Footage has since emerged capturing the US Space Force craft “following” the astronauts in the sky, conspiracists have claimed.
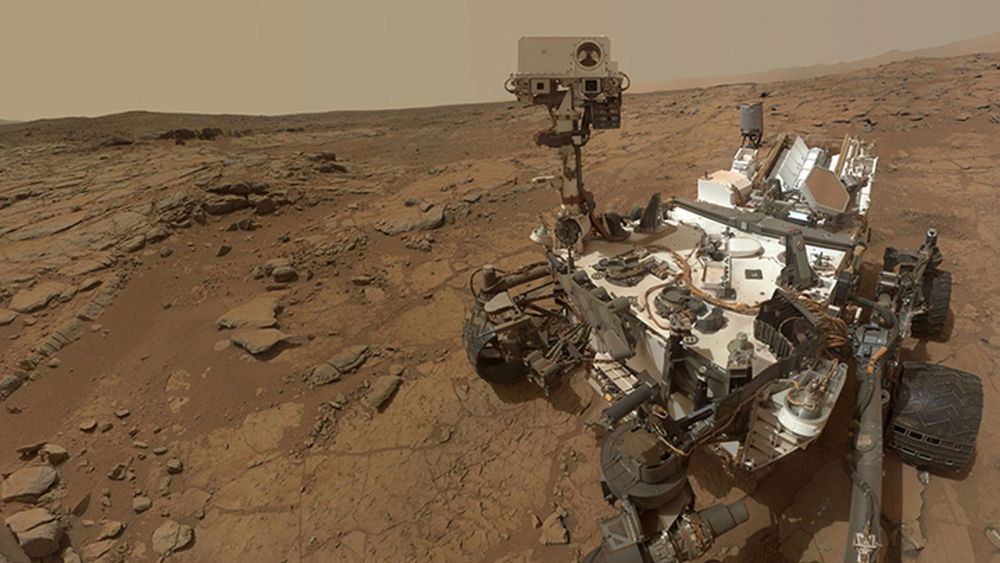



The study of Mars is a constant exercise in problem-solving, and NASA scientists have just been served up a doozy. Data from the Curiosity rover positioned within the planet’s Gale Crater has revealed wild seasonal swings in oxygen levels, something mission scientists neither expected or are able to explain.
This perplexing piece of intel comes courtesy of Curiosity’s Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) tool, an onboard laboratory that has been sucking in the air over the Gale Crater for analysis over the course of three Martian years (almost six Earth years). This has enabled the team to piece together the composition of the planet’s thin atmosphere, with CO2, nitrogen, argon, carbon monoxide and oxygen all part of the mix.
The concentrations of these gases increase and decrease as the weather changes on Mars, as the icy winters lower air pressure across the planet and the summer then raises them again. This leads to regular patterns of concentrations of gases like nitrogen and argon, and in examining the latest data, the scientists expected to see similar trends at play for oxygen.

No matter how elegant your theory is, experimental data will have the last word. Observations of the retrograde motion of the planets were fundamental to the Copernican revolution, in which the sun replaced Earth at the centre of the solar system. And the unusual orbit of Mercury provided a spectacular confirmation of the theory of general relativity. In fact, our entire understanding of the universe is built on observed, unexpected anomalies.
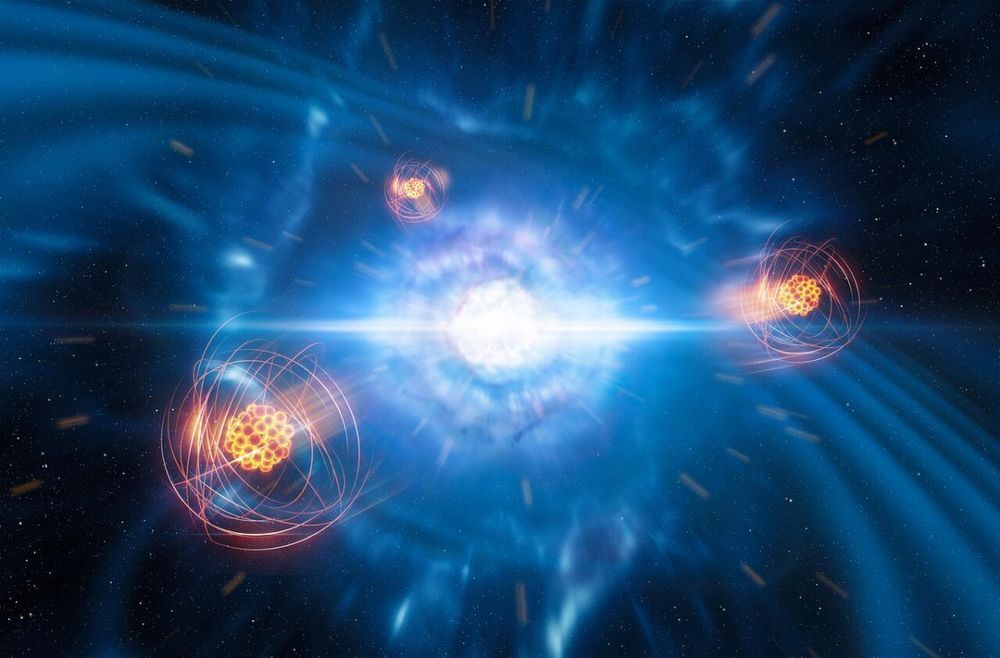

