The price is normally 45$ for two days but use my code: GALAXISGAL to get in for just 15$.



A NASA spacecraft has officially ‘touched’ the sun, after it plunged through the unexplored solar atmosphere known as the corona, passing just eight million miles from the core of the star.
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe battled temperatures of 2370F and radiation 500 times stronger than on Earth as it made its eighth approach to the celestial body, finally passing through its upper atmosphere.
The flight occurred in April but scientists have only just been able to confirm the probe traveled through the corona, after waiting months for the data to arrive back from the spacecraft.
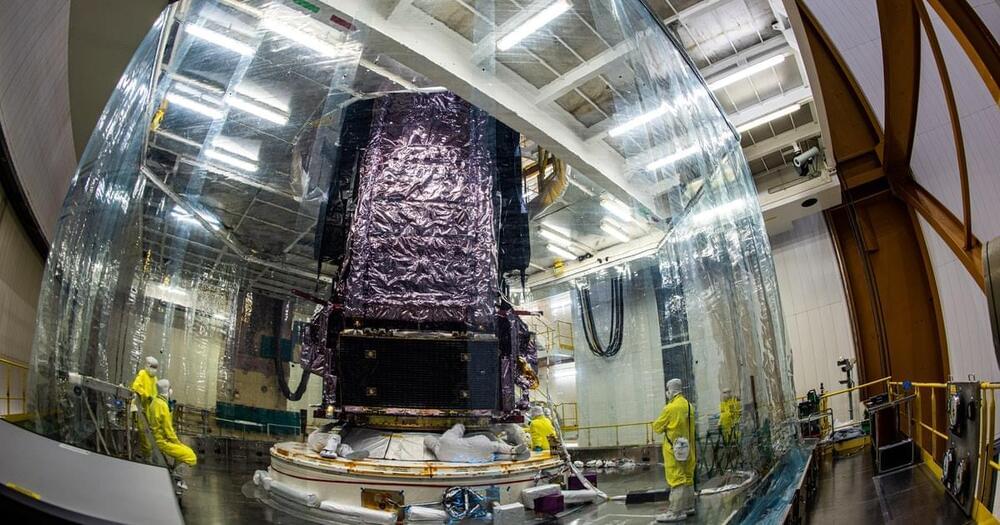
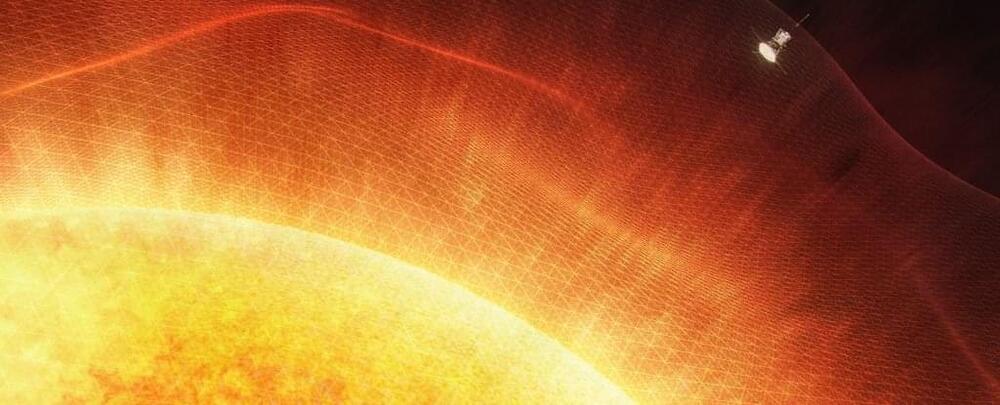


