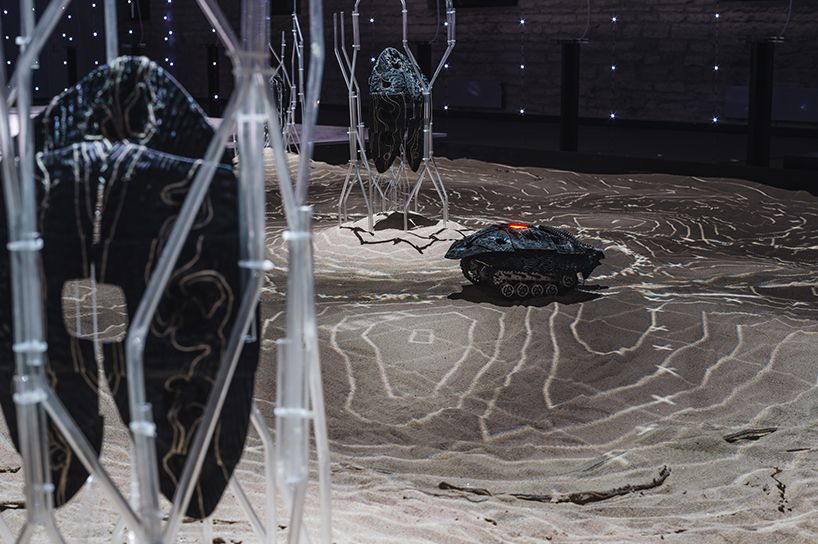 image © tõnu tunnel.
image © tõnu tunnel.
barcelonian based practice noumena has developed a framework to build this narrative based on the cross disciplinary intersection of computational design, mechanical and electronic design, rapid prototyping interaction and mapping. nowadays, computing tools as well as rapid prototyping machines allow to have a quick practical feedback on design solutions and to iterate experimenting different possibility at the same time giving the chance to choose and custom a functional part.
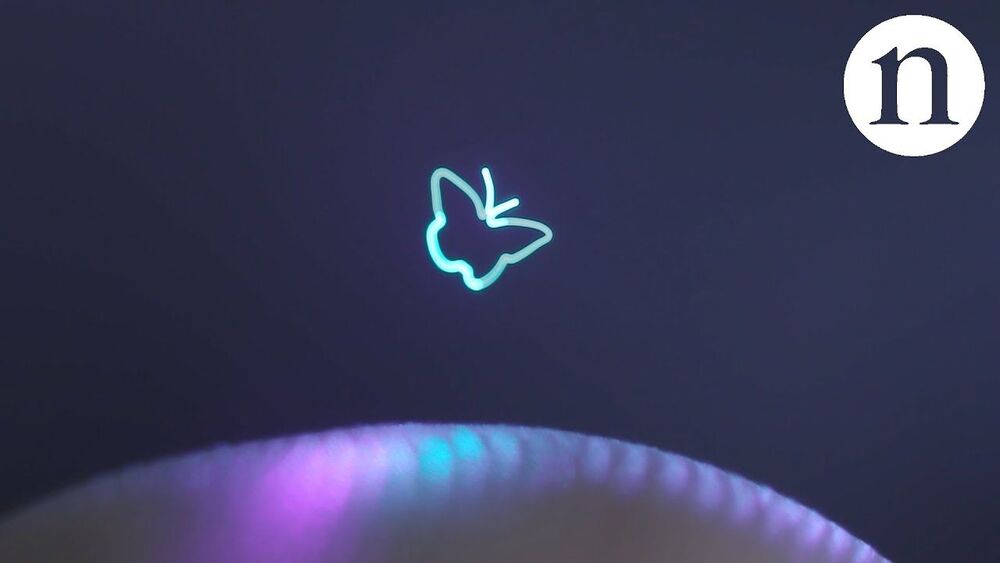


