The “core space operators” deployed by the U.S. military’s controversial newest branch aren’t in orbit, they’re in Qatar.





Data from Southwest Research Institute-led instruments aboard ESA’s Rosetta spacecraft have helped reveal auroral emissions in the far ultraviolet around a comet for the first time.
At Earth, auroras are formed when charged particles from the Sun follow our planet’s magnetic field lines to the north and south poles. There, solar particles strike atoms and molecules in Earth’s atmosphere, creating shimmering curtains of colorful light in high-latitude skies. Similar phenomena have been seen at various planets and moons in our solar system and even around a distant star. SwRI’s instruments, the Alice far-ultraviolet (FUV) spectrograph and the Ion and Electron Sensor (IES), aided in detecting these novel phenomena at comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P/C-G).
“Charged particles from the Sun streaming towards the comet in the solar wind interact with the gas surrounding the comet’s icy, dusty nucleus and create the auroras,” said SwRI Vice President Dr. Jim Burch who leads IES. “The IES instrument detected the electrons that caused the aurora.”

O,.o.
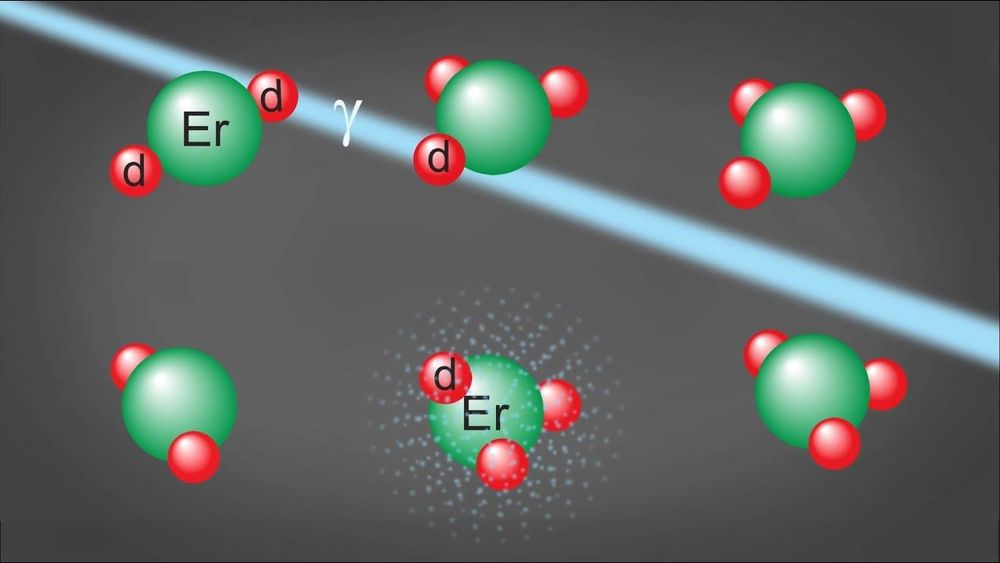
NASA has unlocked nuclear fusion on a tiny scale, with a phenomenon called lattice confinement fusion that takes place in the narrow channels between atoms. In the reaction, the common nuclear fuel deuterium gets trapped in the “empty” atomic space in a solid metal. What results is a Goldilocks effect that’s neither supercooled nor superheated, but where atoms reach fusion-level energy.
☢️ You like nuclear. So do we. Let’s nerd out over it together.