We are in the golden age of science and technology.
In an incredible historic first, a human-made spacecraft has swooped in and made contact with the Sun.
On 28 April 2021, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe actually flew into and through the solar corona, the upper atmosphere of the Sun. Not only did it live to tell the tale – proving the efficacy of Parker’s high-tech heat shielding – it took in situ measurements, giving us a wealth of never-before-seen data on the heart of our Solar System.
“Parker Solar Probe ‘touching the Sun’ is a monumental moment for solar science and a truly remarkable feat,” said astrophysicist Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters.
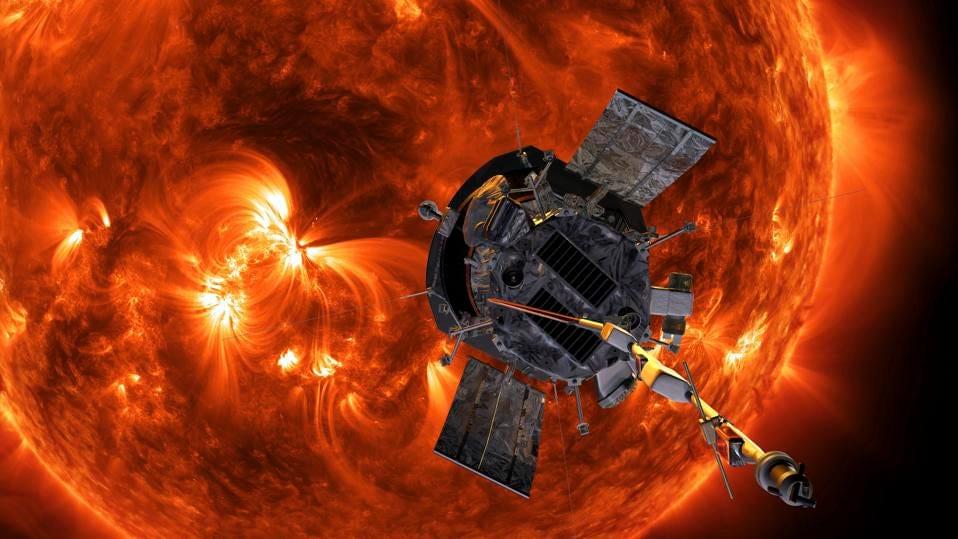

For the first time ever, a manmade object has entered the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona, which inexplicably is thousands of times hotter than our star’s surface (or photosphere).
Researchers led by a team at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor were able to predict where the Sun’s upper atmosphere began, and the probe was able to penetrate it for roughly five hours. The Parker probe was not only able to fly through the Sun’s atmosphere but was also able to sample particles and magnetic fields there, says NASA.
“Flying so close to the Sun, Parker Solar Probe now senses conditions in the magnetically dominated layer of the solar atmosphere — the corona — that we never could before,” Nour Raouafi, the Parker project scientist at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, said in a statement. “We can actually see the spacecraft flying through coronal structures that can be observed during a total solar eclipse.”
On April 28, 2021, during its eighth flyby of the Sun, Parker Solar Probe encountered the specific magnetic and particle conditions some 8.1 million miles above the solar surface, NASA reports. That point, known as the Alfvén critical surface, marks the end of the solar atmosphere and beginning of the solar wind, says NASA.
The surface of the Sun is about 6,000 Celsius, Justin Kasper, the first author of a paper detailing the research in the journal Physical Review Letters, and a professor of climate and space sciences at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told me. Above that, the temperature rises to more than a million degrees, he says.
Full Story:

Complex terrain and Yutu 2’s reliance on solar power limit driving speed.
China’s Yutu 2 lunar rover recently spotted something intriguing on the far side of the moon, but it’ll take the vehicle a few months to reach the object for a closer look.
Yutu 2 photographed a strangely cube-shaped rock last month, during the robot’s 36th lunar day of activities. The rover drive team estimates that the object, which has been dubbed the “mystery hut,” to be around 260 feet (80 meters) away. That doesn’t sound far, but it’ll take careful planning and effort by the Yutu 2 team to cover that distance safely.
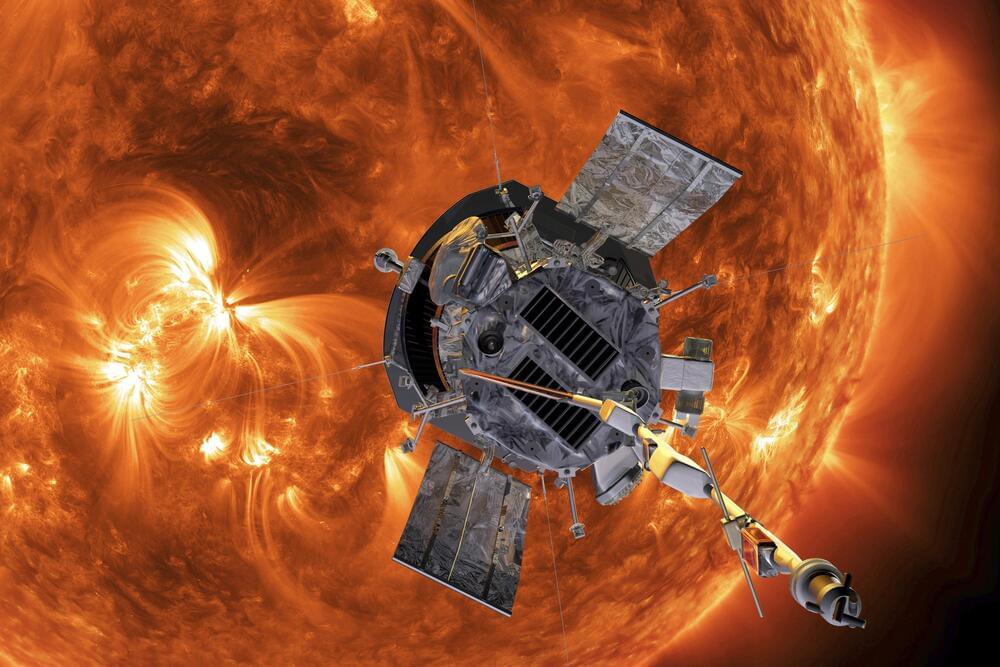