One of the enduring sci-fi moments of the big screen—R2-D2 beaming a 3D image of Princess Leia into thin air in “Star Wars”—is closer to reality thanks to the smallest of screens: dust-like particles.
Scientists have figured out how to manipulate nearly unseen specks in the air and use them to create 3D images that are more realistic and clearer than holograms, according to a study in Wednesday’s journal Nature. The study’s lead author, Daniel Smalley, said the new technology is “printing something in space, just erasing it very quickly.”
In this case, scientists created a small butterfly appearing to dance above a finger and an image of a graduate student imitating Leia in the Star Wars scene.
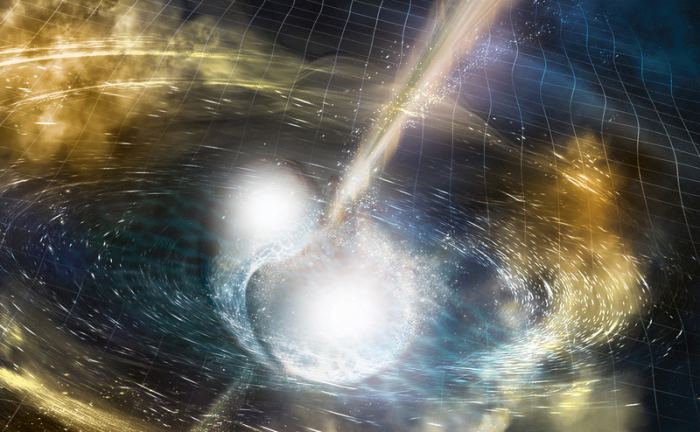

“This unexpected behavior has led to a serious buzz in the scientific community, with astronomers trying to come up with explanations as to what type of physics could be driving these emissions.”
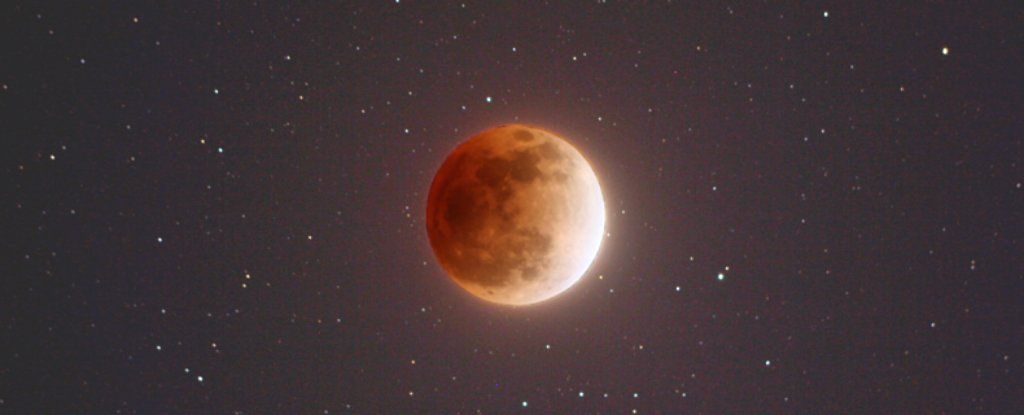


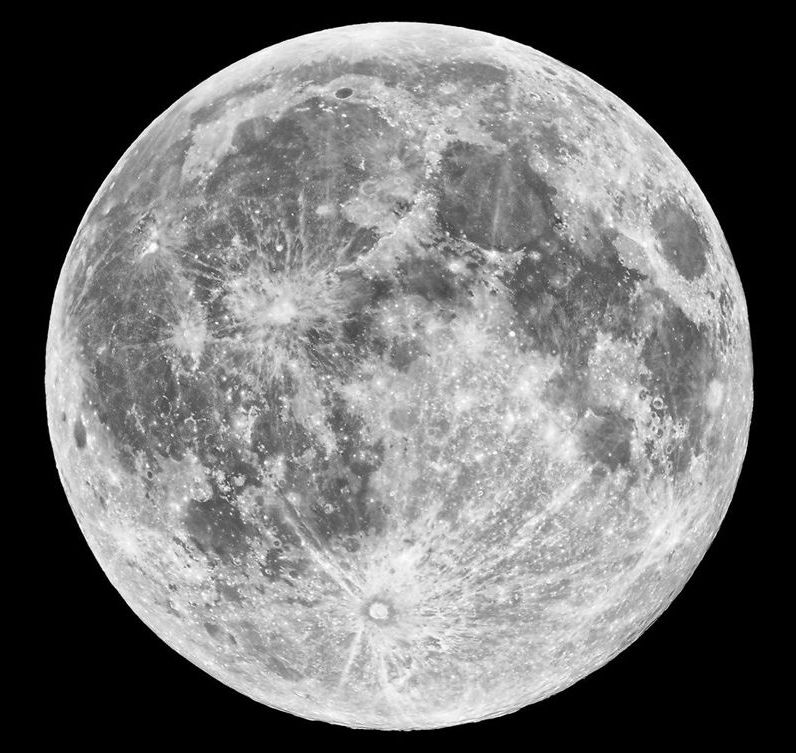
If you were awestruck by the New Year’s Day super moon, hold onto your pants.
On January 31, around midnight, the full moon will not only be super, it will be a blue moon and a blood moon.
The blue moon comes as it will be the second full moon in a month. That happens every two and a half years, hence the saying “once in a blue moon”.

