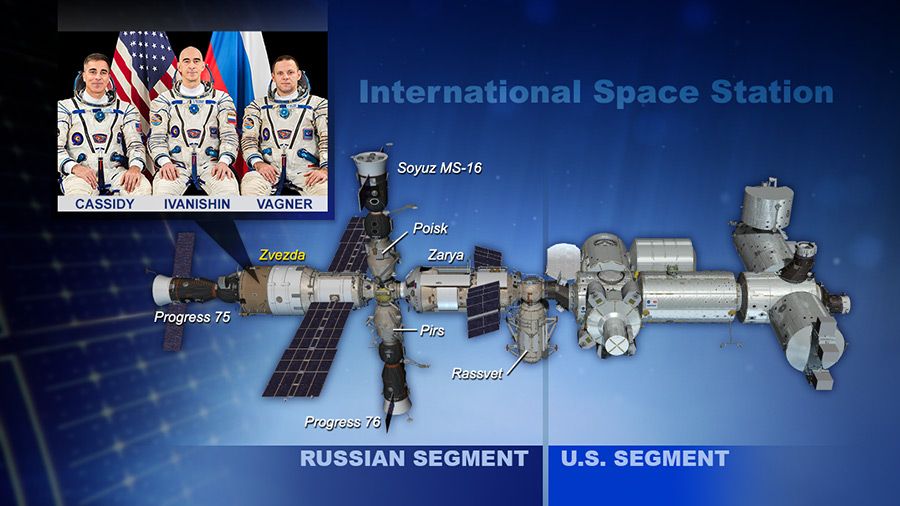
The Expedition 63 crew will stay in the Russian segment’s Zvezda service module during a cabin air leak test this weekend.
As part of ongoing work to isolate the source of a slight increase above the standard cabin air leak rate, the Expedition 63 crew will once again spend the weekend inside the station’s Russian segment. All the space station hatches will be closed this weekend so mission controllers can again monitor the air pressure in each module with the goal of localizing the source of the increased rate. The test presents no safety concern for the crew. Commander Chris Cassidy and his crewmates Ivan Vagner and Anatoly Ivanishin will stay in the Zvezda service module from Friday night into Monday morning.
The crew will spend Friday gathering items for the weekend isolation before closing hatches throughout the station at the conclusion of their crew work day.