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — A NASA spacecraft has officially “touched” the sun, plunging through the unexplored solar atmosphere known as the corona.
Scientists announced the news Tuesday during a meeting of the American Geophysical Union.
The Parker Solar Probe actually flew through the corona in April during the spacecraft’s eighth close approach to the sun. Scientists said it took a few months to get the data back and then several more months to confirm.
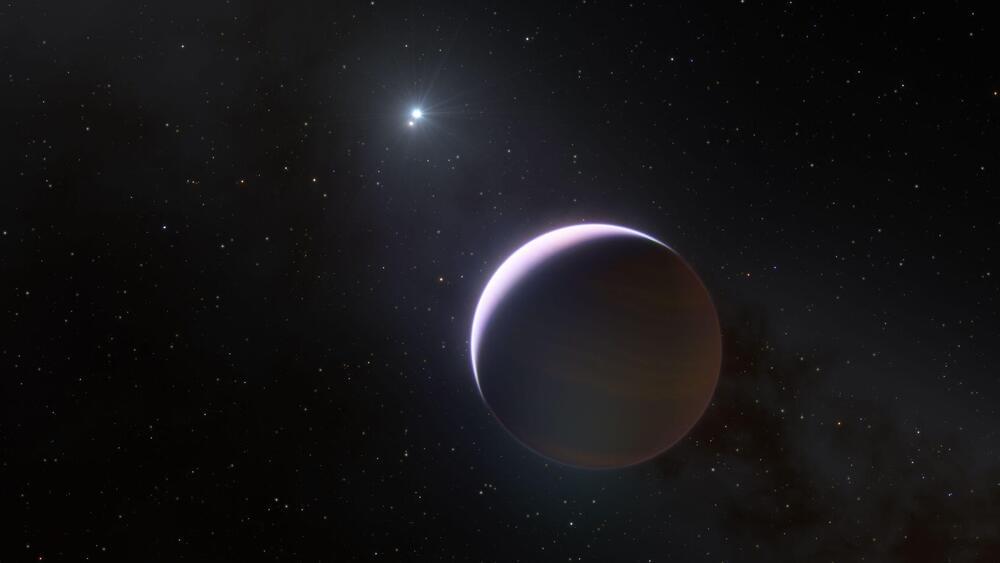

Scientists have discovered a planet 10 times as massive as Jupiter orbiting a pair of stars in another solar system, according to new research.
The research, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, points to the discovery of a planet named b Centauri (AB)b or b Centauri b, with an image captured by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile.
The planet is 10 times as massive as Jupiter and “one of the most massive planets ever found,” according to the observatory.
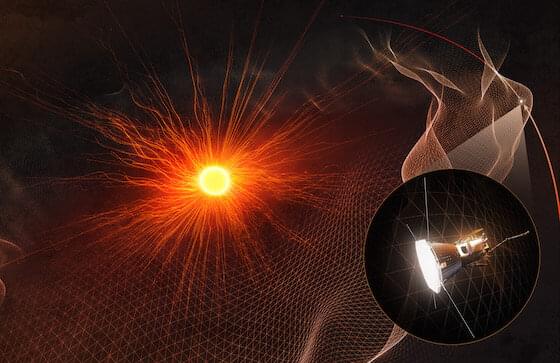
On April 28, 2021, at 933 UT (3:33 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time), NASA’s Parker Solar Probe reached the sun’s extended solar atmosphere, known as the corona, and spent five hours there. The spacecraft is the first to enter the outer boundaries of our sun.
The results, published in Physical Review Letters, were announced in a press conference at the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting 2021 on December 14. The manuscript is open-access and freely available to download.
“This marks the achievement of the primary objective of the Parker mission and a new era for understanding the physics of the corona,” said Justin C. Kasper, the first author, Deputy Chief Technology Officer at BWX Technologies, and a professor at the University of Michigan. The mission is led by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHU/APL).