For the first time, scientists have detected a newly born heavy element in space, forged in the aftermath of a collision between a pair of dead stars known as neutron stars.
The findings shed light on how the universe’s heaviest elements are created, providing a missing piece of the puzzle of chemical element formation, researchers said in a new study describing the findings.

Caterpillar has been synonymous with big, heavy equipment — for farming, construction and mining — since Holt Manufacturing and C. L. Best Tractor merged in 1925 to form the Peoria, Illinois-based company. Over the years, tons of innovation have been built into the iconic yellow products, too, from the Model 20 Track-Type Tractor introduced in 1927 to the ginormous engines that helped power the Apollo 11 mission to the moon 50 years ago.
Coincidentally, one of Cat’s latest breakthroughs is self-driving, or autonomous, and remote-controlled mining equipment, which could very well find itself on the moon when NASA is scheduled to return to the lunar surface in 2024, with plans to build a permanent base near the orb’s south pole, part of the Artemis program.
Just as on terrestrial sites, Caterpillar fully or semi-autonomous bulldozers, graders, loaders and dump trucks could be utilized to build roads, housing and other infrastructure. Operator-less drilling and digging machines might mine water, oxygen-rich rocks and moon dust for use in 3D printing of various materials.


Twentieth Century technology has relied on the use of fuels and chemical propellants to propel our ships, planes, and cars. The propulsion technology of the future will not use chemical combustion to produce thrust, and the 21st century will see the emergence of propellant-less propulsion systems. Such technologies will provide the means to travel faster than ever before at a fraction of current costs and with no pollution by-products.
This becomes absolutely crucial for interplanetary and interstellar travel, as we have stated before in RSF commentary1 reporting on Resonance-based technology may provide inertial mass reduction—the future of space travel will not be performed with chemical propellants. As an example, to date the most viable proposal for an interstellar mission with current technological capabilities is the Breakthrough Starshot project which will use a fleet of light sail probes propelled to 20% percent the speed of light via laser pulses.
Considering the significant limitations of combustion-based propulsion (as well as the harmful environmental impacts), there is a strong drive to develop the next-generation propulsion systems that will move us into the next phase of technological advancement. Torus Tech, a research and development company founded by Nassim Haramein, the founder of the Resonance Science Foundation, is researching quantum vacuum engineering technologies that will enable gravitational control and zero-point energy production.
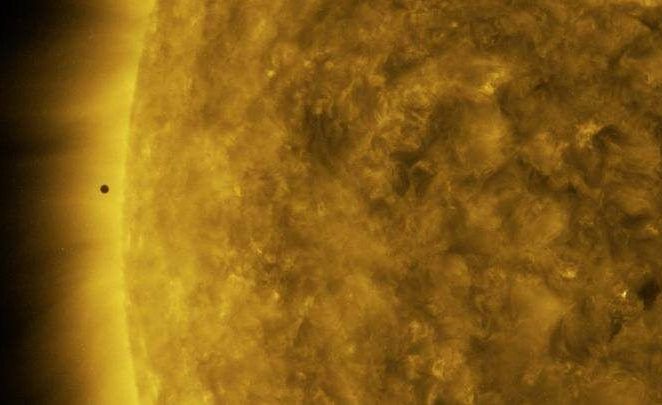


Q: What did Mercury say when it was asked to line up between Earth and the Sun?
A: I’ll pass! 😎
We were in for a rare treat during today’s #MercuryTransit, which only happens about 13 times a century! Revel in the views captured our NASA Sun Science-observing satellite in a variety of a variety of wavelengths of light in the extreme ultraviolet: https://go.nasa.gov/2NF6tQQ