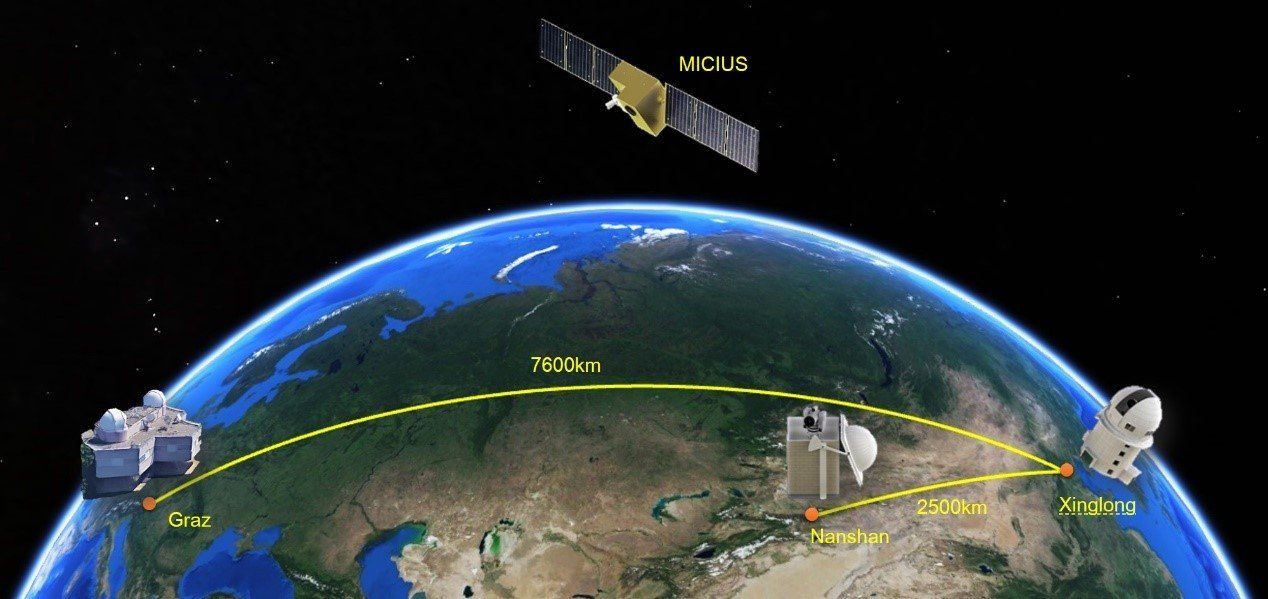
A joint China-Austria team has performed quantum key distribution between the quantum-science satellite Micius and multiple ground stations located in Xinglong (near Beijing), Nanshan (near Urumqi), and Graz (near Vienna). Such experiments demonstrate the secure satellite-to-ground exchange of cryptographic keys during the passage of the satellite Micius over a ground station. Using Micius as a trusted relay, a secret key was created between China and Europe at locations separated up to 7,600 km on the Earth.
Private and secure communications are fundamental for Internet use and e-commerce, and it is important to establish a secure network with global protection of data. Traditional public key cryptography usually relies on the computational intractability of certain mathematical functions. In contrast, quantum key distribution (QKD) uses individual light quanta (single photons) in quantum superposition states to guarantee unconditional security between distant parties. Previously, the quantum communication distance has been limited to a few hundred kilometers due to optical channel losses of fibers or terrestrial free space. A promising solution to this problem exploits satellite and space-based links, which can conveniently connect two remote points on the Earth with greatly reduced channel loss, as most of the photons’ propagation path is through empty space with negligible loss and decoherence.
A cross-disciplinary multi-institutional team of scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, led by Professor Jian-Wei Pan, has spent more than 10 years developing a sophisticated satellite, Micius, dedicated to quantum science experiments, which was launched on August 2016 and orbits at an altitude of ~500 km. Five ground stations in China coordinate with the Micius satellite. These are located in Xinglong (near Beijing), Nanshan (near Urumqi), Delingha (37°22’44.43’‘N, 97°43’37.01” E), Lijiang (26°41’38.15’‘N, 100°1’45.55’‘E), and Ngari in Tibet (32°19’30.07’‘N, 80°1’34.18’‘E).

The asteroid is around 0.7 miles (1.1km) wide — making it longer than the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, which stands at 0.5 miles high (0.8km).
It is set to pass by our planet on the 4th February at a distance of around 2,615,128 miles (4,208,641km) away — which is relatively close in space terms.
For reference, the distance between the Earth and the moon is 238,855 miles (384,400 km).