In a delightful alignment of astronomy and mathematics, scientists at MIT and elsewhere have discovered a “pi Earth”—an Earth-sized planet that zips around its star every 3.14 days, in an orbit reminiscent of the universal mathematics constant.
The researchers discovered signals of the planet in data taken in 2017 by the NASA Kepler Space Telescope’s K2 mission. By zeroing in on the system earlier this year with SPECULOOS, a network of ground-based telescopes, the team confirmed that the signals were of a planet orbiting its star. And indeed, the planet appears to still be circling its star today, with a pi-like period, every 3.14 days.
“The planet moves like clockwork,” says Prajwal Niraula, a graduate student in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS), who is the lead author of a paper published today in the Astronomical Journal, titled: “π Earth: a 3.14-day Earth-sized Planet from K2’s Kitchen Served Warm by the SPECULOOS Team.”
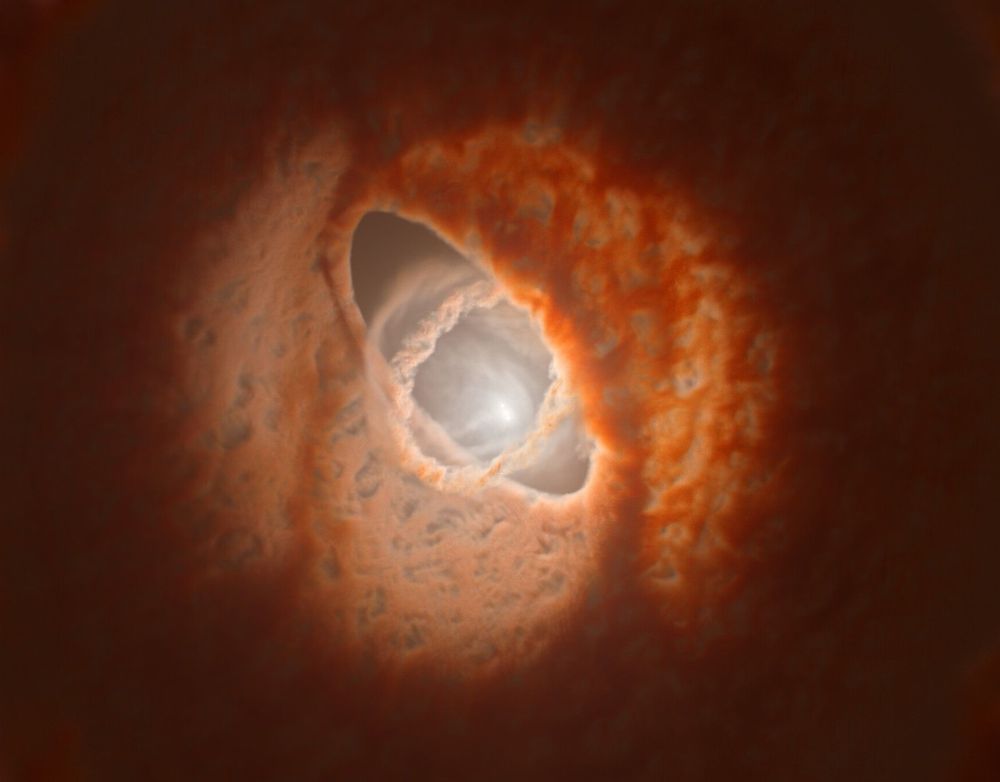
Disc is left with warped and tilted rings.
The young triple star system GW Orionis appears to be surrounded by a ring of gas and dust that has torn away and become misaligned with the rest of the system’s circumstellar disc. That is the conclusion of an international team of astronomers led by Stefan Kraus at the University of Exeter – who combined observations with numerical simulations to identify disc structures that have been confined to theory until now.
Astronomers believe that most stars are born with one or more companions, which interact in complex ways with the disc of planet-forming gas and dust surrounding the stellar system. If this disc is misaligned with the orbital planes of the host stars, previous simulations have predicted that it will warp and tear under their gravitational torque, forming distinct rings in separate planes from the rest of the disc. So far, however, astronomers have yet to identify this tearing in their observations of misaligned discs.
In their study, Kraus’ team aimed to verify this tearing process by making detailed observations of the triple star system, GW Orionis. At just around 1 million years old, the system’s circumstellar disc has yet to collapse to form planets; while at its centre, the orbital planes of its three stars are highly misaligned with each other. Over 11 years beginning in 2008, the researchers used the Very Large Telescope (VLT) and Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) telescopes in Chile to measure thermal emissions and scattered visible light originating from the system. This allowed them to map the distribution of material in the disc.